Compressive myelopathy presenting with paraparesis in pediatric age
Abstract
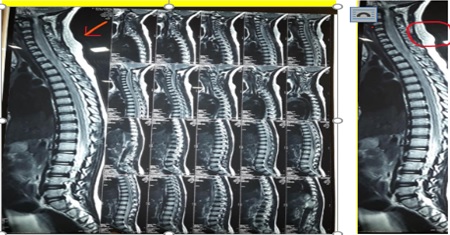
Compressive myelopathy is a common presentation of the adult age group secondary to degenerating etiologies. Trauma is a rare cause of compressive myelopathy, especially in the pediatric age group as the pediatric spine is more elastic than that of adults, especially below 8 years of age. Boys are more commonly injured as compared to girls. The present study reports a case of a six-year-old female patient of compressive myelopathy presenting with jerks with progressive paraparesis. MRI shows posterior subluxation of dens (C2) attached to C2 vertebral effacing anterior – subarachnoid space and indenting spinal cord.
Downloads
References
Nouri A, Tetreault L, Singh A, Karadimas SK, Fehlings MG. Degenerative cervical myelopathy: epidemiology, genetics, and pathogenesis. Spine. 2015;40(12):E675-E693. doi: 10.1097/brs.0000000000000913.
Kewalramani LS, Tori JA. Spinal cord trauma in children. Neurologic patterns, radiologic features, and pathomechanics of injury. Spine. 1980;5(1):11-18. doi: 10.1097/00007632-198001000-00003.
Anderson JM, Schutt AH. Spinal injury in children: a review of 156 cases seen from 1950 through 1978. InMayo Clinic Proceedings. 1980;55(8):499-504.
Bracken MB, Freeman DH Jr, Hellenbrand K. Incidence of acute traumatic hospitalized spinal cord injury in the United States,1970-1977. Am J Epidemiol. 1981;113(6):615-622.
Hamilton MG, Mylks ST. Pediatric spinal injury: review of 174 hospital admissions. J Neurosurg. 1992;77(5):700-704. doi: 10.3171/jns.1992.77.5.0700.
d’Amato C. Pediatric spinal trauma: injuries in very young children. Clin Orthopaed Rel Res. 2005;432:34-40. doi: 10.1097/01.blo.0000156006.20089.85.
Birney TJ, Hanley Jr EN. Traumatic cervical spine injuries in childhood and adolescence. Spine. 1989;14(12):1277-1282. doi: 10.1097/00007632-198912000-00001.
Townsend EH, Rowe ML. Mobility of the upper cervical spine in health and disease. Pediatr. 1952;10(5):567-574.
Hadley MN, Zabramski JM, Browner CM, Rekate H, Sonntag VK. Pediatric spinal trauma: review of 122 cases of spinal cord and vertebral column injuries. J Neurosurg. 1988;68(1):18-24. doi: 10.3171/jns.1988.68.1.0018.
Herkowitz H N, Rothman R H. Subacute instability of the cervical spine. Spine. 1984;9(4):348-357. doi: 10.1097/00007632-198405000-00004.
Leventhal H R. Birth injuries of the spinal cord. J Pediatr. 1960;56(4):447-453. doi: 10.1016/S0022-3476(60)80356-3.
Flynn J M, Closkey R F, Mahboubi S, Dormans J P. Role of magnetic resonance imaging in the assessment of pediatric cervical spine injuries. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 2002;22(5):573-577. doi: 10.1097/00004694-200209000-00002.
Alter M. The epidemiology of Guillain-Barr syndrome. Ann Neurol. 1990;27(S1):S7-S12. doi: 10.1002/ana.410270704.
Smith MD, Phillips WA, Hensinger RN. Fusion of the upper cervical spine in children and adolescents: an analysis of 17 patients. Spine 1991;16(7):695-701.
Copyright (c) 2020 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


