Prevalence of obstructive sleep apnea and central apnea in Overweight and Obese children
Abstract
Introduction: Obstructive sleep disordered breathing with snoring, breathing through the mouth, apnea during sleep is very common among children. Many of these children outgrow the condition as the symptoms are very mild and reduce with age. Enlargement of adenoids or tonsils can lead to tonsilolectomey and adenoidectomy, further leading to OSA.
Materials and Methods: 46 obese or overweight children between the ages 3-15 years with suspected sleep apnea were subjected to vigorous physical and clinical examinations. Demographic details were noted apart from details such as sleep pattern, symptoms and snoring, daily routine, health history etc with reference to the Paediatric Sleep Questionnaire (PSQ). All the children underwent polysomnography testing, Apnea- Hypopnea Index (AHI), oxygen saturation, desaturation levels and sleep efficiency.
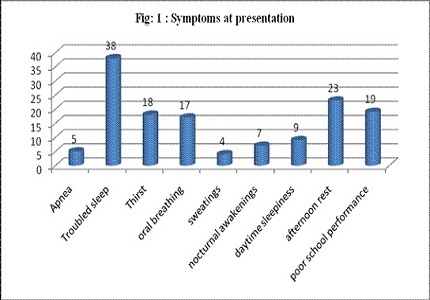
Results: Out of the 46 children, 29 (59.2%) were boys and 17 (40.8%) were girls. The girls were older than the boys with their mean age being 8.6 in comparison to 5.9 of the boys. 31 patients were overweight and 15 were obese. Obstructive sleep apnea was observed in 18 (39.1%) patients with 9 patients each presenting with mild OSA and moderate to severe OSA. Central apnea was observed in 4 obese and 2 overweight children. AHI and desaturation levels were significantly higher among the OSA patients than in the normal range in the other patients.
Conclusion: Though all snoring cases may not be OSA but most of the OSA cases are associated with snoring, it is therefore advisable that all the snoring children with other presentation of SDB be screened for OSA and central apnea.
Downloads
References
2. Elisabeth Hultcrantz and B Lofstrand Tidestrom, The development of sleep disordered breathing from 4 to 12 years and dental arch morphology, 2009, INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF PEDIATRIC OTORHINOLARYNGOLOGY, (73), 9, 1234-1241. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.ijporl.2009.05.012.
3. Ferreira AM, Clemente V, Gozal D, Gomes A, Pissarra C, César H, Coelho I, Silva CF, Azevedo MH. Snoring in Portuguese primary school children. Pediatrics. 2000 Nov;106(5):E64. [PubMed]
4. http://www.entnet.org/content/pediatric-sleep-disordered-breathingobstructive-sleep-apnea.
5. Guilleminault C, Stoohs R. Chronic snoring and obstructive sleep apnea syndrome in children. Lung. 1990;168 Suppl:912-9. [PubMed]
6. Lind MG, Lundell BP. Tonsillar hyperplasia in children. A cause of obstructive sleep apneas, CO2 retention, and retarded growth. Arch Otolaryngol. 1982 Oct;108(10):650-4. [PubMed]
7. Wilkinson AR, McCormick MS, Freeland AP, Pickering D. Electrocardiographic signs of pulmonary hypertension in children who snore. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1981 May 16;282(6276):1579-81. [PubMed]
8. Stradling JR, Thomas G, Warley AR, Williams P, Freeland A. Effect of adenotonsillectomy on nocturnal hypoxaemia, sleep disturbance, and symptoms in snoring children. Lancet. 1990 Feb 3;335(8684):249-53. [PubMed]
9. Croft CB, Brockbank MJ, Wright A, Swanston AR. Obstructive sleep apnoea in children undergoing routine tonsillectomy and adenoidectomy. Clin Otolaryngol Allied Sci. 1990 Aug;15(4):307-14. [PubMed]
10. Svanborg E, Larsson H, Carlsson-Nordlander B. Indications of sleep-related upper airway obstruction in children. In: Peter JH, Penzel T, Podszus T, von Wichert P, eds. Sleep. Berlin: Springer-Verlag, 1991; 468-75.
11. Chervin RD, Archbold KH, Dillon JE, Panahi P, Pituch KJ, Dahl RE, et al. Inattention, hyperactivity, and symptoms of sleep-disordered breathing. Pediatrics. 2002;109:449–56.
12. Epstein LJ, Kristo D, Strollo PJ Jr, Friedman N, Malhotra A, Patil SP, Ramar K, Rogers R, Schwab RJ, Weaver EM, Weinstein MD; Adult Obstructive Sleep Apnea Task Force of the American Academy of Sleep Medicine. Clinical guideline for the evaluation, management and long-term care of obstructive sleep apnea in adults. J Clin Sleep Med. 2009 Jun 15;5(3):263-76.
13. Young T, Palta M, Dempsey J, et al. The occurrence of sleepdisordered breathing among middle-aged adults. N Engl J Med 1993; 328:1230-52. [PubMed]
14. Gislason T, Almqvist M, Eriksson G, Taube A, Boman G. Prevalence of sleep apnea syndrome among Swedish men--an epidemiological study. J Clin Epidemiol. 1988;41(6):571-6. [PubMed]
15. Gislason T, Benediktsdóttir B, Björnsson JK, Kjartansson G, Kjeld M, Kristbjarnarson H. Snoring, hypertension, and the sleep apnea syndrome. An epidemiologic survey of middle-aged women. Chest. 1993 Apr;103(4):1147-51. [PubMed]
16. Stebbens VA, Dennis J, Samuels MP, Croft CB, Southall DP. Sleep related upper airway obstruction in a cohort with Down's syndrome. Arch Dis Child. 1991 Nov;66(11):1333-8. [PubMed]
17. Gislason T, Benediktsdóttir B. Snoring, apneic episodes, and nocturnal hypoxemia among children 6 months to 6 years old. An epidemiologic study of lower limit of prevalence. Chest. 1995 Apr;107(4):963-6. [PubMed]
18. Brunetti L, Rana S, Lospalluti ML, Pietrafesa A, Francavilla R, Fanelli M, Armenio L. Prevalence of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome in a cohort of 1,207 children of southern Italy. Chest. 2001 Dec;120(6):1930-5. [PubMed]
19. Fernbach SK, Brouillette RT, Riggs TW, Hunt CE. Radiologic evaluation of adenoids and tonsils in children with obstructive sleep apnea: plain films and fluoroscopy. Pediatr Radiol. 1983;13(5):258-65. [PubMed]
20. Anuntaseree W, Rookkapan K, Kuasirikul S, Thongsuksai P. Snoring and obstructive sleep apnea in Thai school-age children: prevalence and predisposing factors. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2001 Sep;32(3):222-7.
21. Verhulst SL, Schrauwen N, Haentjens D, Suys B, Rooman RP, Van Gaal L, De Backer WA, Desager KN. Sleep-disordered breathing in overweight and obese children and adolescents: prevalence, characteristics and the role of fat distribution. Arch Dis Child. 2007 Mar;92(3):205-8. Epub 2006 Oct 13.
22. Mallory GB Jr, Fiser DH, Jackson R. Sleep-associated breathing disorders in morbidly obese children and adolescents. J Pediatr. 1989 Dec;115(6):892-7. [PubMed]
23. Silvestri JM, Weese-Mayer DE, Bass MT, Kenny AS, Hauptman SA, Pearsall SM. Polysomnography in obese children with a history of sleep-associated breathing disorders. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1993 Aug;16(2):124-9.
24. Chay OM, Goh A, Abisheganaden J, Tang J, Lim WH, Chan YH, Wee MK, Johan A, John AB, Cheng HK, Lin M, Chee T, Rajan U, Wang S, Machin D. Obstructive sleep apnea syndrome in obese Singapore children. Pediatr Pulmonol. 2000 Apr;29(4):284-90. [PubMed]
25. Marcus CL, Curtis S, Koerner CB, Joffe A, Serwint JR, Loughlin GM. Evaluation of pulmonary function and polysomnography in obese children and adolescents. Pediatr Pulmonol. 1996 Mar;21(3):176-83. [PubMed]
26. Wing YK, Hui SH, Pak WM, Ho CK, Cheung A, Li AM, Fok TF. A controlled study of sleep related disordered breathing in obese children. Arch Dis Child. 2003 Dec;88(12):1043-7. [PubMed]
27. Owens J, Opipari L, Nobile C, Spirito A. Sleep and daytime behavior in children with obstructive sleep apnea and behavioral sleep disorders. Pediatrics. 1998 Nov;102(5):1178-84. [PubMed]
28. Corbo GM, Fuciarelli F, Foresi A, De Benedetto F. Snoring in children: association with respiratory symptoms and passive smoking. BMJ. 1989 Dec 16;299(6714):1491-4. [PubMed]
Copyright (c) 2016 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


