School absenteeism effects on scholastic performance- reality check in India
Abstract
Introduction: School absenteeism is an important issue, which affects educational achievement and also results in false estimation of the prevalence of disease in school programs. This study was carried out to estimate the magnitude and its causes and its relation to school absenteeism.
Objectives: 1. To study the medical causes & social factors affecting school absenteeism. 2. To know the effect of school absenteeism on scholastic performance.
Method: It is a cross sectional study done in randomly selected in the age five to fifteen years. The study sample included 754 children. Socio-demographic profile and pre-designed questionnaires as well as school records were obtained. The marks cards of the entire year where taken to assess the scholastic performance. Significant absenteeism was taken when absenteeism was more than 15 percent.
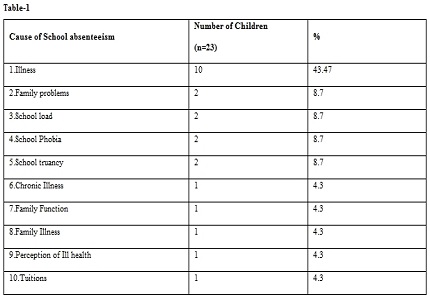
Results: The incidence of school absenteeism was 3.1 percent .Increased incidence was found in children aged 11 to 14 years. There is increased incidence of absenteeism seen in male with the increase in the birth order and family size, with low education status of the parents and in Hindu religion. Majority of the school children were anemic. Illness is the most important cause of school absenteeism. Poor academic performance is significantly associated with incidence of absenteeism.
Conclusion: Illness constituted the major reason of absenteeism. School absenteeism had positive correlation with the academic performance of the students.
Downloads
References
2. Parcel GS, Gilman SC, Nader PR, Harvey B. A comparison of absentee rates of elementary school children with asthma and non asthmatic schoolmates. Pediatrics 1979; 64: 878-881.
3. Millard MW, Johnson PT, Hilton A, Hart M. Children with asthma miss more school: fact or fiction? Chest. 2009 Feb;135(2):303-306. doi: 10.1378/chest.08-1642. Epub 2008 Oct 10.
4. Breuner CC, Smith MS, Womack WM. Factors related to school absenteeism in adolescents with recurrent headache. Headache 2004; 44: 217-222.
5. Unalp A. Prevalence and characteristics of recurrent headaches in Turkish adolescents. Pediatric Neurology 2006; 34: 110-115. [PubMed]
6. Saps M, Seshadri R, Sztainberg M, Schaffer G,Marshall BM, Di Lorenzo C. A prospective school based study of abdominal pain and other common somatic complaints in children. Journal of Pediatrics 2009;154: 322-326.
7. Ananthakrishnan S, Nalini P. School absenteeism in a rural area in Tamil Nadu. Indian Pediatr 2002;39: 847-850. [PubMed]
8. Robert WR. The Phenomenon of problematic school absenteeism [PhD thesis].Faulty of education:Australian Catholic University;2004.
9. Reid K. The self- concept and persistent school absenteeism.Br J Educ Psychol 1982; 52: 179-187.
10. Atkinson, M, Halsey K, Wilkin A, Kinder K. Raising Attendance, Working Practices and Current Initiatives within the Education Welfare Service. National Foundation for Educational Research; 2002 Oct. Report No.2000a.
11. Brown D. Truants, Families and Schools: A Critique of the Literature on Truancy.Educational Review.1983;35:225-235.
12. Malcolm H, Wilson V, DavidsonJ, Kirk S.Absence from School: A study of its causes and effects in seven LEAs.The SCRE Centre, University of Glasgow;2003. Report No.:RR424.
13. Marilyn C, SilvioB ,Gabriella C,Frans C, Raymond P. Ministry of Education, Youth and Employment School attendance improvement Report.Floriana;2005 Oct.
14. Rollings S., King N, Tonge B, Luk E, Heyne D, RamsdellS, et al. Truancy: Interventions with students, families and school personnel. A Stitch in Time: Issues in Child and Adolescent Mental Health. 1999;3:221-224.
15. Andrew JN.Official Hansard: 1999: Proceedings of the 39th Australian Conference of House of Representatives Standing Committee on Employment Education and training, Truancy and Exclusion from School (Canberra);1999 Sep.Report No. 9581-9603.
16. Fisher H. Anglicare Werribee Family Services. Primary School Attendance Intervention.Social Policy Research Centre,University of New South Wales; 2000 Apr. Report No:2/01.
17. Besculides M, Heffernan R, Mostashari F, Weiss D. Evaluation of school absenteeism data for early outbreak detection, New York City. BMC Public Health 2005; 5: 105. [PubMed]
18. Awasthi S, Sharma A. Survey of school health and absenteeism in Lucknow. Indian Pediatr. 2004 May;41(5):518. [PubMed]
19. Sreenivas V , Preena U ,Premila P.School Absenteeism Among Children and its Correlates: A Predictive Model for Identifying Absentees. Indian Pediatrics.2009 Oct30;(1):1-5.
20. Ananthakrishnan S, Nalini P. School absenteeism. in a rural area in Tamil Nadu. Indian Pediatr 2002;39: 847-850. [PubMed]
21. Gupta JP. An exploratory study of absenteeism in a school in a suburban area in New Delhi. Indian J Pediatr 1968; 35: 299-313. [PubMed]
22. Romero M , Lee Y.A National Portrait of Chronic Absenteeism in the Early Grades. National Center for Children in Poverty,Mailman School of Public Health , Columbia University;2007 Oct.
Copyright (c) 2017 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


