Clinical profile and outcome of suspect pediatric COVID-19 patients: Experience from a COVID hospital
Abstract
Introduction: The Indian Council of Medical Research (ICMR) has given clinical criteria for suspecting COVID-19 in the Indian population and admissions to hospitals have been based on the above criteria. Aim - To study the clinical profile and outcomes of children suspected to have COVID-19 infection (based on ICMR criteria) admitted to a designated COVID hospital of North India.
Methods: This was an observational study done in a COVID hospital of North India from April to June 2020. All children </= 18 years of age (including newborns), fulfilling the ICMR criteria and suspected to be COVID infected, from the screening area, were enrolled in the study. Demographic, clinical, laboratory, treatment details, and the final outcome were recorded on a pre-designed data collection proforma. Data was later entered into an MS-EXCEL 2013 spreadsheet and was analyzed using the Epi-info software version 7.2.2.
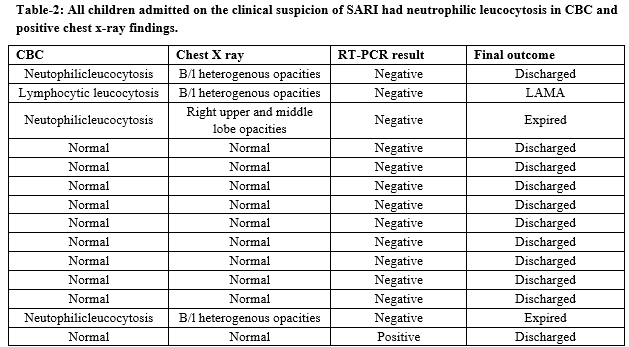
Results: Of the 21 admissions (7 newborns and 14 children>1 month of age) occurring in the COVID suspect ward during the study period, only 1 patient with a positive history of contact, was found to be COVID positive. The mean age of presentation was 10.27 years (Range 0.8-17; SD 7.83). Four children (4/14 = 28.5%) children were admitted on the basis of having symptoms of SARI (Severe Acute Respiratory infection). One patient took leave against medical advice (LAMA) after his RT-PCR report came negative.
Conclusion: The majority of children admitted as per the testing criteria were found to be COVID negative.
Downloads
References
Ludvigsson JF. Systematic Review of COVID-19 in Children Shows Milder Cases and a Better Prognosis Than Adults. Acta Paediatr 2020;109(6):1088-1095. doi: 10.1111/apa.15270.
Licciardi F, Giani T, Baldini L, Favalli EG, Caporali R, Cimaz R. COVID-19 and What Pediatric Rheumatologists Should Know: A Review From a Highly Affected Country. Pediatr Rheumatol Online J. 2020;18(1):35. doi: 10.1186/s12969-020-00422-z.
ICMR Strategy for COVID19 testing in India (Version 52, dated 20/03/2020) Available at https://www.mohfw. gov.in/pdf/ICMRrevisedtestingstrategyforCOVID.pdf 20/3/2020.
ICMR Strategy for COVID19 testing in India (Version 3, dated 09/04/2020) Available at https://www.icmr. gov.in/pdf/covid/strategy/Strategey_for_COVID19_Test_v4_09042020.pdf.
ICMR Strategy for COVID19 testing in India (Version 5, dated 18/05/2020) Available at https://www.icmr.gov.in/pdf/covid/strategy/Testing_Strategy_v5_18052020.pdf.
Chawla D, Chirla D, Dalwai S, Deorari AK, Ganatra A, Gandhi A, et al. Perinatal-Neonatal Management of COVID-19 Infection—Guidelines of the Federation of Obstetric and Gynaecological Societies of India (FOGSI), National Neonatology Forum of India (NNF), and Indian Academy of Pediatrics (IAP). Indian Pediatr. 2020;57(6):536-548. doi: 10.1007/s13312-020-1852-4.
Yuki K, Fujiogi M, Koutsogiannaki S. COVID-19 Pathophysiology: A Review. Clin Immunol. 2020;215:108427. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2020.108427.
Zimmermann P, Curtis N. Coronavirus Infections in Children Including COVID-19: An Overview of the Epidemiology, Clinical Features, Diagnosis, Treatment and Prevention Options in Children. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2020;39(5):355-368. doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000002660.
Qiu H, Wu J, Hong L, Luo Y, Song Q, Chen D. Clinical and Epidemiological Features of 36 Children With Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) in Zhejiang, China: An Observational Cohort Study. Lancet Infect Dis. 2020;20(6):689-696. doi: 10.1016/S1473-3099(20)30198-5.
Zimmermann P, Curtis N. COVID-19 in Children, Pregnancy and Neonates: A Review of Epidemiologic and Clinical Features. Pediatr Infect Dis J. 2020;39(6):469-477 doi: 10.1097/INF.0000000000002700.
Tian Y, Rong L, Nian W, He Y. Review Article: Gastrointestinal Features in COVID-19 and the Possibility of Faecal Transmission. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 2020;51(9):843-851. doi: 10.1111/apt.15731.
Chiotos K, Bassiri H, Behrens EM, Blatz AM, Chang J, Diorio C, et al. Multisystem Inflammatory Syndrome in Children during the COVID-19 pandemic: a case series. J Pediatr Infect Dis Soc. 2020;9(3):393-398. doi: 10.1093/jpids/piaa069.
Sun D, Li H, Lu XX, Xiao H, Ren J, Zhang FR, Liu ZS. Clinical features of severe pediatric patients with coronavirus disease 2019 in Wuhan: a single center’s observational study. World J Pediatr. 2020:1-9. doi: 10.1007/s12519-020-00354-4.
Chen Y, Peng H, Wang L, Zhao Y, Zeng L, Gao H, et al. Infants Born to Mothers With a New Coronavirus (COVID-19). Front Pediatr 2020;8:104. doi: 10.3389/fped.2020.00104.
Su L, Ma X, Yu H, Zhang Z, Bian P, Han Y et al. The Different Clinical Characteristics of Corona Virus Disease Cases Between Children and Their Families in China - The Character of Children With COVID-19. Emerg Microbes Infect. 2020;9(1):707-713.doi: 10.1080/22221751.2020.1744483.
Dhochak N, Singhal T, Kabra SK, Lodha R. Pathophysiology of COVID-19: Why Children Fare Better Than Adults? Indian J Pediatr. 2020;1-10. doi: 10.1007/s12098-020-03322-y.
MMR vaccine could prevent worst symptoms of COVID-19 Available at https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/mmr-vaccine-could-prevent-worst-symptoms-of-covid-19#Training-the-immune-system.
Copyright (c) 2020 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


