Goldenhar syndrome: rare case reported from secondary health care facility in Himachal Pradesh
Abstract
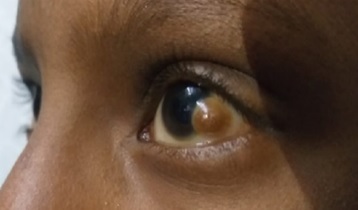
Dr. Maurice Goldenhar, a renowned Swiss ophthalmologist classified the clinical features and named the malformation complex as Goldenhar Syndrome and described it as a congenital defect characterized by constellation of malformations classically involving the face, eyes and ears. Principal deformities of the Goldenhar syndrome are often combined with various malformations, like Cleft lip and/or palate, tongue cleft, unilateral tongue hypoplasia, and parotid gland aplasia, Rib anomalies, Congenital heart disease (ventricular septal defects). A 12-year-old female patient diagnosed with Goldenhar syndrome at secondary care Regional Hospital Bilaspur, Himachal Pradesh. She was diagnosed with a case of Goldenhar syndrome on clinic-radiological investigations. The patient reported to ophthalmology OPD of the hospital with the chief complaint of soft tissue structure in left eye with decreased vision. On examination limbal dermoid was observed. Patient was having pre-auricular tissue tag on both sides, hemifacial micrognathia and microstomia. Correlating the history and physical findings a provisional diagnosis of Goldenhar Syndrome was made with differential diagnosis of Franschetti syndrome or Treacher – Collins syndrome, Nager syndrome or acro-facial dysostosis and Townes-Brocks syndrome. Based on the clinical and radiographic findings a diagnosis of Goldenhar syndrome was made. Severe cases of GS can affect the routine and social life of the patient. Early detection can help avoid complications at a later stage of life. Such patients will have an increased risk for psychosocial difficulties. The study of this condition is still controversial because the symptoms and the physical features may vary greatly in range and severity from case to case.
Downloads
References
Martelli H Jr., Miranda RT, Fernandes CM, Bonan PR, Paranaíba LM, Graner E, et al. Goldenhar syndrome: Clinical features with orofacial emphasis. J Appl Oral Sci 2010;18(6):646-649. doi: https://doi.org/10.1590/s1678-77572010000600019.
Von Arlt F. Clinical presentation of diseases of the eye. 1st ed. Vienna: Braumuller publications; 1881.
Goldenhar M. Associated malformations of eye and ear, particularly dermoid syndrome epibulbar-appendices, congenital auricular fistulas and its relations with Manibulofacial Dysostosis. J Genet Hum. 1952;1:243-282.
Vinay C, Reddy R S, Uloopi K S, Madhuri V, Sekhar R C. Craniofacial features in Goldenhar syndrome. J Indian Soc Pedod Prev Dent 2009;27(2):121-124. doi: https://doi.org/10.4103/0970-4388.55339.
Mahore A, Dange N, Nama S, Goel A. Facio-auriculo-vertebro-cephalic spectrum of Goldenhar syndrome. Neurol India 2010;58(1):141-4. doi: https://doi.org/10.4103/0028-3886.60409.
Sharma JK, Pippal SK, Raghuvanshi SK, Shitij A. Goldenhar-Gorlin’s syndrome: A case report. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2006;58(1):97-101. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02907757.
Kokavec R. Goldenhar syndrome with various clinical manifestations. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2006;43(5):628-634. doi: https://doi.org/10.1597/05-094.
Lessick M, Vasa R, Israel J. Severe manifestations of oculoauriculovertebral spectrum in a cocaine exposed infant. J Med Genet. 1991;28(11):803-804. doi: https://doi.org/10.1136/jmg.28.11.803.
Gorlin RJ, Cohen MM, Levin LS. Branchial arch and oroacral disorders. In: Syndromes of the head and neck. 3ed. New York: Oxford University Press; p.641-8.
Johnson KA, Fairhust J, Clarke NM. Oculoauriculovertebral spectrum: new manifestations. Pediatr Radiol. 1995;25(6):446-448. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02019062.
Regenbogen L, Godel V, Goya V, Godman RM. Further evidence for an autosomal dominant form of oculoauriculovertebral dysplasia. Clin Genet. 1982;21(3):161-167. doi: https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-0004.1982.tb00957.x.
Araneta MR, Moore CA, Olney RS, Edmonds LD, Karcher JA et al., Goldenhar syndrome among infants born in military hospitals to Gulf War veterans. Teratol. 1997;56(4):244-251. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/(sici)1096-9926(199710)56:4%3C244::aid-tera3%3E3.3.co;2-y.
Tsai FJ, Tsai CH. Autosomal dominant inherited oculo-auriculo-vertebral spectrum: report of one family. Zhonghua Min Guo Xiao Er Ke Yi Xue Hui Za Zhi. 1993;34(1):27-31.
Anderson PJ, David DJ. Spinal anomalies in Goldenhar syndrome. Cleft Palate Craniofac J. 2005;42(5):477-480. doi: https://doi.org/10.1597/04-142051r.1.
Ozdemir O, Arda K, Turhan H, Tosun O. Goldenhar’s Syndrome. Asian Cardiovasc Thorac Ann. 2002;10(3):267-269. doi: https://doi.org/10.1177/021849230201000320.
Berker N, Acaroğlu G, Soykan E. Goldenhar’s Syndrome (oculoauriculo-vertebral dysplasia) with congenital facial nerve palsy. Yonsei Med J. 2004;29;45(1):157-160. doi: https://doi.org/10.3349/ymj.2004.45.1.157.
Kumar R, Balani B, Patwari AK, Anand VK, Ahuja B. Goldenhar syndrome with rare associations. Indian J Pediatr. 2000;67(3):231-233. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/bf02723669.
Zaka-ur-Rab Z, Mittal S. Optic Nerve Head Drusen in Goldenhar Syndrome. JK Science 2007;9:33-34.
Narayanan HS, Mohan KS, Manjunatha KR, Channabasavanna SM. An unusual variant of hallermann - streiff syndrome. Indian J Psychiatry. 1985;27(2):159-162.
Verona LL, Damian NG, Pavarina LP, Ferreira CHF, Melo DG. Monozygotic twins discordant for Goldenhar syndrome. J Pediatr (Rio J). 2006;82(1):75-78. doi: https://doi.org/10.2223/JPED.1441.
Castori M, Brancati F, Rinaldi R, Adami L, Mingarelli R, Grammatico P, et al. Antenatal presentation of the oculo‐auriculo‐vertebral spectrum (OAVS). Am J Med Genet Part A 2006;140A(14):1573-1579. doi: https://doi.org/10.1002/ajmg.a.31290.
Schaffer AJ, Hine MK, Levy BM. Tratado de patologia bucal. 4th ed. Rio de Janeiro: Interamericana; 1985. p.631.
Rao VA, Kaliaperumal S, Subramanyan T, Rao KR, Bhargavan R. Goldenhar’s sequence with associated juvenile glaucoma in Turner’s syndrome. Indian J Ophthalmol. 2005;53(4):267-8. doi: https://doi.org/10.4103/0301-4738.18909.
Stringer MD, Tovar JA, McKiernan PJ, Tanner S. Portal vein cavernoma associated with Goldenhar syndrome. J Pediatr Gastroenterol Nutr. 2005;41(3):368-370. doi: https://doi.org/10.1097/01.mpg.0000174333.85463.4f.
Maan MA, Saeed G, Akhtar SJ, Iqbal J. Goldenhar syndrome: case reports with review of literature. JPAD. 2008;18:53-55.
Gajre M, Palaniswamy K, Rathi S, Rathod D, Deshpande V, Agrawal M. Goldenhar Syndrome with Agenesis of Septum Pellucidum. Bombay Hosp J. 2008;50(4):687-688.
Copyright (c) 2020 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


