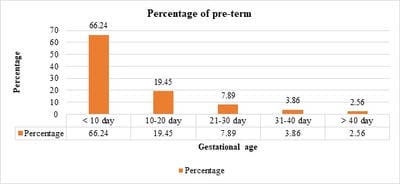
To study the short-term outcome and risk factors for premature neonate born at Dr. Bhimrao Ambedkar Memorial Hospital, Raipur, Chhattisgarh, India
Phuljhele S.1, Bichpuria P.2*, Yusuf S.3, Singh A.4
DOI: https://doi.org/10.17511/ijpr.2020.i04.02
1 Sharja Phuljhele, Professor and HOD, Department of Pediatrics, Pt J.N.M. Medical College, Raipur, Chhattisgarh, India.
2* Prachi Bichpuria, Assistant Professor, Department of Pediatrics, Pt J.N.M. Medical College, Raipur, Chhattisgarh, India.
3 Samreen Yusuf, Postgraduate, Department of Pediatrics, Pt J.N.M. Medical College, Raipur, Chhattisgarh, India.
4 Abha Singh, MS, Department of OBG, Pt J.N.M. Medical College, Raipur, Chhattisgarh, India.
Background: Prematurity is the leading cause of perinatal morbidity and mortality worldwide affecting 5-10% of births. Preterm neonates have a 120 times higher risk of death than neonates. Methods: This is a prospective hospital-based observational study, conducted over a period of 1 year (March 2018 – March 2019), including a total of 1472 preterm babies. Results: A total of 1472 preterm were born during the study period. Preterm male: female was 1.1:1. Common risk factors noted were multiple pregnancies (28.46%) followed by pre-eclampsia (27.03%). A total of 66.71% of neonates were born beyond 34 weeks of gestation, 60.46% were having birth weight between 1500 and 2499 gm, 18.14% were very low birth weight (VLBW) and 4.35% were extremely low birth weight (ELBW). A total of 545 (37.02%) required NICU admission. Major morbidities noted were respiratory distress syndrome (55.59%) followed by sepsis (30.64%), perinatal asphyxia (11.19%), neonatal jaundice (10.64%) and retinopathy of prematurity (9.91%). A negative correlation was noted between gestational age and duration of stay in NICU (r = 0.98, p = 0.022). Birth weight and gestational age of neonates were significantly associated with the treatment outcome (p=0.000). Very low birth weight neonates had the highest mortality (40.85%) followed by ELBW (28.05%). Mortality of 11.14% was noted with respiratory distress syndrome (10.83%) being the major cause followed by sepsis (8.07%). Conclusions: The most common maternal risk factors noted were multiple pregnancies, preeclampsia, eclampsia, antepartum hemorrhage, and gestational hypertension. Common morbidities observed in preterm babies were respiratory distress syndrome, sepsis, perinatal-asphyxia, and neonatal-jaundice.
Keywords: Pre-term, Risk factors for prematurity, Short term outcomes
| Corresponding Author | How to Cite this Article | To Browse |
|---|---|---|
| , Assistant Professor, Department of Pediatrics, Pt J.N.M. Medical College, Raipur, Chhattisgarh, India. Email: |
Phuljhele S, Bichpuria P, Yusuf S, Singh A. To study the short-term outcome and risk factors for premature neonate born at Dr. Bhimrao Ambedkar Memorial Hospital, Raipur, Chhattisgarh, India. Pediatric Rev Int J Pediatr Res. 2020;7(4):166-173. Available From https://pediatrics.medresearch.in/index.php/ijpr/article/view/591 |


 ©
©