Prevalence of early onset neonatal septicemia in babies born to mother with pre-eclampsia
Abstract
Context: Pregnancy induced hypertension (PIH) is one of the important risk factor for preterm delivery. Neutropenia and thrombocytopenia are well recognized neonatal sequelae to maternal hypertension in pregnancy. Preeclampsia-associated neutropenia is a risk factor for an increased incidence of infection in preterm neonates.
Methods & material: 87 neonates born to mother with preeclampsia were included with aim to find prevalence of EOS and their haematological profile. Diagnostic work up includes complete blood count, CRP, blood culture and sensitivity (C/S) and other relevant investigations according to cases.
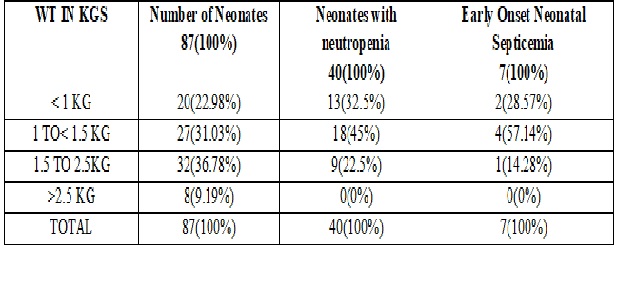
Result: Out of 87 neonates, 7 neonates had EOS (8%) with blood culture proven bacterial sepsis, Klebsiella pneumonia (57.14%) was commonest organism isolated followed by E. Coli (28.57%) and Enterococci (14.28%). About 32 (36.76%) mothers had severe hypertension and 55(68.22%) mothers had mild to moderate preeclampsia. About 60(68.79%) neonates were born preterm. 40 (45%) neonates had neutropenia. 38 (43.65%) babies had thrombo-cytopenia. All 7 septic babies had neutropenia and thrombocytopenia.
Conclusion: Early onset septicemia is more common in babies born to mother with preeclampsia due to associated Prematurity, Neutropenia and Thrombocytopenia. Hence preventive measures should focus on recognition of these high risk neonates with prompt laboratory screening for sepsis and early institution of empirical antibiotics based on local data.
Downloads
References
Muti M, Tshimanga M, Notion GT, et al. Prevalence of pregnancy induced hypertension and pregnancy outcomes among women seeking maternity services in Harare, Zimbabwe. BMC Cardiovasc Disord. 2015 Oct 2;15:111. doi: 10.1186/s12872-015-0110-5.
Sivakumar SB, Bhat V and Badhe A. Effect of Pregnancy Induced Hypertension on Mothers and their Babies. Indian Journal of Paediatrics.2007:74 July:623-26. http://medind.nic.in/icb/t07/i7/icbt07i7 p623.pdf
Solange Regina et al. Pregnancy induced hypertension and the neonatal outcome. Actapul. Enferm Jan/March: 2008; 21.
S H FRASER, DI TUDEHOPE. Neonatal neutropenia and thrombocytopenia following maternal hypertension. J Pediatric child health 1996; 32,31-34
MohannadMoallem, Joyce M. Koenig. Preeclampsia and Neonatal Neutropenia. Neo ReviewsSeptember 2009, VOLUME 10 / ISSUE 9.
Doron MW, Makhlouf RA, Katz VL, et al. Increased incidence of sepsis at birth in neutropenic infants of mothers with preeclampsia. J Pediatr. 1994 Sep;125(3):452-8.
Bhaumik S, Ghosh S, Haldar K.K, Mitra P.K, Manna B. Risk of early onset Neonatal septicemia in babies born to mother with pre-eclampsia. Indian Paediatrics. Jul 2000:37(7):775-9.
DC Dutta, Textbook of obstetrics, 9 th edition, 2018
Mouzinho A, Rosenfeld CR, Sánchez PJ, et al. Revised reference ranges for circulating neutrophils in very-low-birth-weight neonates. Pediatrics. 1994 Jul;94(1):76-82.
Manroe BL, Weinberg AG, Rosenfeld CR, et al. The neonatal blood count in health and disease. I. Reference values for neutrophilic cells. J Pediatr. 1979 Jul;95(1):89-98.
Nadkarni, J. Bahl, P. Parekh, Perinatal out come in pregnancy induced hypertension. Indian Pediatrics 2001; 38: 174-178.
Procianoy RS, Silveira RC, Mussi-Pinhata MM, et al. Sepsis and neutropenia in very low birth weight infants delivered of mothers with preeclampsia. J Pediatr. 2010 Sep;157(3):434-8, 438.e1. doi: 10.1016/j.jpeds.2010.02.066. Epub 2010 Apr 18.
Sikha Maria Siromani et al. Neonatal Outcome In Pregnancy Induced Hypertensive Mothers – A Tertiary Care Centre Experience. IOSR Journal of Dental and Medical Sciences (IOSR-JDMS) e-ISSN: 2279-0853, p-ISSN: 2279-0861.Volume 14, Issue 11 Ver. IX (Nov. 2015), PP 23-27.
Sibai BM. Preeclampsia as a cause of preterm and late preterm (near-term) births. SeminPerinatol. 2006 Feb;30(1):16-9. DOI:10.1053/j.semperi.2006.01.008.
ZibaMosayebi et al ‘Evaluation of Laboratory Disorders in Admitted Neonates in NICU WhoWere Born to Preeclamptic Mothers. Journal of Comprehensive Pediatrics. 2013 November; 3(5): 194-9.
Carl H. Bakers et al. Maternal Preeclampsia and Neonatal Outcomes. Journal of Pregnancy Volume 2011 (2011), Article ID 214365, 7 pages.
Cadnapaphornchai M1, Faix RG. Increased nosocomial infection in neutropenic low birth weight (2000 grams or less) infants of hypertensive mothers. J Pediatr. 1992 Dec;121(6):956-61.
David A Paul, Kathleen H Leef, Anthony Sciscione, Deborah Tuttle and John L Stefano, Neonatal neutropenia associated with preeclampsia does not increase the risk for culture proven sepsis. Pediatric Research 43,250(1998).
Patricia L.N., K.Gillespie, Uday P.D. Effect of early onset bacterial sepsis or pregnancy induced hypertension on neonatal white blood cell and platelet counts in infants less than 1200 grams. The journal of maternal-fetal& neonatal medicine, 1993; 2(1):1-4.
Sandre EJ, J.W. Haynes, R.J. McPherson. Evaluation of neutropenia and neutrophilia in hospitalized preterm infants. Journal of perinatology 2004; 24:150-157.
KRESIMAR MILAS et al Causes of respiratory distress among neonates gestational age 32 weeks and more. SIGNA VITAE 2017;13(SUPPL 4):21–24.
Bhat YR, Cherian CS. Neonatal thrombocytopenia associated with maternal pregnancy induced hypertension. Indian J Pediatr. 2008 Jun;75(6):571-3. doi: 10.1007/s12098-008-0110-x. Epub 2008 Aug 31.
Prekshya L Prakash, P Sunil Kumar, M Venkata Murthy, KR Haricharan. Assessment of haematological profile of newborn at birth, born to mother with gestational hypertension, preeclampsia and eclampsia syndrome. Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences 2013;Vol2, Issue 34, August 26; Page:6360-6369
P.N Tsao, R.J. Teng, J.R. Tang and K.T Yau. Granulocyte colony stimulating factor in the cord blood of premature neonates born to mothers with pregnancy induced hypertension. The Journal of pediatrics, 1999; 135(1):56-59.
Copyright (c) 2019 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


