Cord blood hemoglobin levels in relation to maternal anemia
Abstract
Introduction: Maternal anemia is a significant problem.Mothers with anemia are likely to deliver anemic babies. Cord blood hemoglobin can be used to diagnose neonatal anemia.
Materials and methods: This was a cross sectional study conducted from January 2017 to January 2018 in Department of Pediatrics and Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology at T.S. MisraMedical College andHospital. 100 mothers delivering in labor room and their newborns were included in the study. Maternal hemoglobin was estimated prior to delivery. After the delivery of baby cord blood hemoglobin was collected. Cord blood hemoglobin of anemic and non-anemic mothers were compared. Anemic mothers were categorized as mild, moderate and severe. We compared cord blood hemoglobin of babies in all three groups and also with cord blood hemoglobin of non-anemic mothers.
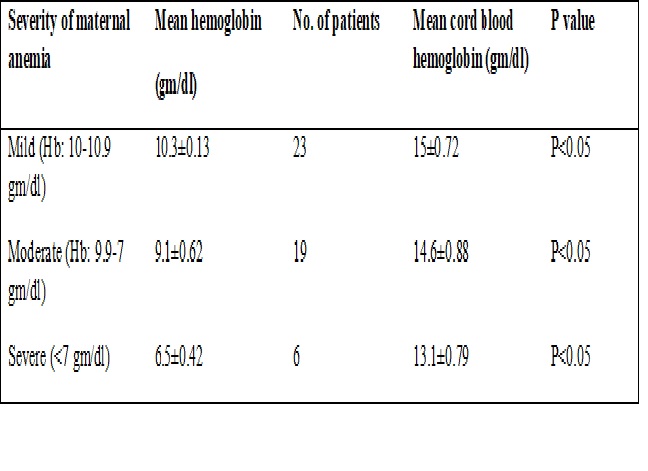
Results:Difference betweenmean cord blood hemoglobin of anemic and non-anemic mothers was found to be statistically significant. Difference between cord blood hemoglobin of all three groups (mild, moderate and severe anemia) found to be statistically significant.
Conclusion:This study shows direct correlation between maternal and fetal hemoglobin levels. We stress the importance of preventing maternal anemia and maintaining adequate iron storage in mothers during pregnancy to ensure better maternal and fetal outcome. We also emphasize the importance of cord blood hemoglobin for early diagnosis of neonatal anemia.
Downloads
References
2. McLean E, Cogswell M, Egli I, et al. Worldwide prevalence of anaemia, WHO Vitamin and Mineral Nutrition Information System, 1993-2005. DOI:10.1017/S1368980008002401.[pubmed]
3. Elagri MM, Waggiallah HA. Assessment of hematological parametres of neonatal cord blood in anemic and non anemicmothers.J Clin Exp Res 2013;1(2):22-25
4. Sweet DG, Savage G,Tubman TRJ, Lappin TRJ. Study of maternal influences on fetal iron status at term using cord blood transferrin receptors. Arch Dis Child fetal Neonatal Ed 2001 Jan;84(1):40-43
5. Sareen A, Mahajan K, Singh S. Maternal anemia and its effect on cord blood hemoglobin. Indian Medical Gazette 2013 May;161-63
6. Debbarma R, Debbarma B, Devi A. Effect of maternal anemia on cord hemoglobin and birth weight of new borns. IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences 2015 July;14(7):19-21
7. Sisson TR, Lund CJ. The influence of maternal iron deficiency on the newborn. DOI:10.1093/ajcn/6.4.376.[pubmed]
8. Nhonoli AM, Kihama, FE, Ramji BD. The relation between maternal and cord serum iron levels and its effect on foetal growth in iron deficient mothers without malarial infection Br J ObstetGynaecol 1975june;82(6):467-70
9.Singla PN, Chand S, Khanna S, Agarwal KN. Effect of maternal anaemia on the placenta and the newborn infant. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1978 Sep;67(5):645-8.[pubmed]
10. Fenton V, Cavill I, Fisher J. Iron stores in pregnancy. Br J Haematol. 1977 Sep;37(1):145-9.[pubmed]
11. Mamoury GH, Hamedy AB, Akhiaghi F. Cord Hemoglobin in Newborns in Correlation with Maternal Hemoglobin in Northeastern Iran . IJMS 2003Sep ; 28(3):166-68.
12. Najeeba CM, Prabhu AS. Maternal Anaemia and its effect on Cord Blood Haemoglobin& Newborn Birth Weight. IOSR 2015July;14(7):30-32.
13. Cantwell RJ. Iron deficiency anemia of infancy:some clinical principles illustrated by the response of Maoriinfants to neonatal parenteral iron administration. DOI:10.1177/000992287201100807
14. Bhargava M, Kumar R, Iyer PU, et al. Effect of maternal anaemia and iron depletion on foetal iron stores, birthweight and gestation. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1989 Mar;78(2):321-2.[pubmed]
15. Rusia U, Madan N, Agarwal N, et al. Effect of maternal iron deficiency anaemia on foetal outcome. Indian J Pathol Microbiol. 1995 Jul;38(3):273-9.[pubmed]
16. Terefe B, Birhanu A, Nigussie P, Tsegaye A. Effect of maternal iron deficiency anemia on the iron store of newborns in ethiopia. DOI:10.1155/2015/808204.[pubmed]
Copyright (c) 2018 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


