Abnormalities of lipid profile in overweight and obese Indian children
Abstract
Objective: To identify the abnormalities of lipid profile early in overweight and obese children.
Study design: Observational study.
Setting: Vydehi Institute of Medical Sciences & Research Centre, Bangalore.
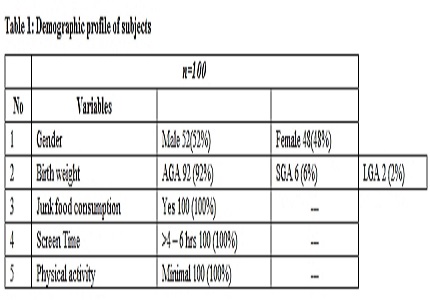
Participants: 100 children who are overweight and obese.
Outcome Measures: Abnormal lipid profile.
Methods: In all patients who are overweight and obese as per IAP growth charts and who are above 6 years of age, a detailed history including antenatal history, birth weight, diet history, personal history were taken. In these patients demographic measures like age, sex, anthropometric measurements weight, height, BMI, waist circumference, waist hip ratio and blood pressure were recorded. In all the patients fasting blood glucose, triglyceride and HDL-C were done.
Results: Out of 100 children studied, 61% (61cases) were overweight and 39% (39 cases) were obese. Males were 52% (52 cases) and females were 48% (48 cases). 92 cases had normal birth weight, 6 cases were SGA and 2cases were LGA babies. 85% had TGL levels less than 150 mg/dl and 15% had high or equal to 150mg/dl. 69% of the cases had HDL-C less than 40mg/dl and 31 % of the cases had HDL-C more than or equal to 40mg/dl.
Conclusions: By doing lipid profile in overweight and obese children, we can identify abnormal lipid profile in these children early and initiate non pharmacological management, behavioral therapy and if required pharmacological therapy thereby preventing these children from developing metabolic syndrome and its associated long term complications.
Downloads
References
2. S. Goenka, D. Prabhakaran, V. S. Ajay, and K. S. Reddy, “Preventing cardiovascular disease in India-Translating evidence to action,” Current Science. 2009;97(3):367–377. [PubMed]
3. Stephen Cook, Rae Ellen W. Kavey, Dyslipidemia and Pediatric Obesity.Pediatr Clin North Am. 2011 Dec; 58(6): 1363–1373. doi: 10.1016/j.pcl.2011.09.003. [PubMed]
4. Laakso M, Sarlund H, Mykkänen L. Insulin resistance is associated with lipid and lipoprotein abnormalities in subjects with varying degrees of glucose tolerance.Arteriosclerosis. 1990 Mar-Apr; 10(2):223-31.
5.Justin P. Zachariah. Improving Blood Pressure in Children Is Protective Over the Long Term. Circulation. 2013;128:198-9. DOI: 10.1161/Circulation AHA.113.003954. [PubMed]
6. N. Mattsson, T. Rönnemaa, M. Juonala,J. S. A. Viikari and O. T. Raitakari.The prevalence of the metabolic syndrome in young adults. The Cardiovascular Risk in Young Finns Study.Journal of Internal Medicine.2007;261,: 159–69.doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2796.2006.01752.x [PubMed]
7. Adeli K., Taghibiglou C., van Iderstine S. C., Lewis G. F. Mechanisms of hepatic very low-density lipoprotein overproduction in insulin resistance. Trends in Cardiovascular Medicine. 2001;11(5):170–176. doi: 10.1016/s1050-1738(01)00084-6. [PubMed]
8. Rio-Navarro BE, Velazquez-Monroy O, Sanchez-Castillo CP, et al. The high prevalence of overweight and obesity in Mexican children.Obes Res. 2004;12:215-23. [PubMed]
9. Gilles Plourde.Impact of obesity on glucose and lipid profiles in adolescents at different age groups in relation to adulthood.BMC FamPract.2002; 3: 18.doi: 10.1186/1471-2296-3-18. [PubMed]
10. Anoop Misra,Naval K VikramInsulin resistance syndrome (metabolic syndrome) and obesity in Asian Indians: evidence and implications.2004;20(5):482–91 .DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.nut.2004.01.020. [PubMed]
11. Back GI, Caramelli B, Pellanda L, Duncan B, Mattos S, Fonseca FH. I Guidelines of Prevention of Atherosclerosis in Childhood and Adolescence. Arq Bras Cardiol. 2005;85(Suppl 6):4–36. [PubMed]
12. Alfredo Halpern, Marcio C Mancini, Maria Eliane C Magalhães,et al.Metabolic syndrome, dyslipidemia, hypertension and type 2 diabetes in youth: from diagnosis to treatment.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2010; 2: 55.
13. Chahil TJ, Ginsberg HN.Diabetic dyslipidemia.EndocrinolMetabClin North Am. 2006;35(3):491-510, vii-viii. [PubMed]
14. Ginsberg, H. N., Zhang, Y.-L. and Hernandez-Ono, A. (2006), Metabolic Syndrome: Focus on Dyslipidemia. Obesity, 14: 41S–49S. doi: 10.1038/oby.2006.281. [PubMed]
Copyright (c) 2016 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


