Incidence, risk factors, clinical profile, and determinants (affecting outcome) of new onset acute kidney injury developing in critically Illpatients in pediatric intensive care unit of a tertiary hospital in middle India
Abstract
Aim/Objectives: To study the incidence, clinical-profile of AKI developing in critically-ill children after admission to PICU, including its risk-factors and determinants affecting patient outcome.
Material/Methods: This prospective observational study was conducted at a tertiary teaching hospital (Pt JNM Medical College Raipur, CG, India) over a study period of 12 months (August 2017-July 2018). Those patients who satisfied the inclusion-criteria of having critical-illness requiring PICU admission, age between 1month to 18 years,anddevelopingin-hospital AKI were enrolled; and after obtaining written informed-consent from parents, their basic demographic, clinical details and laboratory reports were entered from case records into predesigned proforma and then data was compiled in Microsoft Excel-Sheet. AKI staging was obtained using pRIFLE criteria (2007) and compared with renal-recovery and patient-survival. SPSS software (version 21) was used for data-analysis and p-value <0.05 was taken for statistical significance.
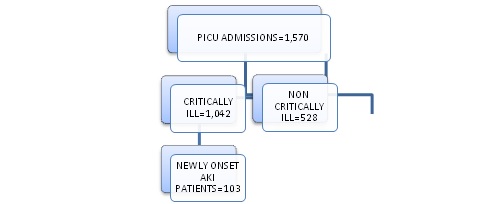
Results: Out of total 1042 critically-ill children admitted during study-period, 103 developed new-onset AKI in PICU (overall incidence 9.8%). Among them, 96 patients died (93.2%cases). Maximum subjects developing in-hospital AKI had three major associated fatal risk-factors like refractory shock (80.5%), severe sepsis (68%) and MODS (62.1%). But only MODS (p=0.002) and refractory-shock (p=0.0001) showed significant association with fatal outcome. Maximum new-onset AKI cases developed within 3 days of PICU admission (62%). No statistically-significant association was observed between different AKI-stages and renal-recovery or patient-survival.
Conclusion: Sepsis was common underlying risk-factor for new-onset AKI in critically-ill patients admitted in PICU, while association of MODS and/or refractory shock majorly determined poor survival-outcome.
Downloads
References
2. Krishnamurthy S, Mondal N, Narayanan P, et al. Incidence and etiology of acute kidney injury in southern India. Indian J Pediatr. 2013 Mar;80(3):183-9. doi: 10.1007/s12098-012-0791-z. Epub 2012 Jun 14.[pubmed]
3. Al-Jboor W, Almardini R, Al Bderat J, et al. Acute kidney injury in critically ill child. Saudi J Kidney Dis Transpl. 2016 Jul-Aug;27(4):740-7. doi: 10.4103/1319-2442.185236.[pubmed]
4. Palmieri T, Lavrentieva A, Greenhalgh D. An assessment of acute kidney injury with modified RIFLE criteria in pediatric patients with severe burns. Intensive Care Med. 2009 Dec;35(12):2125-9. doi: 10.1007/s00134-009-1638-6. Epub 2009 Sep 15.[pubmed]
5. Kendirli T, Ekim M, Ozçakar ZB, et al. Renal replacement therapies in pediatric intensive care patients: experiences of one center in Turkey. Pediatr Int. 2007 Jun;49(3):345-8. DOI:10.1111/j.1442-200X.2007.02376.x.
6. Bellomo R, Ronco C, Kellum JA, et al. Acute renal failure - definition, outcome measures, animal models, fluid therapy and information technology needs: the Second International Consensus Conference of the Acute Dialysis Quality Initiative (ADQI) Group. Crit Care. 2004 Aug;8(4):R204-12. Epub 2004 May 24. DOI:10.1186/cc2872.[pubmed]
7. Akcan-Arikan A, Zappitelli M, Loftis LL, et al. Modified RIFLE criteria in critically ill children with acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2007 May;71(10):1028-35. Epub 2007 Mar 28. DOI:10.1038/sj.ki.5002231.
8. Singh-Naz, Nalini; Sprague, Bruce M.; Patel, Kantilal M.; Pollack, Murray M. Risk Factors For Nosocomial Infection In Critically Ill Children: A Prospective Cohort Study. Crit Care Med. 1996May;24 (5): 875-8.
9. Deep A, Ghildiyal R, Kandian S, et al. Clinical and microbiological profile of nosocomial infections in the pediatric intensive care unit (PICU). Indian Pediatr. 2004 Dec;41(12):1238-46.[pubmed]
10. Touza Pol P, Rey Galán C, Medina Villanueva JA, et al. [Severe acute kidney injury in critically ill children: Epidemiology and prognostic factors]. AnPediatr (Barc). 2015 Dec;83(6):367-75. doi: 10.1016/j.anpedi.2015.01.009. Epub 2015 Mar 6.
11. Bagshaw SM, Lapinsky S, Dial S, et al. Acute kidney injury in septic shock: clinical outcomes and impact of duration of hypotension prior to initiation of antimicrobial therapy. Intensive Care Med. 2009 May;35(5):871-81. doi: 10.1007/s00134-008-1367-2. Epub 2008 Dec 9.[pubmed]
12. Yegenaga I, Tuglular S, Ari E, et al. Evaluation of sepsis/systemic inflammatory response syndrome, acute kidney injury, and RIFLE criteria in two tertiary hospital intensive care units in Turkey. Nephron Clin Pract. 2010;115(4):c276-82. doi: 10.1159/000313486. Epub 2010 Apr 28.[pubmed]
Copyright (c) 2019 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


