Correlation between NT pro-b-type Natriuretic peptide and left ventricular ejection fraction in children presenting with Dyspnea – a prospective cohort study
Abstract
Introduction: Simple screening tests exist for congenital heart diseases but the same cannot be said for cardiac failure in children. Although echocardiography is considered the gold standard for the detection of left ventricular dysfunction, it is relatively expensive and is not often readily available. We aim to prove that NT pro-B-type natriuretic peptide levels may be useful in ruling out the diagnosis of heart failure in children presenting to the emergency room with dyspnea by studying the relation between left ventricular ejection fraction and NT pro-BNP.
Methods: Seventy four patients presenting to the emergency department with dyspnea and fulfilling the modified Ross’ criteria for heart failure were included in the study. NT pro-BNP levels were measured for all the patients and a two-dimensional echocardiographic study was performed for them. Statistical analyses were performed using chi square test for independent samples and Pearson correlation tests.
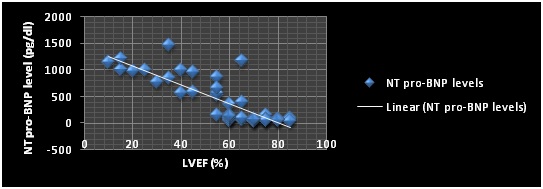
Results: A significant inverse correlation was observed between NT pro-BNP levels and left ventricular ejection fraction (r=-0.789, p=0.003).
Conclusion: NT pro-BNP assay appears to hold promise as a potent and cost effective test of choice for acutely dyspneic children, which could replace chest x-ray and echocardiography as first investigation in such patients in urgent care settings.
Downloads
References
2. Maher KO, Reed H, Cuadrado A, Simsic J, Mahle WT, DeGuzman M et al. B-Type Natriuretic Peptide in the Emergency Diagnosis of Critical Heart Disease in Children. Pediatrics, June 2008; 121(6):e1484-1488.DOI: 10.1542/peds.2007-1856.
3. Hospital stays, hospital charges, and in-hospital deaths among infants with selected birth defects–United States, 2003. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2007;56(2):25–29
4. Rusconi PG, Ludwig DA, Ratnasamy C, Mas R, Harmon WG, Colan SD, Lipshultz SE. Serial measurements of serum NT-proBNP as markers of left ventricular systolic function and remodeling in children with heart failure. American heart journal. 2010 Oct 1;160(4):776-83
5. Nir A, Nasser N. Clinical value of NT-ProBNP and BNP in pediatric cardiology. J Card Fail. 2005 Jun;11(5 Suppl):S76-80.[pubmed]
6. Lin CW, Zeng XL, Jiang SH, Wu T, Wang JP, Zhang JF, Ou YH. Role of the NT-proBNP level in the diagnosis of pediatric heart failure and investigation of novel combined diagnostic criteria. Experimental and therapeutic medicine. 2013 Oct 1;6(4):995-9.
7. Ootaki Y, Yamaguchi M, Yoshimura N, Oka S, Yoshida M, Hasegawa T. Secretion of A-type and B-type natriuretic peptides into the bloodstream and pericardial space in children with congenital heart disease. The Journal of thoracic and cardiovascular surgery. 2003 Nov 1;126(5):1411-6.
8. Fernandes BA, Maher KO, Deshpande SR. Cardiac biomarkers in pediatric heart disease: A state of art review. World journal of cardiology. 2016 Dec 26;8(12):719.[pubmed]
9. Ross RD. The Ross classification for heart failure in children after 25 years: a review and an age-stratified revision. PediatrCardiol. 2012 Dec;33(8):1295-300. doi: 10.1007/s00246-012-0306-8. Epub 2012 Apr 5.[pubmed]
10. Zhou FJ, Zhou CY, Tian YJ, et al. Diagnostic value of analysis of H-FABP, NT-proBNP, and cTnI in heart function in children with congenital heart disease and pneumonia. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2014;18(10):1513-6.[pubmed]
11. Das S, Chanani NK, Deshpande S, Maher KO. B-type natriuretic peptide in the recognition of critical congenital heart disease in the newborn infant. PediatrEmerg Care 2012; 28: 735-738 [PMID: 22858747 DOI: 10.1097/PEC.0b013e3182624a12]
12. Cohen S, Springer C, Avital A, et al. Amino-terminal pro-brain-type natriuretic peptide: heart or lung disease in pediatric respiratory distress? Pediatrics. 2005 May;115(5):1347-50. DOI:10.1542/peds.2004-1429.[pubmed]
13. Koulouri S, Acherman RJ, Wong PC, et al. Utility of B-type natriuretic peptide in differentiating congestive heart failure from lung disease in pediatric patients with respiratory distress. PediatrCardiol. 2004 Jul-Aug;25(4):341-6. DOI:10.1007/s00246-003-0578-0.[pubmed]
14. Iacob D, Butnariu A, Leucuţa DC, Samaşca G, Deleanu D, Lupan I. Evaluation of NT-proBNP in children with heart failure younger than 3 years old. Romanian Journal of Internal Medicine. 2017 Jun 1;55(2):69-74.
15. Mir TS, Marohn S, Läer S, et al. Plasma concentrations of N-terminal pro-brain natriuretic peptide in control children from the neonatal to adolescent period and in children with congestive heart failure. Pediatrics. 2002 Dec;110(6):e76.[pubmed]
16. Lubien E, DeMaria A, Krishnaswamy P, et al. Utility of B-natriuretic peptide in detecting diastolic dysfunction: comparison with Doppler velocity recordings. Circulation. 2002 Feb 5;105(5):595-601.[pubmed]
17. Vasan RS, Benjamin EJ, Levy D. Prevalence, clinical features and prognosis of diastolic heart failure: an epidemiologic perspective. J Am Coll Cardiol. 1995 Dec;26(7):1565-74. DOI:10.1016/0735-1097(95)00381-9
18. Bonow RO, Udelson JE. Left ventricular diastolic dysfunction as a cause of congestive heart failure. Mechanisms and management. Ann Intern Med. 1992 Sep 15;117(6):502-10.[pubmed]
Copyright (c) 2018 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


