Prevalence of hypertension among adolescents
Abstract
Introduction: Adolescence is a significant period of growth and maturation. The emergence of obesity and its sequel as public health problems has renewed interest in the adolescents as Overweight and obesity act as risk factors for obesity related diseases. Familial aggregation of blood pressure is noted among adults, which has been traced to childhood, as early as one year of age.
Methods: a cross sectional study involving 1000 boys and girls each were subjected to measurement of anthropometry, blood pressure and BMI.
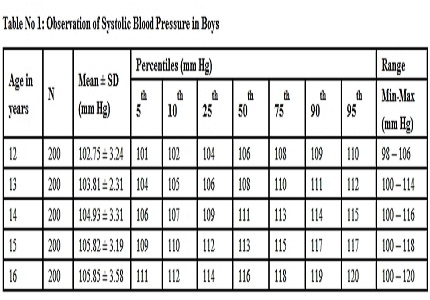
Results: The Incidence of Raised Blood Pressure in our study was 1.3%. The mean systolic blood pressure in boys increased from 102.75±3.24mmHg at 12years of age to 105.85±3.58 mmHg at 16years. In girls it rises from 102.04±2.53mmHg at 12 years to 106.48±3.59 mmHg at 16 years. The mean diastolic blood pressure increased from 66.85±3.45 mmHg at 12years of age to 67.95±4.24 mmHg at 16years, in boys. In girls it rises from 66.90±3.38mmHg at 12years to 68.95±4.53 mmHg at 16years. Blood pressure recordings showed an increasing trend steadily with age in the present study.
Conclusion: There is a strong correlation between systolic blood pressure and weight and height in both sexes. Majority of the children who were labeled as hypertensive’s are likely to be suffering from essential hypertension, because of the asymptomatic nature of their condition. Hence the adolescent period the most precious stage for early detection and primary prevention on hypertension.
Downloads
References
2. Use and interpretation of anthropometric indicators of nutritional status. WHO Working Group. Bull World Health Organ. 1986;64(6):929-41. [PubMed]
3. Ke-You G, Da-Wei F. The magnitude and trends of under- and over-nutrition in Asian countries. Biomed Environ Sci. 2001 Jun;14(1-2):53-60. [PubMed]
4. Sawaya AL, Dallal G, Solymos G, de Sousa MH, Ventura ML, Roberts SB, Sigulem DM. Obesity and malnutrition in a Shantytown population in the city of São Paulo, Brazil. Obes Res. 1995 Sep;3 Suppl 2:107s-115s. [PubMed]
5. Griffiths PL, Bentley ME. The nutrition transition is underway in India. J Nutr. 2001 Oct;131(10):2692-700. [PubMed]
6. Smoak CG, Burke GL, Webber LS, Harsha DW, Srinivasan SR, Berenson GS. Relation of obesity to clustering of cardiovascular disease risk factors in children and young adults. The Bogalusa Heart Study. Am J Epidemiol. 1987 Mar;125(3):364-72.
7. Must A, Jacques PF, Dallal GE, Bajema CJ, Dietz WH. Long-term morbidity and mortality of overweight adolescents. A follow-up of the Harvard Growth Study of 1922 to 1935. N Engl J Med. 1992 Nov 5;327(19):1350-5. [PubMed]
8. Physical status: the use and interpretation of anthropometry. Report of a WHO Expert Committee. World Health Organ Tech Rep Ser. 1995;854:1-452. [PubMed]
9. Biron P, Mongeau JG. Familial aggregation of blood pressure and its components. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1978 Feb;25(1):29-33. [PubMed]
10. Loggie JMH, Editorial, Symposium on pediatric hypertension, Paediatrics Clinics of North America, 1978, p. 25. [PubMed]
11. Kelishadi R, Hashemipour M, Bashardoost N. Blood pressure in children of hypertensive and normotensive parents. Indian Pediatr. 2004 Jan;41(1):73-7. [PubMed]
12. Hurst, The Heart, Volume 2, 10th Edition, 2001, Chapter 51, pp. 1587-88. [PubMed]
13. Chadha SL, Tandon R, Shekhawat S, Gopinath N. An epidemiological study of blood pressure in school children (5-14 years) in Delhi. Indian Heart J. 1999 Mar-Apr;51(2):178-82.
14. Nelson’s Textbook of Pediatrics, 17th Edition, Treatment of Hypertension, 2004. p. 1596.
15. Moss AJ. Indirect methods of blood pressure measurement. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1978 Feb;25(1):3-14. [PubMed]
16. Albert R. Rocchini, 1984 December, Childhood hypertension etiology, Diagnosis and treatment, Paediatrics Clinics of North America, December 1984, 31(6):15 25.
17. Anand NK and Lalit Tandoon, Prevalence of hypertension in school going children, Indian Journal of Paediatrics, 1996, 33, 377-391.
18. Agarwal VK, Sharan R, Srivastava AK, Kumar P, Pandey CM. Blood pressure profile in children of age 3-15 years. Indian Pediatr. 1983 Dec;20(12):921-5. [PubMed]
19. Foster TA, Voors AW, Webber LS, Frerichs RR, Berenson GS. Anthropometric and maturation measurements of children, ages 5 to 14 years, in a biracial community--the Bogalusa Heart Study. Am J Clin Nutr. 1977 Apr;30(4):582-91. [PubMed]
20. Voors AW, Webber LS, Berenson GS. Epidemiology of essential hypertension in youth--implications for clinical practice. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1978 Feb;25(1):15-27. [PubMed]
21. Agarwal R, Mandowara SL, Bhandari B, Garg OP. II. Prevalence of hypertension in apparently healthy school children. Indian Pediatr. 1982 Sep;19(9):779-84. [PubMed]
22. Sachdev Y. Normal blood pressure and hypertension in Indian children. Indian Pediatr. 1984 Jan;21(1):41-8. [PubMed]
23. Laroia D, Sharma M, Diwedi V, Belapurkar KM, Mathur PS. Profile of blood pressure in normal school children. Indian Pediatr. 1989 Jun;26(6):531-6. [PubMed]
24. Londe S, Gollub SW, Goldring D. Blood pressure in black and in white children. J Pediatr. 1977 Jan;90(1):93-5. [PubMed]
25. Berenson GS, Cresanta JL, Webber LS. High blood pressure in the young. Annu Rev Med. 1984;35:535-60. [PubMed]
26. Londe S, Bourgoignie JJ, Robson AM, Goldring D. Hypertension in apparently normal children. J Pediatr. 1971 Apr;78(4):569-77. [PubMed]
27. Blaufox MD. Systemic arterial hypertension in pediatric practice. Pediatr Clin North Am. 1971 May;18(2):577-93. [PubMed]
28. Loggie JM, Rauh LW. Persistent systemic hypertension in the adolescent. Med Clin North Am. 1975 Nov;59(6):1371-83. [PubMed]
29. Park JK and Park K (Eds), Textbook of Preventive and Social Medicine, 17th Edition, 2002.
30. Dhillon MJ, Modern management of hypertension, Recent Advances in Pediatrics, Churchill Livingstone, 1984, p. 35.
Copyright (c) 2015 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


