Study of hypoglycemia in neonates with low birth weight
Abstract
Background: Glucose metabolism disorders are common in low birth weight (LBW) infants and are associated with high morbidity and mortality. Neonatal hypoglycemia, a common metabolic problem, often goes unnoticed owing to a lack of specific symptoms. Hypoglycemia both symptomatic and asymptomatic can lead to long term neurological sequelae. Therefore, it needs early management to prevent brain damage in a developing neonate.
Objective: This study was conducted to evaluate the prevalence and risk factors associated with hypoglycemia in low birth weight infants.
Design: A hospital-based prospective longitudinal study.
Duration: One year (October 2017-October 2018).
Setting: Niloufer Hospital, Hyderabad.
Participants: 50 LBW neonates with birth weight less than 2500 grams.
Methods: Blood glucose values were measured at the age of 1 h, 6 h, 12 h, 24 h, and 48 h after delivery which was independent of feeding time. Blood glucose value of less than 40 mg/dl (2.2 mmol/l) was defined as hypoglycemia. For statistical analysis, SPSS software version 20 was used.
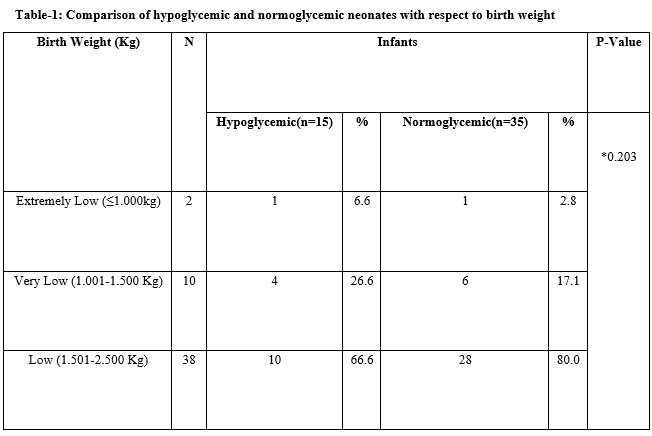
Results: Out of 50 neonates, 15 (30%) had one or more episodes of hypoglycemia. Overall 22 episodes were recorded. Out of 15 hypoglycemic neonates, 8 (53.3%) were small for gestational age (SGA) and 7 (46.7%) were AGA. Sepsis was significantly noticed after hypoglycemia. The pattern of blood glucose levels was significantly different among hypoglycemic babies and normoglycemic babies over the first 72 hours.
Conclusion: Hypoglycemia was frequent among low birth weight babies more so in SGA babies in the first 24 hours.
Downloads
References
World Health Organization. Division of Child Health and Development and World Health Organization. Maternal Health and Safe Motherhood Programme. (1997). Hypoglycaemia of the newborn : review of the literature. World Health Organization. https://apps.who.int/iris/handle/10665/63362.
Ktorza A, Bihoreau MT, Nurjhan N, Picon L, Girard J. Insulin and glucagon during the perinatal period: secretion and metabolic effects on the liver. Neonatology. 1985;48(4):204-220. doi: https://doi.org/10.1159/000242173.
Adamkin DH. Postnatal Glucose Homeostasis in Late preterm and term infants. A clinical report from American Academy of Pediatrics, Committee on Fetus and Newborn Pediatrics. Pediatr. 2011;127(3):575-579. doi: https://doi.org/10.1542/peds.2010-3851.
Barbara J. Stoll. The Endocrine System. Nelson Textbook of Pediatrics. 18th ed., vol. 1. Part XI, Chapter 107. Mosby, Churchill Livingstone: Elsevier Saunders; 2007. p. 782-785.
Hawdon JM, Ward Platt MP, Aynsley-Green A. Patterns of metabolic adaptation for preterm and term infants in the first neonatal week. Arch Dis Child. 1992;67(4 Spec No):357-365. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1136%2Fadc.67.4_spec_no.357.
Hewitt V, Watts R, Robertson J, Haddow G. Nursing and midwifery management of hypoglycaemia in healthy term neonates. Int J Evid‐Based Healthc. 2005;3(7):169-205. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1111/j.1479-6988.2005.00025.x.
Hoseth E, Joergensen A, Ebbesen F, Moeller M. Blood glucose levels in a population of healthy, breast fed, term infants of appropriate size for gestational age. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 2000;83(2):F117-F119. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1136/fn.83.2.f117.
Dias E, Gada S. Glucose levels in newborns with special reference to hypoglycemia: a study from rural India. J Clin Neonatol. 2014;3(1):35-8. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.4103/2249-4847.128729.
Jonas D, Dietz W, Simma B. Hypoglycemia in newborn infants at risk. Klin Padiatr. 2014;226(5):287-291. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.1055/s-0034-1385928. Epub 2014 Aug 25.
Yoon JY, Chung HR, Choi CW, et al. Blood glucose levels within 7 days after birth in preterm infants according to gestational age. Ann Pediatr Endocrinol Metab. 2015;20(4):213-219. doi: https://dx.doi.org/10.6065/apem.2015.20.4.213. Epub 2015 Dec 31.
Dashti N, Einollahi N, Abbasi S. Neonatal hypoglycemia: prevalence and clinical manifestations in Tehran children’s hospital. Pakistan J Med Sci Online. 2007;23(3):340-343.
Singhal PK, Singh M, Paul VK. Prevention of hypoglycemia. A controlled evaluation of sugar fortified feeding in small for date infants. Indian Pediatr. 1992;29:1365-1369.
Anderson S, Shakya KN, Shrestha LN, de L Costello AM. Hypoglycemia: A common problem among uncomplicated newborn infants in Nepal. J Trop Pediatr. 1993;39(5):273-277. doi: https://doi.org/10.1093/tropej/39.5.273.
Holtrop PC. The frequency of hypoglycemia in full-term large and small for gestational age newborns. Am J Perinatol. 1993;10(2):150-154. doi: https://doi.org/10.1055/s-2007-994649.
Srinivasan G, Pildes RS, Cattamanchi G, Voora S, Lilien LD. Plasma glucose values in normal neonates: a new look. J Pediatr. 1986;109(1):114-117. doi: https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80588-1.
Bhat MA, Kumar P, Bhansali A, Majumdar S, Narang A. Hypoglycemia in small for gestational age babies. Indian J Pediatr. 2000;67(6):423-427. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02859459.
Lubchenco LO, Bard H. Incidence of hypoglycemia in newborn infants classified by birth weight and gestational age. Pediatr. 1971;47(5):831-838.
Copyright (c) 2020 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


