Comparison of geneXpert versus sputum/gastric aspirate smearfor AFB for the diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis in children
Abstract
Introduction:This was a hospital based observational study for the comparison of geneXpert versus sputum /Gastric aspirate sample for AFB, for diagnosing pulmonary TB in children.The study was donein need for the useful diagnostic test, which is easy toperform, more sensitive and quicker. Gene Xpert assay is a single tube, cartridge based, real time PCR assay for the detection of tuberculosis.
Materials and Methods: We enrolled 50 children for our study. Children attending inpatient or outpatient department were screened using aquestionnaire.Suspected children were investigated with Complete Blood count, ESR, Chest Xray andMantoux test. Sputum (in older children) was collected in a sterile container for AFB, and inspecialized container for geneXpert studies. In smaller children gastric aspirates were collected and sent for analysis and the results were compared.
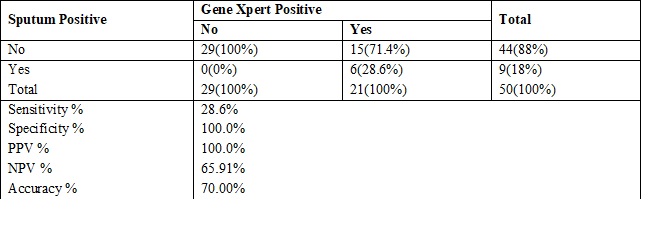
Results: Of the 50 children who were included in the study,42 (84%) were less than 10 years, 8 (16%) were 11-16 years. 46% of patients had positive contact history of tuberculosis. History of clinical tuberculosis was present in 58% of the patients. Gene X pert analysis came positive in 42% of the patients whereas sputum/gastric aspirate analysis for AFB came positive in 12% of the patients. In our study, sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value and negative predictive value of Gene Xpert analysis came as 28.6%, 100%, 100% and 65.9% with 70% accuracy.
Conclusion: Gene Xpert analysis can be effectively used as a quick and accurate diagnostic test for the diagnosis of pulmonary tuberculosis in children, especially in a low resource setting, although the bacteriological culture remains the gold standard.
Downloads
References
2. World Health Organization. Automated real-time nucleic acid amplification technology for rapid and simultaneousdetection of tuberculosis and rifampicin resistance: XpertMTB/RI assay for the diagnosis of pulmonary and extra-pulmonary TB in adults and children. Policy update.available from http://apps.who.int/iris/bitstream/10665/112472/1/9789241506335_eng.pdf. Accessed November 5,2014
3. World Health Organization. Guidance for nationaltuberculosisprograms onthe management oftuberculosis in children.Second edition Availablfrom:http://apps.who.int/medicinedocs/documents/s21535en/s21535en.pdf.
4. Government of India. Central TB Division DirectorateGeneral of Health Services, Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. TB India 2014 Revised National TB Control Programme.AnnualStatusRep: www.tbcindia.nic.in/pdfs/TB%20INDIA%202014.pdf.
5. Kumar A, Das S, Paul DK. A Study on the Role of Cartridge Based Nucleic Acid Amplification Test (CBNAAT) for DiagnosingPediatric Tuberculosis in a Tertiary Care Hospital in Eastern India. Acad J Ped Neonatol. 2018; 6(3): 555745. DOI: 10.19080/AJPN.2018.06.555745.
6. Nhu NT, Ha DT, Anh ND, et al. Evaluation of Xpert MTB/RIF and MODS assay for the diagnosis of pediatric tuberculosis. BMC Infect Dis. 2013 Jan 23;13:31. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-13-31.[pubmed]
7. Rachow A, Clowes P, Saathoff E, Mtafya B, Michael E, NtinginyaEn, Kowour D, Rojas-Ponce G, Kroidl A, Maboko L, et al: Incresed and expedited case detection by xpert MTB/RIF assay in childhood tuberculosis: a prospective cohort study. Clin Infect Dis. 2012, 54 (10): 1388-1396.DOI: 10.1093?cid/cis 190. Epub 2012 Apr 3.
8. Sekadde MP, Wobudeya E, Joloba ML, et al. Evaluation of the Xpert MTB/RIF test for the diagnosis of childhood pulmonary tuberculosis in Uganda: a cross-sectional diagnostic study. BMC Infect Dis. 2013 Mar 12;13:133. doi: 10.1186/1471-2334-13-133.[pubmed]
9. Boehme CC, Nicol MP, NabetaP, Michael JS, Gotuzzo E, Tahirli R, Gler MT, Blackemore R, Worodria W, Gray C et al: Feasibility, diagnostic accuracy, and effectiveness of decentralized use of the Xpert MTB/RIF test for diagnosis of tuberculosis and multidrug resistance; a multicenter implementation study. Lancet. 2011, 377 (9776): 1495-1505. Doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60438-8
10. Monika Agarwal, Ashish Bajaj, Vinay Bhatia et al. Comparative study of Gene Xpert with Zn stain and Culture in samples of suspected Pulmonary Tuberculosis. J Clin Diagn Res. 2016 May; 10(5): DC09-DC12.
Doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2016/18837.7755
11. GandraNR, Jayasri Helen Gali. GeneXpert: a game changer in the detection and diagnosis of childhood tuberculosis. Int J ContempPediatr. 2018 Jan;5(1):35-41.DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3291.ijcp20175087
Copyright (c) 2018 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


