Study of morbidity and mortality profile among low birth weight neonates in sick newborn care unit of a rural medical college and hospital.
Abstract
Introduction: Low birth weight is one of the major health problems in children both in developed and developing countries. Birth asphyxia, neonatal sepsis, hypothermia, hypoglycemia, hyperbilirubinemia, hypocalcemia, MAS, NEC, polycythemia, IVH, meningitis, apnea, BPD, etc are the major risk factors for LBW babies morbidity and mortality. This study was conducted in a tertiary care center to find out morbidity and mortality profiles among low birth weight neonates and short-term neurodevelopmental outcome. A cross-sectional observational study. 404 low birth weight babies admitted from 1st June 2016 to 31st May 2017.
Methods: Both clinical and laboratory data of all the patients were retrieved, compiled, and analyzed.
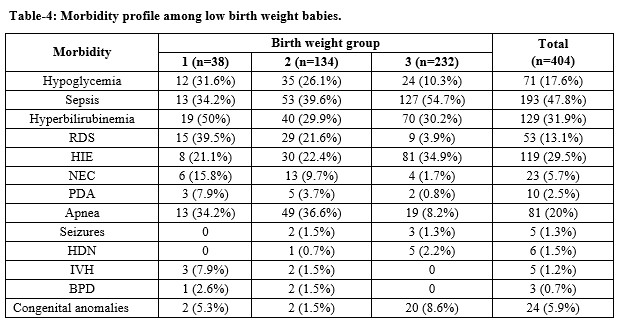
Results: Out of 404 LBW 38 (9.4%) were ELBW,134 (33.2%) were VLBW and rest 232 (57.4%) were between 1500-<2500gm weight, 88 (21.8%) were preterm and IUGR, 219 (54.2%) were male and rest 185 (45.8%) were female. Major cause of morbidity includes hypoglycemia (17.6%), RDS (13.1%), HIE (29.5%), NEC (5.7%), Sepsis (47.8%), hyperbilirubinemia (31.9%), PDA (2.5%), Apnea (5.9%), IVH (1.25%), congenital anomalies (5.9%) etc.
Conclusion: In the present series the mortality rate was (23.5%) was high. Sepsis, RDS, Birth Asphyxia, and Apnea were the main causes of morbidity and mortality among low birth weight babies. Proper asepsis, judicious use of antibiotics, timely intervention like CPAP, etc reduce the mortality. Proper counseling while discharge regarding feeding, warmth care, asepsis, danger sign and need for follow up plays a pivotal role in the neurodevelopmental outcome.
Downloads
References
WHO. International statistical classification of diseases and related health problems. 10th Revision: Geneva: World Health Organization, 1992;2:151-152.
United Nations Administrative Committee on Coordination/Sub-Committee on Nutrition(ACC/SCN). Fourth Report on the World Nutrition Situation. Geneva: ACC/SCN incollaboration with International Food Policy Research Institute (IFPRI), 2000.
India Newborn Action Plan. Ministry of health and family welfare, Govt of India; 2014.
The State of the World’s Children,UNICEF,2014.
Evidence Based Clinical Practice Guidelines. National Neonatology Forum India2010.
Nair MK, George B, Philip E, Lekshmi MA, Haran JC, Sathy N. Trivandrum Developmental Screening Chart. Indian Pediatr. 1991;28(8):869-872.
Fenton TR. Preterm Growth Chart 2003 calculations. Available from: http://members.Shaw. Ca/growth chart/Fenton Growth Chart calculations.xls.
Altuncu E, Kavuncuoğlu S, Özdemir Gökmirza P, Albayrak Z, Arduç A. The incidence of low birth weight in 5000 liveborn infants and the etiology of fetal risk factors. Marmara Med J. 2006;19(2):46-51.
Kayastha S, Tuladhar H. Study of low birth weight babies in Nepal MedicalCollege. Nepal Med Coll J: NMCJ. 2007;2008;9(4):266-269.
D. Manikyamba, N. Madhavi, Morbidity and Mortality Profile of LBW Babies and Their Growth and Neurodevelopment Outcome at 1 year- NICU, Government General Hospital, Kakinada. Sch J App Med Sci. 2015;3(4B):1721-1725.
Agarwal K, Agarwal A, Agarwal VK, Agalwal P, Chaudhary V. Prevalance and determinants of low birth weight among institutional deliveries. Ann Nigerian Med. 2011;5(2):48-52.
Were FN, Mukhwana BO, Musoke RN. Neonatal survival of infants less than 2000 grams born at Kenyatta National Hospital. East African Med J. 2002;79(2):77-79.
Makhoul IR, Sujov P, Smolkin T, Lusky A, Reichman B. Epidemiological, clinical and microbiological characteristics of late onset sepsis among Very low birth weight infants in Israel. Pediatr. 2002;109(1):34-39.
Narang A, Kumar P, Kumar R. Neonatal jaundice in Very low birth weight babies. Indian J Pediatr 2001;68(41):307-315.
Caner I, Tekgunduz KS, Temuroglu A, Demirelli Y, Kara M. Evaluation of Premature Infants Hospitalized in Neonatal Intensive Care Unit between 2010–2012. Eurasian J Med. 2015;47(1):13.
Parkash A, Haider N, Khoso ZA, Shaikh AS. Frequency, causes and outcome of neonates with respiratory distress admitted to Neonatal Intensive Care Unit, National Institute of Child Health, Karachi. J Pak Med Assoc. 2015;65(7):771-775.
Fitzhardinge PM. Early growth and development in low-birthweight infants following treatment in an intensive care nursery. Pediatr. 1975;56(2):162-172.
Bhalla JN, Bhalla M, Srivastava JR. Effects of intrauterine growth and gestational maturity on the morbidity and mortality pattern of babies. Requiring special case, Indian Pediatr. 1979:16(1):41.
Gregory KE. Clinical predictors of necrotizing enterocolitis in premature infants. Nurs Res. 2008;57(4):260-270.
Van Overmeire B, Van de Broek H, Van Laer P, Weyler J, Vanhaesebrouck P. Early versus late indomethacin treatment for patent ductus arteriosus inpremature infants with respiratory distress syndrome. J Pediatr. 2001;138(2):205-211.
Fanaroff AA, Stoll BJ, Wright LL, Carlo WA, Ehrenkranz RA, Stark AR, et al. Trends in neonatal morbidity and mortality for very low birth weight infants. Am J Obstet Gynecol. 2007;196(1):147e1.
Devi GR, Rao KR, Reddy VV. Morbidity and Mortality of Low Birth weight Newborns Admitted in SNCU/NICU in A Tertiary Care Hospital. J Dent Med Sci. 2017;16(1):28-32.
Debbarma R, De A, Debbarma S. Incidence of intracranial haemorrhage in low-birth weight infants and its outcome: a hospital based prospective study. Int J Res Med Sci. 2016;4(10):4279-4285.
Dincsoy MY, Siddiq F, Kim YM. Intracranial hemorrhage in hypothermic Low birth weight neonates. Child Nan Cyst.1990;6(5):245-248.
Acharya N, Mishra P, Shrestha N, Gupta V. Immediate Outcome of Vlbw And Elbw Babies in a Tertiary Care Center of Nepal. J Nepalgunj Med Coll. 2014;12(1):32-34.
Poudel P, Budhathoki S, Shrivastava MK. Maternal risk factors and morbidity pattern of very low birth weight infants: a NICU based study at eastern Nepal. J Nepal Pediatr Soc. 2009;29(2):59-66.
Shankaran S, Fanaroff AA, Wright LL, Stevenson DL, Donovan FF, Ehrenkranz RA, et al. Risk factors for early death among extremely low birth weight infants. Am J Obstet Gynaecol. 2002;186(4):796- 802.
Patki VK, Antin JV. Maternal antenatal profile and immediate neonatal outcome in very low birth weight babies. Int J Med Pediatr Oncol. 2017;3(2):64-70.
Bavadekar AR, Vaidya UV, Bhave SA, Pandit AN. Catch up growth and its determinants in low birth weight babies: A study using Z scores. Indian Pediatr. 1994;31:1483-1490.
Modi M, Saluja S, Kler N, Batra A, Kaur A, Garg P, Suman P. Growth and neurodevelopment outcome of VLBW infants at 1-year corrected age at 2 years. Indian J Pediatrics, 2013;50(6):573-467.
Mukhopadhaya K, Malhi P, Mahajan R, Narang A. Neurodevelopmental and behavioural outcome of VLBW babies at corrected age of 2 years. Indian J Pediatrics. 2010;77(9):963-967.
Copyright (c) 2020 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


