A study on glycemic control and related complications in type I diabetic children
Abstract
Introduction: Type I Diabetes Mellitus is a common, chronic, metabolic syndrome characterized by hyperglycaemia as a cardinal biochemical feature. Patients with diabetes mellitus face an increased risk of morbidity and mortality due to micro and macrovascular complications caused by diabetes. There is lack of Indian studies on diabetic children. Hence this study was undertaken to know glycaemic control and related complications in type I diabetes mellitus.
Materials and methods: This is a Prospective study conducted in Diabetic Clinic at Indira Gandhi institute of Child Health, Bengaluru for 1 year. Study group had 34 diabetic children; they were followed up for period of one year to assess glycaemic control and complications of the disease.
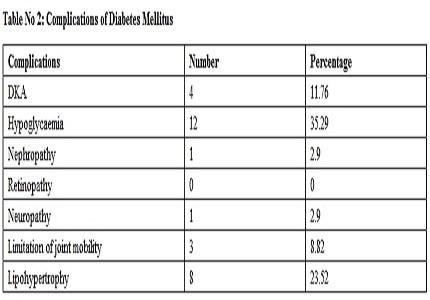
Results: 34 children were followed up for a period of one year to study glycaemic control and related complications. Glycaemic control was assessed using HbA1c. Seven children had good and 27 had poor glycaemic control. Factors associated with poor glycemic control were analyzed. Age at onset of the disease more than 12, duration of disease more than 5 years, female children in pre-pubertal age were associated with poor control. Children were followed up for development of complications. 4 children presented with DKA (11.76%), 12 had hypoglycaemia (35.29%).
Conclusion: Poor glycaemic control was associated with longer duration of disease, female sex and disease being diagnosed in pubertal period.
Downloads
References
2. Diabetes in the young in International Diabetes Federation. IDF Diabetes Atlas. 5th edition. International Diabetic Federation: Brussels, Belgium, 2011. p.34. https://www.idf.org/sites/default/files/21991_diabAtlas_5thEd.pdf
3. Svensson M, Eriksson JW, Dahlquist G. Early glycemic control, age at onset, and development of microvascular complications in childhood-onset type 1 diabetes: a population-based study in northern Sweden. Diabetes Care. 2004 Apr;27(4):955-62. [PubMed]
4. Keen H, Lee ET, Russell D, Miki E, Bennett PH, Lu M. The appearance of retinopathy and progression to proliferative retinopathy: the WHO Multinational Study of Vascular Disease in Diabetes. Diabetologia. 2001 Sep;44(Suppl 2):S22-30. [PubMed]
5. The DIAMOND Project Group. Incidence and trends of childhood Type 1 diabetes worldwide 1990-1999. Diabet Med 2006;23(8):857-866. [PubMed]
6. Patterson CC, Dahlquist GG, Gyurus E, Green A, Soltész G; EURODIAB Study Group. Incidence trends for childhood type 1 diabetes in Europe during 1989-2003 and predicted new cases 2005-20: a multicentre prospective registration study. Lancet 2009 Jun;373(9680):2027-33. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(09)60568-7.
7. Green A, Brutti G, Patterson CC, et al. Variation and trends in incidence of childhood diabetes in Europe. EURODIAB ACE study group. Lancet 2000 Mar;355(9207):873-6.
8. Barrett JC, Clayton DG, Concannon P, Akolkar B, Cooper JD, Erlich HA et al. Genome-wide association study and meta-analysis find that over 40 loci affect risk of type 1 diabetes. Nat Genet. 2009 Jun;41(6):703-7. doi: 10.1038/ng.381. Epub 2009 May 10. [PubMed]
9. Concannon P, Chen WM, Julier C, Morahan G, Akolkar B, Erlich HA et al. Genome-wide scan for linkage to type 1 diabetes in 2,496 multiplex families from the Type 1 Diabetes Genetics Consortium. Diabetes 2009 Apr;58(4):1018-1022. [PubMed]
10. Lambert AP, Gillespie KM, Thomson G, Cordell HJ, Todd JA, Gale EA et al. Absolute risk of childhood-onset type 1 diabetes defined by human leukocyte antigen class II genotype: a population-based study in the United Kingdom. J ClinEndocrinolMetab. 2004 Aug;89(8):4037-4043.\
11. Skyler JS, Krischer JP, Wolfsdorf J, Cowie C, Palmer JP, Greenbaum C et al. Effects of oral insulin in relatives of patients with type 1 diabetes: The Diabetes Prevention Trial - Type 1. Diabetes Care 2005 May;28(5):1068-76. [PubMed]
12. American Diabetes Association. Diagnosis and Classification of Diabetes Mellitus. Diabetes Care. 2010 Jan;33(Suppl 1): S62–S69. doi: 10.2337/dc10-S062. [PubMed]
13. American Diabetes Association. Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes. Diabetes Care. 2011 Jan;34 (Suppl 1): S11-S61. doi: 10.2337/dc11-S011.
14. Wolfsdorf J, Craig ME, Daneman D, Dunger D, Edge J, Lee W, et al. ISPAD Clinical Practice Consensus Guidelines 2009 Compendium. Diabetic ketoacidosis in children and adolescents with diabetes. Pediatr Diabetes. 2009 Sep;10(Suppl. 12):118–133. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-5448.2009.00569.x.
15. Ballantyne JA, Hooper G. The hand and diabetes. Current Orthopaedics.2004;18:118–25.
16. Kim RP, Edelman SV, Kim. Musculoskeletal Complications of Diabetes Mellitus. Clinical Diabetes. 2001;19(3):132-5. [PubMed]
17. Vanelli M, Cerutti F, Chiarelli F, Lorini R, Meschi F; MCDC-Italy Group. Nationwide cross sectional survey of 3560 children and adolescents with diabetes in Italy. J Endocrinol Invest. 2005 Sep; 28(8):692-9. [PubMed]
18. Mohammed HA, Farghaly HS, Metwalley KA, Monazea EM, Abd El-Hafeez HA. Predictors of glycaemic control in children with type 1 diabetes mellitus in Assiut Egypt. Indian J of Endocrinol Metab. 2012 Sep;16(5):796-802. doi: 10.4103/2230-8210.100679. [PubMed]
19. Setoodeh A, Mostafavi F, Rabbani A, Hedayat T. Female sex as a risk factor for glycaemic control and complications in Iranian patients with type one diabetes mellitus. Iran J Pediatr 2011 Sep;21(3):373-8. [PubMed]
20. Gerstl EM, Rabl W, Rosenbauer J, Gröbe H, Hofer SE, Krause U et al. Metabolic control as reflected by HbA1c in children, adolescents and young adults with type-1 diabetes mellitus: combined longitudinal analysis including 27,035 patients from 207 centers in Germany and Austria during the last decade. Eur J Pediatr. 2008 Apr;167(4):447–53. Epub 2007 Oct 9.
21. Mortensen HB, Hougaard P. Comparison of metabolic control in a cross sectional study of 2,873 children and adolescents with IDDM from 18 countries. The Hvidore study group on childhood diabetes. Diabetes Care. 1997 May;20(5):714–20.
22. Revers et al. Diabetic Ketoacidosis, Diabetic care,29;2006:1190-1220.
23. Craig ME, Jones TW, Silink M, Ping YJ. Diabetes care, glycemic control, and complications in children with type 1 diabetes from Asia and the Western Pacific Region. J Diabetes Complications. 2007 Sep-Oct;21(5):280–7. [PubMed]
24. Izumi K; Hoshi M; Kuno S; Okuno G; Yamazaki Y; Isshiki G et al. Glycemic control, growth and complications in children with insulin-dependent diabetes mellitus - a study of children enrolled in a summer camp program for diabetics in Kinki district, Japan. Diabetes research and clinical practice. 1995 Jun;28(3):185-90.
25. Donaghue, KC, Fairchild JM, Craig ME, Chan AK, Hing S, Cutler LR et al. Do all prepubertal years of diabetes duration contribute equally to diabetes complications? Diabetes Care. 2003 Apr; 26(4),1224-9.
26. Mohsin F, Craig ME, Cusumano J, Chan AK, Hing S, Lee JW et al. Discordant trends in microvascular complications in adolescents with type 1 diabetes from 1990 to 2002. Diabetes Care. 2005 Aug;28(8):1974–80. [PubMed]
27. Silverstein JH, Gordon G, Pollock BH, Rosenbloom AL: Long-term glycemic control influences the onset of limited joint mobility in type 1 diabetes. J Pediatr. 1998 Jun;132(6):944–7. [PubMed]
Copyright (c) 2015 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


