Clinical profile and complications of acute malaria caused by different species of Plasmodium
Abstract
Introduction: Malaria is more severe in children than in adults and 78% of all deaths due to malaria occur in children under 5years. Plasmodium vivax has long been considered to have benign course. However during past few years several studies reported severe complicated cases of vivax malaria.
Methodology: Children in the age group of 6 months to 15 years admitted in the Department of Pediatrics with clinical malaria were tested for malaria using peripheral smear, QBC and rapid diagnostic test. Children with positivity of any of these tests were enrolled in the study. Complete clinical profile is noted. Investigations like complete blood counts, LFT, RFT etc., were done.
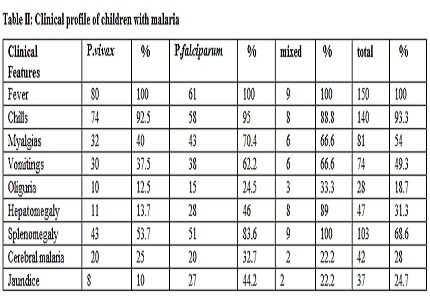
Results: Out of 150 children enrolled in the study 80 had Plasmodium vivax monoinfection. 61 had Plasmodium falciparum monoinfection and 9 had mixed infection. 41% of them were under 5years of age. The incidence of complications like severe anemia (10% vs. 18%), jaundice (10% vs. 44%), transaminitis (6% vs.13%), azotemia (6% vs. 36%) and thrombocytopenia (12.5% vs. 26%) were more common in P falciparum than in P vivax malaria with statistical significance (p < 0.05). There was no statistically significant difference in the incidence of hypoglycemia and cerebral malaria in P vivax and P falciparum malaria.
Conclusion: The incidence of severe malaria in P. vivax infection is comparable to that in P. falciparum infection and it is no more benign. Hence robust efforts are required for reduction and elimination of P vivax transmission.
Downloads
References
2. Tripathy R, Parida S, Das L, Mishra DP, Tripathy D, Das MC, Chen H, Maguire JH, Panigrahi P. Clinical manifestations and predictors of severe malaria in Indian children. Pediatrics. 2007 Sep;120(3):e454-60. [PubMed]
3. Barcus MJ, Basri H, Picarima H, Manyakori C, Sekartuti, Elyazar I, Bangs MJ, Maguire JD, Baird JK. Demographic risk factors for severe and fatal vivax and falciparum malaria among hospital admissions in northeastern Indonesian Papua. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2007 Nov;77(5):984-91. [PubMed]
4. Tjitra E, Anstey NM, Sugiarto P, Warikar N, Kenangalem E, Karyana M, Lampah DA, Price RN. Multidrug-resistant Plasmodium vivax associated with severe and fatal malaria: a prospective study in Papua, Indonesia. PLoS Med. 2008 Jun 17;5(6):e128. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0050128.
5. Genton B, D'Acremont V, Rare L, Baea K, Reeder JC, Alpers MP, Müller I. Plasmodium vivax and mixed infections are associated with severe malaria in children: a prospective cohort study from Papua New Guinea. PLoS Med. 2008 Jun 17;5(6):e127. doi: 10.1371/journal.pmed.0050127.
6. Singh R, Kumar S, Rana SK, Thakur B, Singh SP. A comparative study of clinical profiles of vivax and falciparum malaria in children at a tertiary care centre in uttarakhand. J Clin Diagn Res. 2013 Oct;7(10):2234-7. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2013/6914.3479. Epub 2013 Sep 18.
7. Desai Pankti D, Vasavda Halak, Vora Hetal D, Mansuri S H, Patel Bhavesh. Clinical spectrum, complications & treatment outcomes of malaria (in pediatric patients). National Journal of Integrated Research in Medicine. 2013 Mar-Apr; 4(2): 140-143. [PubMed]
8. Kaushik JS, Gomber S, Dewan P. Clinical and epidemiological profiles of severe malaria in children from Delhi, India. J Health Popul Nutr. 2012 Mar;30(1):113-6. [PubMed]
9. Kochar DK, Tanwar GS, Khatri PC, Kochar SK, Sengar GS, Gupta A, Kochar A, Middha S, Acharya J, Saxena V, Pakalapati D, Garg S, Das A. Clinical features of children hospitalized with malaria--a study from Bikaner, northwest India. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2010 Nov;83(5):981-9. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.2010.09-0633. [PubMed]
10. Singh R, Kumar S, Rana SK, Thakur B, Singh SP. A comparative study of clinical profiles of vivax and falciparum malaria in children at a tertiary care centre in uttarakhand. J Clin Diagn Res. 2013 Oct;7(10):2234-7. doi: 10.7860/JCDR/2013/6914.3479. Epub 2013 Sep 18. [PubMed]
11. Kaur D, Wasir V, Gulati S, Bagga A. Unusual presentation of Plasmodium vivax malaria with severe thrombocytopenia and acute renal failure. J Trop Pediatr. 2007 Jun;53(3):210-2. Epub 2007 Jan 30. [PubMed]
12. Thapa R, Biswas B, Mallick D, Sardar S, Modak S. Childhood Plasmodium vivax malaria with severe thrombocytopenia and bleeding manifestations. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol. 2009 Oct;31(10):758-9. doi: 10.1097/MPH.0b013e3181b7eb12.
13. Harish R, Gupta S. Plasmodium vivax malaria presenting with severe thrombocytopenia, cerebral complications and hydrocephalus. Indian J Pediatr. 2009 May;76(5):551-2. doi: 10.1007/s12098-009-0087-0. Epub 2009 Apr 23. [PubMed]
14. Bhatia V, Bhatia J. Severe thrombocytopenia with bleeding manifestations in two children secondary to Plasmodium vivax. Platelets. 2010;21(4):307-9. doi: 10.3109/09537100903518278. [PubMed]
15. Saharan S, Kohli U, Lodha R, Sharma A, Bagga A. Thrombotic microangiopathy associated with Plasmodium vivax malaria. Pediatr Nephrol. 2009 Mar;24(3):623-4. doi: 10.1007/s00467-008-0945-4. Epub 2008 Aug 8.
16. Lacerda MV, Fragoso SC, Alecrim MG, Alexandre MA, Magalhaes BM, et al (2012) Postmortem characterization of patients with clinical diagnosis of Plasmodium vivax malaria: to what extent does this parasite kill? Clin Infect Dis 2012 Oct;55(8):e67-74. Epub 2012 Jul 6. [PubMed]
17. Shaikh S, Memon H, Iohano B, Shaikh A, Ahmed I, Baird JK. Severe disease in children hospitalized with a diagnosis of Plasmodium vivax in south-eastern Pakistan. Malar J. 2012 May 2;11:144. doi: 10.1186/1475-2875-11-144.
18. www.who.int/entity/malaria/mpac/sep2012/p vivax
Copyright (c) 2016 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


