A study of accidental ingestion of hydrocarbons in children in a medical college hospital in central Kerala
Abstract
Background: The accidental ingestion of various chemicals especially the hydrocarbons are seen worldwide in the paediatric population. Inspite of all awareness programmes in the community hydrocarbons especially petrol, diesel, turpentine and kerosene are always in the reach of children. The side effects and clinical spectrum is alarming after ingestion. So it is vital to prevent hydrocarbon ingestion.
Objective: To understand the clinical profile of accidental ingestion of hydrocarbons (AIH) in children, assess the radiological changes and treatment.
Materials and Methods: The retrospective study was conducted analysing the hospital records of children hospitalized between January 1st 2010 and December 31st 2015 with accidental poisoning due to various causes in the paediatric intensive care unit (PICU) with special reference to AIH. A standard proforma included age, sex of the children, types of poisoning agents including hydrocarbons (HC), clinical presentations and treatment given.
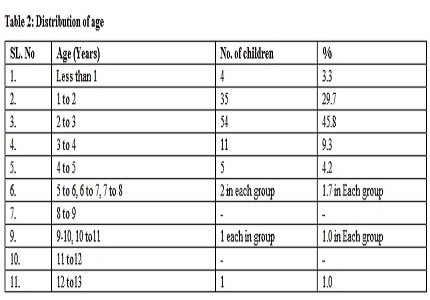
Results: In the PICU out of a total of 5806 patients admitted, 401 (6.9%) were due to acute poisoning. Among them AIH was noted in 118 (29.4%) patients. These children were admitted initially in the PICU stabilized and there was no mortality following AIH during the period of study.
Conclusion: AIH is a common cause of poisoning in children. The main reason is the easy availability in the house itself due to various reasons. The morbidity and mortality can be prevented by education of the society especially the care takers of the children in the community.
Downloads
References
2. Hyder AA, Wali S, Fishman S, Schenk E. The burden of unintentional injuries among the under-five population in South Asia . Acta Paediatrica. 2008 Mar; 97(3):267–275. [PubMed]
3. Anderson CE, Loomis GA. Recognition and prevention of inhalant abuse. Am Fam Physician. 2003 Sep 1;68(5):869-74. [PubMed]
4. Mowry JB, Spyker DA, Cantilena LR Jr, McMillan N, Ford M. 2013 Annual Report of the American Association of Poison Control Centers' National Poison Data System (NPDS): 31st Annual Report. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2014 Dec. 52(10):1032-283. [PubMed]
5. Beamon RF, Siegel CJ, Landers G, Green V. Hydrocarbon ingestion in children: a six-year retrospective study. JACEP. 1976 Oct; 5(10):771-5. [PubMed]
6. Seymour FK, Henry JA. Assessment and management of acute poisoning by petroleum products. Hum Exp Toxicol. 2001 Nov; 20 (11):551-62. [PubMed]
7. Rodricks A, Satyanarayana M, D'Souza GA, Ramachandran P. Turpentine-induced chemical pneumonitis with broncho-pleural fistula. J Assoc Physicians India. 2003 Jul; 51:729-30. [PubMed]
8. Klein BL, Simon JE. Hydrocarbon poisonings. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1986 Apr;33(2):411-9. [PubMed]
9. Algren JT, Rodgers GC Jr. Intravascular hemolysis associated with hydrocarbon poisoning. Pediatr Emerg Care. 1992 Feb 8(1):34-5. [PubMed]
10. Siddiqui EU1, Razzak JA, Naz F, Khan SJ. Factors associated with hydrocarbon ingestion in children. J Pak Med Assoc. 2008 Nov; 58(11):608-12. [PubMed]
11. Benjelloun A, Ait Benasser MA Driouche A.Hydrocarbon pneumonitis. A case report. Rev Pneumol Clin. 2006 Jun; 62(3):191-4. [PubMed]
12. Khanna P, Devgan SC, Arora VK, Shah A.Hydrocarbon pneumonitis following diesel siphonage. Indian J Chest Dis Allied Sci. 2004 Apr-Jun; 46(2):129-32. [PubMed]
13. Janssen S, van der Geest S, Meijer S, Uges DR.Impairment of organ function after oral ingestion of refined petrol. Intensive Care Med. 1988; 14(3):238-40. [PubMed]
14. Fracas M, Wabersich J. Petrol ingestion poisoning in a pregnant woman. Clin Exp Obstet Gynecol. 1997;24(4):223-5. [PubMed]
15. Güzel A, Açıkgöz M. A lethal danger in the home: turpentine poisoning. Turk J Pediatr. 2015 Mar-Apr; 57(2):177-9.
16. Rodricks A, Satyanarayana M, D'Souza GA, Ramachandran P.Turpentine-induced chemical pneumonitis with broncho-pleural fistula. J Assoc Physicians India. 2003 Jul; 51:729-30. [PubMed]
17. Monnet P, Thome J. Acute poisoning by turpentine oil in a 23-month-old infant Pediatrie. 1961;16:270-3. [PubMed]
18. Crosslin K, Tsai R.Unintentional ingestion of cleaners and other substances in an immigrant Mexican population: a qualitative study. Inj Prev. 2016 Apr;22(2):140-3. doi: 10.1136/injuryprev-2014-041446. Epub 2015 Mar 17. [PubMed]
19. Shotar AM..Kerosene poisoning in childhood: a 6-year prospective study at the Princess Rahmat Teaching Hospital. Neuro Endocrinol Lett. 2005 Dec; 26(6):835-8. [PubMed]
20. Reed RP, Conradie FM.The epidemiology and clinical features of paraffin (kerosene) poisoning in rural African children. Ann Trop Paediatr. 1997 Mar;17(1):49-55. [PubMed]
21. Tormoehlen LM, Tekulve KJ, Nañagas KA.Hydrocarbon toxicity: A review. Clin Toxicol (Phila). 2014 Jun; 52(5):479-89. [PubMed]
22. Cobaugh DJ, Seger DL, Krenzelok EP.Hydrocarbon toxicity: an analysis of AAPCC TESS data. Przegl Lek. 2007; 64(4-5):194-6. [PubMed]
23. Sen V, Kelekci S, Selimoglu Sen H, Yolbas I, Günes A, Abakay O, Fuat Gurkan M. An evaluation of cases of pneumonia that occurred secondary to hydrocarbon exposure in children. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2013 Feb;17 Suppl 1:9-12. [PubMed]
24. Majeed HA, Bassyouni H, Kalaawy M, Farwana S.Kerosene poisoning in children: a clinico-radiological study of 205 cases. Ann Trop Paediatr. 1981 Jun;1(2):123-30. [PubMed]
25. Krenzelok EP.New developments in the therapy of intoxications. Toxicol Lett. 2002 Feb 28;127(1-3):299-305.
26. Lamour C, Bouchaud C, Doré P, d'Arlhac M, Bodin J.Pneumonitis caused by hydrocarbon inhalationRev Mal Respir. 2003 Dec;20(6 Pt 1):959-64. [PubMed]
27. Munro S-A, Van Niekerk A, Seedat M. Childhood unintentional injuries: the perceived impact of the environment, lack of supervision and child characteristics. Child Care Health Dev. 2006 May;32:269–79. [PubMed]
Copyright (c) 2016 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


