Blood glucose measurement by glucometer in comparison with standard method in the diagnosis of hypoglycemia in sick neonates
Abstract
Hypoglycemia is a serious risk factor in neonates. The signs and symptoms are non-specific. Early diagnosis is essential to reduce the associated morbidity and mortality.
Objective: To determine the efficacy and correlation of capillary and venous bedside glucose estimation using a glucometer in comparison with laboratory blood glucose analysis by glucose oxidase method in sick hypoglycemic neonates.
Methods: Blood glucose estimation was done in 200 sick neonates admitted to NICU by glucometer and by glucose oxidase method in the laboratory using the same venous sample at the time of admission. In addition, glucose estimation of capillary blood was also done using the same glucometer. Statistical analysis was done by Pearson correlation.
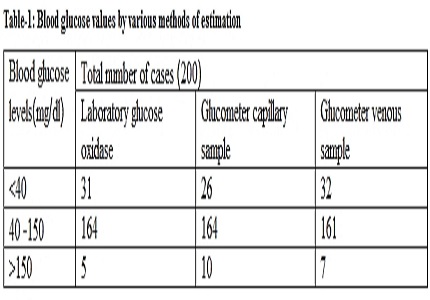
Results: The incidence of hypoglycemia in sick neonates by laboratory analysis was 15.5%. When laboratory values were used as gold standard, capillary blood glucose estimates had a sensitivity of 74.19%, specificity of 98.2%, PPV of 88.4% and NPV of 95.4%,whereas venous blood glucose estimates had a sensitivity of 93.55%, specificity of 98.23%, PPV of 90.62% and NPV of 98.8% in identifying hypoglycemia by glucometer in sick neonates.
Conclusion: Venous and capillary blood glucose estimation by glucometer has a good sensitivity and negative predictive value in detecting hypoglycemia in sick neonates. Further, the sensitivity of glucometer using venous blood is superior to capillary sample estimates. Laboratory blood glucose estimation should still be performed if bedside venous or capillary blood glucometer values are in the hypoglycemic range.
Downloads
References
2. Boyd R, Leigh B, Stuart P. Capillary versus venous bedside blood glucose estimations. Emerg Med J. 2005 Mar;22(3):177-79. doi:10.1136/emj.2003.011619.
3. Atkin SH, Dasmahapatra A, Jaker MA, Chorost MI, Reddy S. Fingerstick glucose determination in shock. Ann Intern Med. 1991 Jun 15;114(12):1020-4. [PubMed]
4. Jain A, Aggarwal R, Jeevasanker M, Agarwal R, Deorari AK, Paul VK. Hypoglycemia in the newborn. Indian J Pediatr. 2008 Jan;75(1):63-7. [PubMed]
5. Elusiyan JB, Adeodu OO, Adejuyigbe EA. Evaluating the validity of a bedside method of detecting hypoglycemia in children. Pediatr Emerg Care. 2006 Jul;22(7):488-90. [PubMed]
6. Hamid MH, Chishti AL, Maqbool S. Clinical utility and accuracy of a blood glucose meter for the detection of neonatal hypoglycemia. J Coll Physicians Surg Pak. 2004Apr;14(4);225-8. [PubMed]
7. Ngerncham S, Piriyanimit S, Kolatat T, Wongsiridej P, Inchgarm L, Kitsommart R, Vutrapongwatana P, Jeerapaet K. Validity of two point of care glucometers in the diagnosis of neonatal hypoglycemia. Indian Pediatr. 2012 Aug;49(8):621-5. Epub 2011 Jan 17. [PubMed]
8. Hay Jr WW, Raju TNK, Higgins RD, et al. Knowledge gaps and research needs for understanding and treating neonatal hypoglycemia: workshop report from Eunice Kennedy Shriver National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. J Pediatr. 2009Nov;155(5):612–7.doi:10.1016/j.jpeds.2009.06.044.
9. Cornblath M, Hawdon JM, Williams AF, Aynsley-Green A, Ward-Platt MP, Schwartz R, Kalhan SC. Controversies regarding definition of neonatal hypoglycemia: suggested operational thresholds. Pediatrics. 2000 May;105(5):1141-5.
10. Singhal PK, Singh M, Paul VK, Deorari AK, Ghorpade MG, Malhotra A. Neonatal hypoglycemia--clinical profile and glucose requirements. Indian Pediatr. 1992 Feb;29(2):167-71. [PubMed]
11. Misra PK, Sharma B. Hypoglycemia in newborns-a prospective study. Indian Pediatr. 1977 Feb;14(2):129-32.
12. Anderson S, Shakya KN, Shrestha LN, Costello AM. Hypoglycaemia: a common problem among uncomplicated newborn infants in Nepal. J Trop Pediatr. 1993 Oct;39(5):273-7. [PubMed]
13. Harish J, Srinivas HA, Soumya A. Comparative study of glucometer and laboratory glucoseoxidase method for the estimation of blood glucose levels inneonates: jemds.2015 Feb; 4(16): 2652-63.doi:10.14260/jemds/2015/383.
14. Sreenivasa B, Kumar GV. Comparative study of blood glucose levels in neonates using glucometer and laboratory glucose oxidase method. CurrPediatr Res. 2015;19(1&2);29-32.
15. De AK,Biswas R, Samanta M, Kundu CK. Study of blood glucose level in normal and low birth weight newborns and impact of early breast feeding in a tertiary care center. Ann Nigerian Med. 2011;5(2):53-8.doi:10.4103/0331-3131.92951.
16. Nayeri F, Shariat M, Mousavi Behbahani HM, Dehghan P, Ebrahim B. Blood glucose measurement by glucometer in comparison with standard method in diagnosis of neonatal hypoglycemia. Acta Med Iran. 2014;52(8):619-22. [PubMed]
17. Ho HT, Yeung WK, Young BW. Evaluation of point of care devices in the measurement of low bloods glucose in neonatal practice. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2004 Jul;89(4):F356-F359. [PubMed]
Copyright (c) 2017 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


