Incidence of acute kidney injury in birth asphyxia and its correlation with severity of hypoxic ischemic encephalopathy (HIE) in newborns with perinatal asphyxia in SNCU at DR. BRAM Hospital, Raipur (CG)
Abstract
Introduction: Perinatal asphyxia is an important contributor of neonatal morbidity, mortality and adverse outcome in India. Due to any reason, if blood supplied through placenta is hampered, it leads to asphyxial injury. Renal involvement is frequent in perinatal asphyxia. The severity of renal involvement and adverse outcome are correlated with severity of asphyxia and HIE stage. We performed this study to determine the incidence of renal failure in birth asphyxia by estimating urine output, serum creatinine and blood urea.
Aim and Objective: To study incidence of Acute Kidney Injury (AKI) in Hypoxic Ischemic Encephalopathy (HIE) and its association with severity of HIE in Newborns.
Material Methods: Cross-sectional observational hospital based study was conducted over a period of six months from March 2018 to August 2018 in Special Newborn Care Unit (SNCU) of Dr. BRAM hospital, Raipur. Sarnat and Sarnat staging was used to classify HIE. Statistical analyses were performed by using SPSS21.0 software. Chi square test, P- value and likelihood ratio were calculated using appropriate tests.
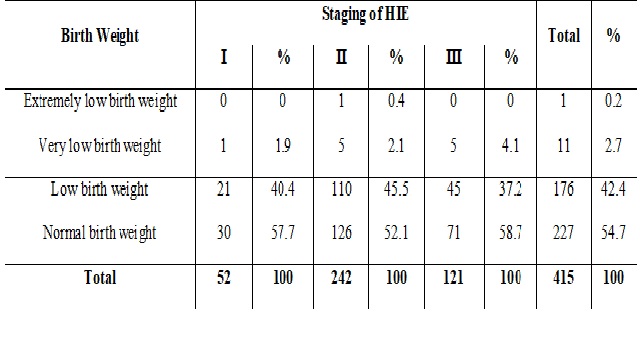
Result: Total 1318 newborns were admitted in SNCU during study period. 415 newborns were admitted with HIE following perinatal asphyxia. Out of these 52 (12.5%) were HIE-I cases, 242(58.3%) were HIE-II and 121(29.1%) were HIE-III. Total 70(16.9%) newborns developed AKI. None of newborn in HIE I developed AKI. 20(8.2%) newborns with HIE II developed AKI while in HIE III 50 (41.3%) newborns had AKI. There was significant correlation between HIE III and AKI (P value- 0.157).
Conclusion: There is significant correlation of HIE with AKI. As severity of HIE progresses from stage-I to stage-III, there is increased risk of developing AKI.
Downloads
References
2. McGuire W. Perinatal asphyxia. BMJ Clin Evid. 2007 Nov 7;2007. pii: 0320.[pubmed]
3. National Neonatal Perinatal Database; Report 2002 2003 .Available from: http://www. New bornwhocc.org/ pdf/ HRRC Report_2002 03.pdf [Last accessed on 2019 Apr 5]
4. Martín-Ancel A, García-Alix A, Gayá F, et al. Multiple organ involvement in perinatal asphyxia. J Pediatr. 1995 Nov;127(5):786-93.[pubmed]
5. World Health Organizaton. Perinatal mortality: a listing of available information.FRH/MSM. 96.7.Geneva: WHO,1996
6. Report of the National Neonatal Perinatal Database (National Neonatology Forum,India) 2000
7. Perlman JM, Tack ED, Martin T, Shackelford G, Amon E. Acute systemic organ injury in term infants after asphyxia. Am J Dis Child 1989; 143: 617-620.[pubmed]
8. Cohn HE, Sacks EJ, Heymann MA, et al. Cardiovascular responses to hypoxemia and acidemia in fetal lambs. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 1974 Nov 15;120(6):817-24.[pubmed]
9. Rudolph AM. The fetal circulation and its response to stress. J Dev Physiol. 1984 Feb;6(1):11-9.[pubmed]
10. Aggarwal A, Kumar P, Chowdhary G, et al. Evaluation of renal functions in asphyxiated newborns. J Trop Pediatr. 2005 Oct;51(5):295-9. Epub 2005 Jul 6.[pubmed]
11. Mehta RL, Kellum JA, Shah SV, et al. Acute Kidney Injury Network: report of an initiative to improve outcomes in acute kidney injury. Crit Care. 2007;11(2):R31. DOI:10.1186/cc5713.[pubmed]
12. Gouyon JB, Guignard JP. Management of acute renal failure in newborns. Pediatr Nephrol. 2000 Sep;14(10-11): 1037-44.[pubmed]
13. Hentschel R, Lödige B, Bulla M. Renal insufficiency in the neonatal period. Clin Nephrol. 1996 Jul;46(1):54-8.[pubmed]
14. Askenazi D, Smith LB, Furth S, Warady BA. Acute kidney injury and chronic kidney disease. In: Avery‟s Diseases of the Newborn .9th ed. Philadelphia: Elsevier Saunders; 2012. p. 1205‑21.
15. Medani SA, Kheir AE, Mohamed MB. Acute kidney injury in asphyxiated neonates admitted to a tertiary neonatal unit in Sudan. Sudan J Paediatr. 2014;14(2):29-34.[pubmed]
16. Gupta BD, Sharma P, Bagla J, et al. Renal failure in asphyxiated neonates. Indian Pediatr. 2005 Sep;42 (9):928-34.[pubmed]
17. Nouri S, Mahdhaoui N, Beizig S, et al. Acute renal failure in full term neonates with perinatal asphyxia. Prospective study of 87 cases. Arch Pediatr. 2008 Mar;15(3):229-35. doi: 10.1016/j.arcped.2008.01.011. Epub 2008 Mar 7.[pubmed]
18. Alaro D, Bashir A, Musoke R, et al. Prevalence and outcomes of acute kidney injury in term neonates with perinatal asphyxia. Afr Health Sci. 2014 Sep;14(3):682-8. doi: 10.4314/ahs.v14i3.26.[pubmed]
19. Karlowicz MG, Adelman RD. Nonoliguric and oliguric acute renal failure in asphyxiated term neonates. Pediatr Nephrol. 1995 Dec;9(6):718-22.[pubmed]
20. Jayashree, G., et al. “Acute renal failure in asphyxiated newborns.” Indian pediatrics 28.1 (1991): 19-23.
21. Gupta BD, Sharma P, Bagla J, et al. Renal failure in asphyxiated neonates. Indian Pediatr. 2005 Sep;42(9):928-34.[pubmed]
22. Aggarwal A, Kumar P, Chowdhary G, et al. Evaluation of renal functions in asphyxiated newborns. J Trop Pediatr. 2005 Oct;51(5):295-9. Epub 2005 Jul 6.DOI:10.1093/tropej/fmi017.[pubmed]
23. Pammi V. Mohan, Pragnya M. Pai. Renal insult in asphyxia neonatorum. Indian Pediatr 2000; 37: 1102-1106.[pubmed]
24. Stapleton FB, Jones DP, Green RS. Acute renal failure in neonates: incidence, etiology and outcome. Pediatr Nephrol. 1987 Jul;1(3):314-20.[pubmed]
25. Hentschel R1, Lödige B, Bulla M. et al. Renal insufficiency in the neonatal period. Clin Nephrol. 1996 Jul;46(1):54-8.[pubmed]
Copyright (c) 2019 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


