Erosive esophagitis with transient respiratory distress in newborns: a case report
Keywords:
Erosive esophagitis, Newborn, Respiratory Distress
Abstract
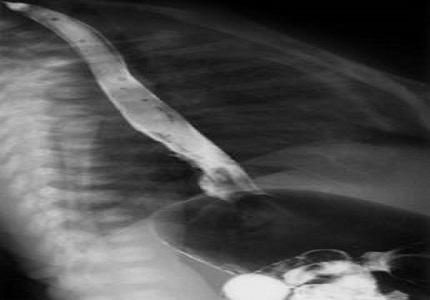
Isolated esophagitis is very rare in newborn infants at birth, although it may occur a few days or weeks later but is gener-ally associated with gastritis or gastroesophageal reflux, infections or trauma. Respiratory distress is a very unusual clini-cal feature of esophagitis. We hereby report two newborns who presented with symptoms of respiratory distress at birth and had isolated erosive esophagitis. Symptoms resolved with treatment of esophagitis.
Downloads
Download data is not yet available.
References
1. Edwards MO, Kotecha SJ, Kotecha S. Respiratory distress of the term newborn infant. Paediatr Respir Rev. 2013 Mar;14(1):29-36; quiz 36-7. doi: 10.1016/j.prrv.2012.02.002. Epub 2012 Mar 2. [PubMed]
2. Wilmott RW, Boat TF, Bush A, Chernick V, Deterding RR. Kendig and Chernick’s Disorders of the Respiratory Tract in Children. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2012.
3. Aly H. Respiratory disorders in the newborn: identification and diagnosis. Pediatr Rev. 2004 Jun;25(6):201-8. [PubMed]
4. Warren JB, Anderson JM. Newborn respiratory disorders. Pediatr Rev. 2010 Dec;31(12):487-95; quiz 496. doi: 10.1542/pir.31-12-487. [PubMed]
5. Suzanne Reutter, Chuanpit Moser, Michelle Baack. Respiratory Distress in the Newborn. Pediatrics in Review, 2014, vol.35 issue 10.
6. Maki M, Ruuska T, Kuusela AL, Karikoski-Leo R, Ikonen RS. High prevalence of asymptomatic esophageal and gastric lesions in preterm infants in intensive care. Critical Care Medicine.1993, 21(12):1863-7.
7. Bedu A, Faure C, Sibony O, Vuillard E, Mougenot JF, Aujard Y. Prenatal gastrointestinal bleeding caused by esopha-gitis and gastritis. J Pediatr. 1994 Sep;125(3):465-7. [PubMed]
8. Wen HH, Chen MH, Ho MM, Hwang KC. Fetal gastric ulcer presenting with bloody amniotic fluid. Journal of Pedia-tric Gastroenterology & Nutrition. 1992, 15(4):455-7.
9. Lucas A, Adrian TE, Christofides N, Bloom SR, Aynsley-Green A. Plasma motilin, gastrin, and enteroglucagon and feeding in the human newborn. Arch Dis Child. 1980 Sep;55(9):673-7. [PubMed]
10. Lichtenberger LM, Gardner JW, Barreto JC, Morriss FH, Jr. Evidence for a role of volatile amines in the development of neonatal hypergastrinemia. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology & Nutrition. 1991, 13(4):342-6. [PubMed]
11. EBERS DW, GIBBS GE, SMITH DI. Gastric acidity on the first day of life. Pediatrics. 1956 Nov;18(5):800-2. [PubMed]
12. Grand RJ, Watkins JB, Torti FM. Development of the human gastrointestinal tract. A review. Gastroenterology. 1976 May;70(5 PT.1):790-810. [PubMed]
13. Azimi PH, Willert J, Petru A. Severe esophagitis in a newborn infant. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal. 1996, 15(4):385.
14. Taylor MJ, McCulloch DL. Visual evoked potentials in infants and children. J Clin Neurophysiol. 1992 Jul;9(3):357-72. [PubMed]
15. Aaronson A, Cywes S, Louw JH. Spontaneous esophageal rupture in the newborn. J Pediatr Surg. 1975 Aug;10(4):459-66. [PubMed]
16. Hyman PE. Gastroesophageal reflux: one reason why baby won't eat. J Pediatr. 1994 Dec;125(6 Pt 2):S103-9. [PubMed]
17. de Boissieu D, Dupont C, Barbet JP, Bargaoui K, Badoual J. Distinct features of upper gastrointestinal endoscopy in the newborn. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology & Nutrition. 1994 18(3):334-8. [PubMed]
18. Sherman NJ, Clatworthy HW Jr. Gastrointestinal bleeding in neonates: a study of 94 cases. Surgery. 1967 Oct;62(4):614-9. [PubMed]
19. Borowitz SM. Ulcerative esophagitis. A rare source of upper gastrointestinal bleeding in a neonate. Use of fiberoptic endoscopy for diagnosis. Clinical Pediatrics. 1989, 28(2):89-91. [PubMed]
20. Bartocci M, Bergqvist LL, Lagercrantz H, Anand KJ. Pain activates cortical areas in the preterm newborn brain. Pain. 2006 May;122(1-2):109-17. Epub 2006 Mar 13. [PubMed]
21. Lightdale JR, Gremse DA; Section on Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition. Gastroesophageal reflux: man-agement guidance for the pediatrician. Pediatrics. 2013 May;131(5):e1684-95. doi: 10.1542/peds.2013-0421. Epub 2013 Apr 29.
2. Wilmott RW, Boat TF, Bush A, Chernick V, Deterding RR. Kendig and Chernick’s Disorders of the Respiratory Tract in Children. Philadelphia, PA: Elsevier Saunders; 2012.
3. Aly H. Respiratory disorders in the newborn: identification and diagnosis. Pediatr Rev. 2004 Jun;25(6):201-8. [PubMed]
4. Warren JB, Anderson JM. Newborn respiratory disorders. Pediatr Rev. 2010 Dec;31(12):487-95; quiz 496. doi: 10.1542/pir.31-12-487. [PubMed]
5. Suzanne Reutter, Chuanpit Moser, Michelle Baack. Respiratory Distress in the Newborn. Pediatrics in Review, 2014, vol.35 issue 10.
6. Maki M, Ruuska T, Kuusela AL, Karikoski-Leo R, Ikonen RS. High prevalence of asymptomatic esophageal and gastric lesions in preterm infants in intensive care. Critical Care Medicine.1993, 21(12):1863-7.
7. Bedu A, Faure C, Sibony O, Vuillard E, Mougenot JF, Aujard Y. Prenatal gastrointestinal bleeding caused by esopha-gitis and gastritis. J Pediatr. 1994 Sep;125(3):465-7. [PubMed]
8. Wen HH, Chen MH, Ho MM, Hwang KC. Fetal gastric ulcer presenting with bloody amniotic fluid. Journal of Pedia-tric Gastroenterology & Nutrition. 1992, 15(4):455-7.
9. Lucas A, Adrian TE, Christofides N, Bloom SR, Aynsley-Green A. Plasma motilin, gastrin, and enteroglucagon and feeding in the human newborn. Arch Dis Child. 1980 Sep;55(9):673-7. [PubMed]
10. Lichtenberger LM, Gardner JW, Barreto JC, Morriss FH, Jr. Evidence for a role of volatile amines in the development of neonatal hypergastrinemia. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology & Nutrition. 1991, 13(4):342-6. [PubMed]
11. EBERS DW, GIBBS GE, SMITH DI. Gastric acidity on the first day of life. Pediatrics. 1956 Nov;18(5):800-2. [PubMed]
12. Grand RJ, Watkins JB, Torti FM. Development of the human gastrointestinal tract. A review. Gastroenterology. 1976 May;70(5 PT.1):790-810. [PubMed]
13. Azimi PH, Willert J, Petru A. Severe esophagitis in a newborn infant. Pediatric Infectious Disease Journal. 1996, 15(4):385.
14. Taylor MJ, McCulloch DL. Visual evoked potentials in infants and children. J Clin Neurophysiol. 1992 Jul;9(3):357-72. [PubMed]
15. Aaronson A, Cywes S, Louw JH. Spontaneous esophageal rupture in the newborn. J Pediatr Surg. 1975 Aug;10(4):459-66. [PubMed]
16. Hyman PE. Gastroesophageal reflux: one reason why baby won't eat. J Pediatr. 1994 Dec;125(6 Pt 2):S103-9. [PubMed]
17. de Boissieu D, Dupont C, Barbet JP, Bargaoui K, Badoual J. Distinct features of upper gastrointestinal endoscopy in the newborn. Journal of Pediatric Gastroenterology & Nutrition. 1994 18(3):334-8. [PubMed]
18. Sherman NJ, Clatworthy HW Jr. Gastrointestinal bleeding in neonates: a study of 94 cases. Surgery. 1967 Oct;62(4):614-9. [PubMed]
19. Borowitz SM. Ulcerative esophagitis. A rare source of upper gastrointestinal bleeding in a neonate. Use of fiberoptic endoscopy for diagnosis. Clinical Pediatrics. 1989, 28(2):89-91. [PubMed]
20. Bartocci M, Bergqvist LL, Lagercrantz H, Anand KJ. Pain activates cortical areas in the preterm newborn brain. Pain. 2006 May;122(1-2):109-17. Epub 2006 Mar 13. [PubMed]
21. Lightdale JR, Gremse DA; Section on Gastroenterology, Hepatology, and Nutrition. Gastroesophageal reflux: man-agement guidance for the pediatrician. Pediatrics. 2013 May;131(5):e1684-95. doi: 10.1542/peds.2013-0421. Epub 2013 Apr 29.
CITATION
DOI: 10.17511/ijpr.2017.i01.10
Published: 2017-01-31
How to Cite
Dr. Sasidharan Ponthenkandath, & Dr. Jayasree Chandramati. (2017). Erosive esophagitis with transient respiratory distress in newborns: a case report. Pediatric Review: International Journal of Pediatric Research, 4(1), 47-51. https://doi.org/10.17511/ijpr.2017.i01.10
Section
Case Report
Copyright (c) 2017 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


