Internet addiction in school going adolescents of different socio economic classes in Western India
Abstract
Background: Adolescents use internet as the primary medium for communication and socialization. But excessive use of internet may affect family and interpersonal relationships, academic performance and emotional development among adolescents. Excessive and incorrect use of internet is identified as Internet Addiction (IA). The present study was conducted to assess the pattern of internet use among school going adolescents of different socio-economic status as there are growing concerns worldwide for internet addiction.
Methods: After taking consent of school principal, students were given a questionnaire for socio-demographic details. Internet addiction test (IAT) was explained to them.
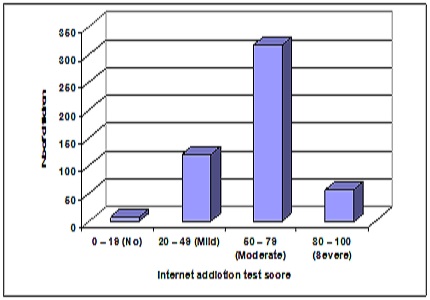
Results: In this study maximum number of children had moderate (50-79) level of internet addiction test score i.e. 317 (63.4%), 120 (24%) were in mild (20-49) level of internet addiction test score, 56 (11.2%) were in severe (80 – 100) level of internet addiction test score. Internet addiction is more common in boys than girls. Socio economic class II children had significantly more internet addiction score thanclass III andIV in study group (p<0.0001).
Conclusion: In this study, prevalence of internet addiction is high among boys of 12 to 17 years. Internet addiction should be lowered with the help of media literacy. As addiction of media is increasing, there is an urgentneed to use a comprehensive approach combining periodical awareness to the students and parents andincorporating good practices of internet use.
Downloads
References
2. http://www.internetworldstats.com/stats3.html
3. Gold berg I. Internet Addiction 1996. [Last accessed on 20 jan2017].Available from:http://web.urz. uniheidel berg.de/Netzdienste/anleitung/wwwtips/8/addict.html .
4. Daniel T, Shek L, Rachel C, Sun F, Lu YU. Neuroscience in the 21 st Century from Basic to Clinical. 2 ended. New York: Springer Science+ Business Media LLC; 2013.
5. Young KS. 1st Ed. New York: John wiley and Sons; 1998. Caught in the net: How to recognize the sings of internet addiction and a winning strategy for recovery.
6. Durkee T, Kaess M, Carli V, Parzer P, Wasserman C, Floderus Betal, Apter A, Balazs J, Barzilay S, Bobes J, Brunner R, Corcoran P, Cosman D, Cotter P, Despalins R, Graber N, Guillemin F, Haring C, Kahn JP, Mandelli L, Marusic D, Mészáros G, Musa GJ, Postuvan V, Resch F, Saiz PA, Sisask M, Varnik A, Sarchiapone M, Hoven CW, Wasserman D. Prevalence of pathological internet use among adolescents in Europe: demographic and socialfactors.Addiction. 2012 Dec;107(12):2210-22. doi: 10.1111/j.1360-0443.2012.03946.x.Epub 2012 Jul 26.
7. Tsitsika A, Janikian M, Schoenmakers TM, Tzavela EC, Olafsson K, Wójcik S, Macarie GF, Tzavara C, Richardson C. Internet addictive behavior in adolescence: a cross-sectional study in seven European countries. Cyberpsy chol Behav Soc Netw. 2014 Aug; 17 (8): 528-35. doi: 10.1089/cyber. 2013. 0382. Epub 2014 May 22.
8. Tavakolizadeh J, Atarodi A, Ahmadpour S, Pourgheisar A. The prevalence of excessive mobile phone use and its relation with mental health status and demographic factors among the students of Gonabad university of medical sciences in 2011 – 2012. Razavi Int J Med. 2014; 2(1): e15527.
9. Demirci K, Akgönül M, Akpinar A. Relationship of smartphone use severity with sleep quality, depression, and anxiety in university students. J Behav Addict. 2015; 4 (2):85-92. the main causes of Internet addiction.
10. Simon Kemp. Social, Digital and Mobile in India. 2014. Website: http://wearesocial.net/tag/india/ [Last accessed on 18th dec 2016].
11. Widyanto L, McMurran M. The psychometric properties of the internet addiction test. Cyberpsychol Behav. 2004 Aug; 7(4):443-50.
12. Lam LT, Peng ZW. Effect of pathological use of the internet on adolescent mental health: a prospective study. Arch Pediatr Adolesc Med. 2010 Oct; 164 (10): 901-6. doi: 10.1001/archpediatrics. 2010.159.
13. Milani L, Osualdella D, Di Blasio P. Quality of interpersonal relationships and problematic Internet use in adolescence.CyberpsycholBehav. 2009 Dec;12(6): 681-4. doi: 10.1089/cpb.2009.0071. [PubMed]
14. Nalwa K, Anand AP. Internet addiction in students: a cause of concern. Cyberpsychol Behav. 2003 Dec;6 (6): 653-6.
15. Anderson KJ. Internet use among college students: an exploratory study.J Am Coll Health. 2001 Jul;50 (1):21-6. [PubMed]
16. Kim EJ, Namkoong K, Ku T, Kim SJ. The relationship between online game addiction and aggression, self-control and narcissistic personality traits. Eur Psychiatry. 2008 Apr;23(3):212-8. doi: 10.1016/j .eurpsy.2007.10.010. Epub 2007 Dec 31.
17. Siomos KE, Dafouli ED, Braimiotis DA, Mouzas OD, Angelopoulos NV. Internet addiction among Greek adolescent students. Cyberpsychol Behav. 2008 Dec;11 (6): 653-7. doi: 10.1089/cpb.2008.0088.
18. Tsitsika, A., Critselis, E., Louizou, A., Janikian, M., Freskou, A., Marangou, E., Kormas, G., and Kafetzis, D.A. (2011) Determinants of Internet addiction among adolescents: a case-control study. The Scientific World Journal: TSW Child Health& Human Development, 11, 866–874. DOI 10.1100/tsw.2011.85.
19. Smahel D, Brown BB, Blinka L. Associations between online friendship and Internet addiction among adolescents and emerging adults. Dev Psychol. 2012 Mar; 48 (2):381-8. doi: 10.1037/a0027025.
20. Morrison CM, Gore H. The relationship between excessiveInternet use and depression: a questionnaire-basedstudy of 1,319 youngpeople and adults. Psycho-pathology. 2010;43(2):121-6. doi: 10.1159/000277001. Epub 2010 Jan 23. [PubMed]
21. Nalwa K, Anand AP.Internetaddiction in students: a cause of concern.CyberpsycholBehav. 2003 Dec;6(6): 653-6.
22. Casey, B. J., Tottenham, N., Liston, C., &Durston, S. Imaging the developing brain: What have we learned about cognitive development? Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 2005; 9, 104-110.
Copyright (c) 2018 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


