Maternal risk factors for term low birth weight neonates: a retrospective hospital based study at Guntur district, Andhra Pradesh
Abstract
Introduction: The incidence, morbidity, mortality of low birth weight babies can be reduced if the maternal risk factors are detected early and managed by simple techniques.
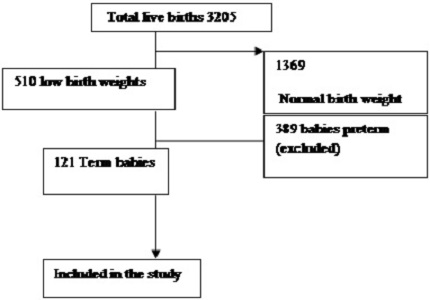
Materials and Methods: A retrospective analysis of term babies with low birth weight were studied over a period of 1 year using hospital records with emphasis on age, parity, height, BMI and maternal diseases.
Results: A total of 121 babies were included. The average birth weight in women aged 15-20 years was 1.89 kg, 21- 30 years it was 2.2 kg, more than 30 years, it was 2.12 kg, and difference in weight of babies born to mothers aged 15-20 years was statistically lower. The average birth weight among Gravida1 (G1) mothers was 1.95 kg. Among G2 mothers, it was 2.27 kg and G3 was 2.28 kg. Difference in weights of babies of G1 mothers was significantly lower than babies born to G2 mothers (p<0.0001). The weight of babies of mothers with height <145cm was 2.04 kg, between 145-155cm was 2.12 kg, >155cm was 2.13 kg. The weight of babies of mothers with hemoglobin 7-10 gm/dl (1.88) was lower than weight of babies of mothers with hemoglobin >10 gm/dl (2.25). This was highly significant statistically (p value<0.0001). The weight of babies of mothers with BMI<25 was 2.08 kg, with BMI 20-25 was 2.12 kg, BMI>30 was 2.15 kg, this was not statistically significant.
Conclusion: We hereby conclude that lesser age, primiparity and anemia are associated with low birth weight in term infants.
Downloads
References
2. Wardlaw TM, editor. Low birthweight: country, regional and global estimates. UNICEF; 2004.
3. International Institute for Population Sciences .India National Family Health Survey (NFHS-3),2005-06.
4. International Institute for Population Sciences;2007.
5. Marcdante K,Kleigman RM.Nelson essentials of pediatrics.Elsevier Health Sciences;2014 Feb 25.
6. Singh M. Care of the Newborn.7 th Edition. Sagar Publications;2010.
7. Chiarotti F, Castignani AM, Puopolo M, Menniti-Ippolito F, Minniti DS, Di Paolo A. [Effects of socio-environmental factors on neurocognitive performance in premature or low-birth weight preschoolers]. Annali dell'Istituto superiore di sanita. 2000 Dec;37(4):553-9.
8. Barker DJ. The developmental origins of adult disease. Journal of the American College of Nutrition. 2004 Dec 1;23(sup6):588S-95S. [PubMed]
9. Kramer MS. Determinants of low birth weight: methodological assessment and meta-analysis. Bulletin of the World Health Organization. 1987;65(5):663. [PubMed]
10. Kumar SG, Kumar HH, Jayaram S, Kotian MS. Determinants of low birth weight: a case control study in a district hospital in Karnataka. The Indian Journal of Pediatrics. 2010 Jan 1;77(1):87-9. [PubMed]
11. Dhall K, Bagga R. Maternal determinants of birth weight of north Indian babies. The Indian Journal of Pediatrics. 1995 May 1;62(3):333-44.
12. Nair NS, Rao RP, Chandrashekar S, Bhat HV. Socio-demographic and maternal determinants of low birth weight: a multivariate approach. The Indian Journal of Pediatrics. 2000 Jan 1;67(1):9-14. [PubMed]
13. Mann LI, Tejani NA, Weiss RR. Antenatal diagnosis and management of the small-for-gestational age fetus. American Journal of Obstetrics & Gynecology. 1974 Jan 12;120(7):A42. [PubMed]
14. Deshpande Jayant D, Phalke DB, Bangal VB, D Peeyuusha BS. Maternal risk factors for low birth weight neonates: a hospital based casecontrol study in rural area of western maharashtra, India. National Journal of Community Medicine. 2011 Oct;2(3):394-8.
15. Mavalankar DV, Gray RH, Trivedi CR. Risk factors for preterm and term low birthweight in Ahmedabad, India. International journal of epidemiology. 1992 Apr 1;21(2):263-72. [PubMed]
16. Anand K,Garg BS.A study of factors affecting LBW. Indian journal of community medicine.2000 Apr:6
17. Deshmukh JS, Motghare DD, Zodpey SP, Wadhva SK. Low birth weight and associated maternal factors in an urban area. Indian pediatrics. 1998 Jan 1;35(1):33-6. [PubMed]
18. Amin N,Abel R, Sampathkumar V. Maternal risk factors associated with low birth weight. The Indian Journal of Pediatrics.1993 Mar1;60(2):269-274. [PubMed]
19. Malik S, Ghidiyal RG, Udani R, Waingankar P. Maternal biosocial factors affecting low birth weight. The Indian Journal of Pediatrics. 1997 May 1;64(3):373-7. [PubMed]
20. Shrestha I, Sunuwar L, Bhandary S, Sharma P. Correlation between gestational weight gain and birth weight of the infants. Nepal Medical College journal: NMCJ. 2010 Jun;12(2):106-9.
Copyright (c) 2016 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


