Hallervorden Spatz disease (Pantothenate Kinase associated Neurodegeneration): a rare case report
Abstract
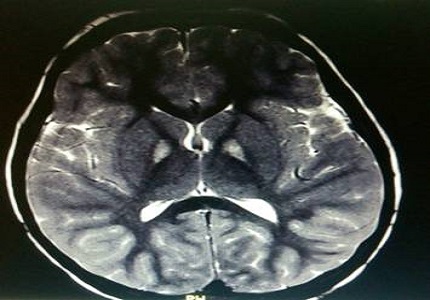
Hallervorden Spatz disease (HSD), is an autosomal recessive disorder characterised by regression of attained milestones, mental retardation and movement disability. We present a case of 6 year old male child admitted with regression of attained milestones, mainly language, ataxia and extrapyramidal symptoms since 2 years. MRI brain with contrast had shown typical “eye of the tiger” sign. Child was symptomatically improved with Tab. Trihexyphenidyl. Reporting such cases would benefit us to be familiarised with this rare disease and to differentiate it from other static and progressive neurological illnesses.
Downloads
References
2. Hartig MB, Hortnagel K, Garavaglia B, Zorzi G, Kmiec T, Klopstock T, Rostasy K, Svetel M, Kostic VS, Schuelke M, Botz E, Weindl A, Novakovic I, Nardocci N, Prokisch H, Meitinger T. Genotypic and phenotypic spectrum of PANK2 mutations in patients with neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation. Ann Neurol. 2006;
59(2):248-56. [PubMed]
3. Kaushik A, Longia S, Jagadeesh R, Kishore V. Hallervorden-spatz disease. Indian Pediatr 1995;32:483-5. [PubMed]
4. Singhi PD, Mitra S. Hallervorden spatz disease: Late infantile type. J Child Neurol 1997;12:281-2. [PubMed]
5. Shah J, Patkar D, Patankar T, Krishnan A, Prasad S, Limdi J. Hallervorden spatz disease: MR imaging. J Postgrad Med 1999;45:114-7. [PubMed]
6. Rao C, Murthy V, Hedge R, Asha, Vishwanath. Hallervorden spatz disease. Indian J Pediatr 2003;70:513-14. [PubMed]
7. Neumann M, Adler S, Schulter D, et al. Alpha- synuclein accumulation in a case of neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation type 1 (NBIA-1, formely hallervorden-spatz syndrome) with widespread cortical and brainstem-type lewy bodies. Acta Neuropathol (Berl) 2000; 100 (5); 568-574.
8. Gregory A, Hayflick SJ. Folia Neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation. Neuropathology 2005;43:286- 96. [PubMed]
9. Schneider SA, Hardy J, Bhatia K. Iron Accumulation in Syndromes of Neurodegeneration with Brain Iron Ac cumulation 1 and 2 - causative or consequential?. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2009(Jan); 80(6); 589-90. [PubMed]
10. M.C.Sharma, N. Aggarwal, M. Bihari, V. Goyal, S. Gaikwed, S. Vaishya, C. Sarkar Hallervorden Spatz disease: MR and pathological findings of a rare case Neurology India March 2005 Vol 53 Issue 1:102-104. [PubMed]
11. Swaiman KF. Hallervorden - Spatz syndrome and brain iron metabolism. Arch Neurology 1991; 48: 1285-1293. [PubMed]
12. Sethi KD, Adams RJ, Loring DW, el Gammal T. Hallervorden-Spatz syndrome: Clinical and magnetic resonance imaging correlations: Ann Neurol. 1988;24: 692-94.
13. Castelnau P, Cif L, Valente EM, Vayssiere N, Hemm S, Gannau A, Digiorgio A, Coubes P. Pallidal stimulation improves pantothenate kinase-associated neurodegeneration. Ann Neurol. 2005;57:738–741.
14. Shachar DB, Kahana N, Kampel V, Warshawsky A, Youdim MB. Neuroprotection by a novel brain permeable iron chelator, VK-28, against 6- hydrodopamine lesion in rats. Neuropharmacology 2004;46: 254-63. [PubMed]
Copyright (c) 2016 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


