Role of cord blood bilirubin and albumin levels as predictors of subsequent hyperbilirubinemia in newborns
Abstract
Introduction: Neonatal hyperbilirubinemia is one of the most common problems in term and preterm babies. Development of hyperbilirubinemia in neonates is fretful for the parents and a concern for the pediatrician too. Healthy babies born through normal vaginal delivery who are getting discharged early are being readmitted for the treatment of hyperbilirubinemia.
Aim sand Objectives: The present study is done to determine the correlation of cord blood bilirubin, albumin and neonatal hyperbilirubinemia in identifying newborn babies at risk of developing significant hyperbilirubinemia and to establish the cutoff values of cord blood bilirubin and cord blood albumin levels to identify such high-risk neonates.
Materials and Methods: In present study, 303 term neonates who are delivered in ASRAM, Eluru from January 2012-January 2013, were included after parental consent. Cord blood bilirubin, Blood grouping and typing, Cord blood albumin and serum bilirubin levels were done in all babies.
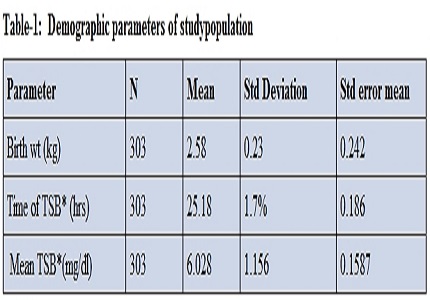
Results: The incidence of significant hyperbilirubinemia in this study was 23.7%. Cord serum unconjugated bilirubin level ≥2.0 mg/dl and total cordserum bilirubin level ≥ 2.5mg/dl as high risk indicator towards predicting neonatal hyperbilirubinemia in first week of life. 58.53% babies had cord serum albumin level < 2.8gm/dl.
Conclusion: Cord serum unconjugated bilirubin level ≥2mg/dl and total cord serum bilirubin level ≥2.5mg/dl, cord blood albumin <2.8g/dl is a high-risk indicator towards predicting neonatal hyperbilirubinemia in the first week of life.
Downloads
References
2. Arimbawa IM, Soetjininsih, Kari IK. Adverse effect of hyperbilirubinemia on the development of healthy term infants. Paediatr Indones 2006; 47; 51-56.
3. Seidman DS, Stevenson DK, Ergaz Z, Gale R. Hospital readmission due to neonatal hyperbilirubinemia. Pediatrics. 1995 Oct;96(4 Pt 1):727-9. [PubMed]
4. Alpay et al. Value of first day bilirubin measurement in predicting the development of significant jaundice in healthy term newborns. Pediatrics 2000 Aug;106(2):16. [PubMed]
5. Robinson GC, Dunn HG and Wong LC. Clinical and laboratory findings in heterospecific pregnancy, with a note on incidence of ABO hemolytic disease. Acta Pediatrica 1960; 49:53-62.
6. Simpson L, Deoarari AK, Paul VK. Cord bilirubin as a predictor of pathological jaundice-a cohort study; Indian Pediatr 2002; 39:724-730. [PubMed]
7. Rosenfeld J. Umbilical cord bilirubin levels as a predictor of subsequent hyperbilirubinemia. J Fam Pract. 1986 Dec;23(6):556-8. [PubMed]
8. Shanti Ghosh, S.H. Ahmed, Sudershan Kumari and S.K. Bhargava. Neonatal bilirubinaemia and its relationship to long term neurological deficits. Ind pediat 1971; 8(10): 704.
9. Narang A, Gathwala G, Kumar P. Neonatal jaundice: an analysis of 551 cases. Indian Pediatr. 1997 May;34(5):429-32. [PubMed]
10. Anand VR, Magotra ML. Neonatal jaundice: its incidence and aetiology. Indian Pediatr. 1978 Feb;15(2):155-60. [PubMed]
11. National Neonatology Forum. Neonatal morbidity and mortality - Report of the National Neonatal - Perinatal Database. Indian Pediatr. 1997;34(11):1039-42.
12. Friedman L, Lewis PJ, Clifton P, Bulpitt CJ. Factors influencing the incidence of neonatal jaundice. Br Med J. 1978 May 13;1(6122):1235-7. [PubMed]
13. Rosenfeld J. Umbilical cordbilirubinlevels as a predictor of subsequenthyperbilirubinemia. J Fam Pract.1986Dec;23(6):556-8. [PubMed]
14. Knudsen A. Prediction of the development of neonatal jaundice by increased umbilical cord blood bilirubin. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1989 Mar;78(2):217-21. [PubMed]
15. Knudsen A. Prediction of the development of neonatal jaundice by increased umbilical cord blood bilirubin. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1989 Mar;78(2):217-21. [PubMed]
16. Agarwal R, Deorari AK. Unconjugated hyperbilirubinemia in newborns: current perspective. Indian Pediatr. 2002 Jan;39(1):30-42. [PubMed]
17. Awasthi S, Rehman H. Early prediction of neonatal hyperbilirubinemia. Indian J Pediatr. 1998 Jan-Feb;65(1):131-9. [PubMed]
18. Rataj J, Kornacka M, Korman E. [Usefulness of measuringbilirubinlevels in cord blood for predictinghyperbilirubinemia in newborns]. Ginekol Pol.1994Jun;65(6):276-80. [PubMed]
19. Seidman DS, Ergaz Z, Revel Vilk S, et al. The use of bilirubin measurements on the first day of life for prediction of neonatal jaundice. In: Program and Abstracts of the Ross Special Conference, Hot Topics ’96 in Neonatology. Columbus, OH: Professional Services Department, Ross Products Division, Abbott Laboratories; 1996:284-294.
20. Amar Taksande, Krishna Vilhekar, Manish Jain, Preeti Zade, S uchita Atkari, Sherin Verkey. Prediction of the development of neonatal hyperbilirubinemia by increased umbilical cord blood bilirubin. Curr Pediatr Res 2005; 9 (1 & 2): 5-9.
21. Sun G, Wang YL, Liang JF, Du LZ. [Predictivevalue of umbilical cord bloodbilirubinlevel for subsequentneonatal jaundice]. Zhonghua Er Ke Za Zhi.2007Nov;45(11):848-52. [PubMed]
22. Bernaldo AJ, Segre CA,Sao Paulo. Bilirubin dosage in cord blood : could it predict neonatal hyperbilirubinemia, Med J, 2004; 122(3): 99-103.
23. Burtis CA, Ashwood AR, Bruns DE. Tietz text book of clinical chemistry and molecular diagnosis, 4th ed Elsevier; 2008:2254.
24. Suchanda Sahu, Rebecca Abraham, Joseph John, Alina Ann Mathew; Cord blood albumin as a predictor of neonatal jaundice; IJ Biomed Res; 2011; 2(1) 436-438.
Copyright (c) 2017 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


