A single centre experience in the management of undescended testes
Abstract
Introduction: Undescended testes (UDT) is one of the most common congenital anomalies of the urogenital system. In spite of its common occurrence, lots of variations are still reported regarding the time of surgery, mode of investigation and surgery. The present study tried to report the single centre experience of management of UDT.
Materials and Methods: The data of patients with UDT including time of presentation, time of surgery, position of testes, investigations, associated urogenital anomalies, complications were collected over a period of 9 years and 6 months and analysed.
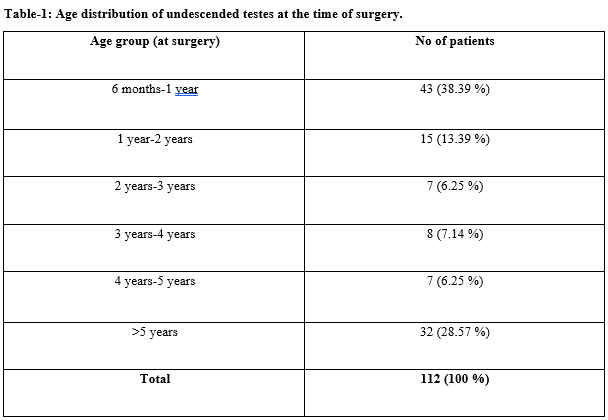
Results: A total of 118 children were recorded of which the testes of 6 infants became descended before the age of 6 months. Out of the remaining, 112 children, 24 children had bilateral UDT, 24 children had nonpalpable testes (NPT). Ultrasound could locate 19 NPT pre-operatively. Maximum children were operated between 6 months to 1 year in 43 children (38.39 %). Laparoscopy was done for intra-abdominal testes and NPT whose locations could not be located by US and the rest by open inguinal exploration. Four children had pre-operative complications with obstructed inguinal hernias (2 cases) and testicular torsion (2 cases).
Conclusion: Majority of the children were being operated before the age of 1 year and US is a good non-invasive to effectively locate the NPT.
Downloads
References
Cortes D. Cryptorchidism – aspects of pathogenesis, histology and treatment. Scand J Urol Nephrol Suppl. 1998;196:1-54.
Barthold JS, Gonzalez R. The epidemiology of congenital cryptorchidism, testicular ascent and orchiopexy. J Urol. 2003;170(6):2396–401. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ju.0000095793.04232.d8.
Virtanen HE, Bjerknes R, Cortes D, Jorgensen N, Rajpert-De Meyts E, Thorsson AV, et al. Cryptorchidism: classification, prevalence and long-term consequences. Acta Paediatr. 2007;96(5):611-616. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1651-2227.2007.00241.x.
John Radcliffe Hospital Cryptorchidism Study Group. Cryptorchidism: a prospective study of 7500 consecutive male births, 1984–8. Arch Dis Child. 1992;67(7):892-899. doi: http://dx.doi.org/10.1136/adc.67.7.892.
Bay K, Main KM, Toppari J, Skakkebaek NE. Testicular descent: INSL3, testosterone, genes and the intrauterine milieu. Nat Rev Urol. 2011;8:187-196. doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/nrurol.2011.23.
Hutson JM. Journal of Pediatric Surgery-Sponsored Fred McLoed Lecture. Undescended testis: the underlying mechanisms and the effects on germ cells that cause infertility and cancer. J Pediatr Surg. 2013;48(5):903-908. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2013.02.001.
Kaplan GW. Nomenclature of cryptorchidism. Eur J Pediatr. 1993;152(2):S17-S19. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02125427.
Stang A, Ahrens W, Bromen K, Baumgardt-Elms C, Jahn I, Stegmaier C, Krege S, Jöckel KH. Undescended testis and the risk of testicular cancer: importance of source and classification of exposure information. Int J Epidemiol. 2001;30(5):1050-1056. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/ije/30.5.1050.
Kolon TF, Herndon CD, Baker LA, Baskin LS, Baxter CG, Cheng EY et al. Evaluation and treatment of cryptorchidism: AUA guideline. J Urol. 2014;192(2):337-345. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2014.05.005.
Hensel KO, Caspers T, Jenke AC, Schuler E, Wirth S. Operative management of cryptorchidism: guidelines and reality - a 10-year observational analysis of 3587 cases. BMC Pediatrics. 2015;15:116. doi: https://doi.org/10.1186/s12887-015-0429-1.
Hoefling K, Sperling P, Meyer T. [Time of Operative Treatment of Maldescensus Testis in Childhood - Wishes and Reality]. Zentralbl Chir. 2014;139(6:)627-631. doi: https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0032-1315123.
Springer A, Huber C, Reck CA, Fengler D, Horcher E. Delayed referral despite appropriate knowledge in cryptorchidism as a cause of delayed orchidopexies in Austria. Klin Padiatr. 2010;222(4):248-251. doi: https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0030-1248260.
Kokorowski PJ, Routh JC, Graham DA, Nelson CP. Variations in timing of surgery among boys who underwent orchidopexy for cryptorchidism. Pediatr. 2010;126:e576-582. doi: https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2010-0747.
Fahlenkamp D, Rassweiler J, Fornara P, Frede T, Loening SA. Complications of laparoscopic procedures in urology: experience with 2,407 procedures at 4 German centers. J Urol. 1999;162(3 Pt 1):765-770. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/00005392-199909010-00038.
Thorup JM, Cortes D, Visfeldt J. Germ cells may survive clipping and division of the spermatic vessels in surgery for intraabdominal testes. J Urol. 1999;162(3 Pt 1):872-874. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/00005392-199909010-00080.
Graif M, Czerniak A, Avigad I, Strauss S, Wolfstein I, Itzchak Y. High-resolution sonography of the undescended testis in childhood: an analysis of 45 cases. Isr J Med Sci 1990;26(7):382-385.
Elder JS: Ultrasonography is unnecessary in evaluating boys with a nonpalpable testis. Pediatr. 2002; 110:748-751. doi: https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.110.4.748.
Nguyen HT, Coakley F, Hricak H: Cryptorchidism: strategies in detection. Eur Radiol 1999; 9:336-343. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/s003300050676.
Kullendorff CM, Hederstrom E, Forsberg L: Preoperative ultrasonography of the undescended testis. Scand J Urol Nephrol 1985;19(1):13-15. doi: https://doi.org/10.3109/00365598509180215.
Pekkafali MZ, Sahin C, Ilbey YO, Albayrak S, Yildirim S, Basekim CC: Comparison of ultrasonographic and laparoscopic findings in adult nonpalpable testes cases. Eur Urol 2003;44(1):124-127. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0302-2838(03)00145-3.
Hrebinko RL, Bellinger MF: The limited role of imaging techniques in managing children with undescended testes. J Urol 1993;150(2 pt 1):458–460. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-5347(17)35510-6.
Gapanya C, Freya P, Cachatb F, Gudinchetc F, Jichlinskie P, Meyrata B, Ramseyera P, Theintzd G, Burnandf B. Management of cryptorchidism in children: guidelines. Swiss Med Wkly 2008;138(33–34):492–498.
Berkowitz GS, Lapinski RH, Dolgin SE, Gazella JC, Bodian CA, Holzman IR. Prevalence and natural history of cryptorchidism. Pediatr. 1993;92(1):44-49.
Kinderchirurgie DGf. Leitlinien Kinderchirurgie: Hodenhochstand - Maldeszensus testis, 2009. AWMF; 2009. Register-Nr. 006–022: http://www.awmf.org/leitlinien/detail/ll/006-022.html
Ibrahim AHM, Al-Malki TA, Ghali AM, and Musalam AO. Undescended Testes: Do We Need to Fix Them Earlier? Ann Pediatr Surg. 2005;1(1):21-25.
Lee PA. Fertility after cryptorchidism: epidemiology and other outcome studies. Urol. 2005;66(2):427-431. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/j.urology.2005.01.017.
Snodgrass W, Chen K, Harrison C. Initial scrotal incision for unilateral nonpalpable testis. J Urol. 2004;172(4):1742-1745. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/01.ju.0000140211.71113.58.
Kollin C, Hesser U, Ritzen EM, Karpe B. Testicular growth from birth to two years of age, and the effect of orchidopexy at age nine months: a randomized, controlled study. Acta Paediatr. 2006;95(3):318-324. doi: https://doi.org/10.1080/08035250500423812.
Copyright (c) 2020 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


