Study of Serum IgE levels in Recurrent Respiratory illness in children 6 months to 5 years of age
Abstract
Objective: The present study was undertaken to study the serum IgE levels in recurrent respiratory tract illnesses in children greater than 6 months to less than 5 years of age and to find the correlation between them.
Methods: This was a prospective observational cross-sectional study. The study was undertaken to determine the correlation of serum IgE levels with recurrent respiratory tract illness. A total of 99 children were included in this study. 2ml of blood was drawn by peripheral venous phlebotomy in airtight screw-capped plastic vials for measuring serum IgE levels. The Serum IgE level is assessed by chemiluminescence.
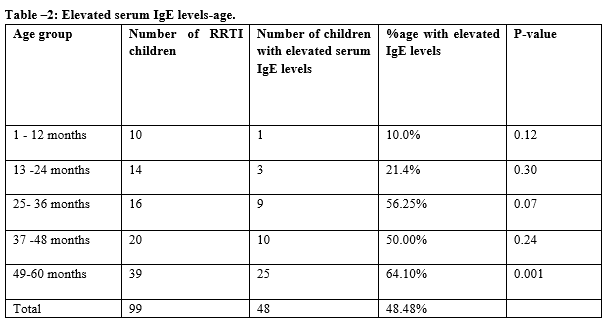
Results: Out of 99 children, 48 children had elevated serum IgE levels and 51 had normal serum IgE levels. Serum IgE levels were significantly higher (66.07%) in males as compared to females (25.58%) with a p-value of 0.0003 (<0.05). The elevation of serum IgE levels was 48.48% in all children (48 out of 99 children). It’s noticed that the number of children suffering from RRTI and the number of children with elevated serum IgE levels increased with increasing age. There is a significant increase in serum IgE levels from 10.00% in infancy to 64.10% in the 49-60th month.
Conclusion: This study showed an increasing number of children with recurrent respiratory tract illness and serum IgE levels with increasing age. Males, preterm and bottle-fed babies are more prone. There was a significant role in a family history of recurrent respiratory tract illness in children with elevated serum IgE levels.
Downloads
References
Bellanti JA, Olivieri D, Serrano E. Ribosomal immunostimulation. BioDrugs. 2003;17(5):355-367. doi: 10.2165/00063030-200317050-00005.
Graham NM. The epidemiology of acute respiratory infections in children and adults: a global perspective. Epidemiol Rev. 1990;12:149-178. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.epirev.a036050.
Teele DW, Klein JO, Rosner B, Greater Boston Otitis Media Study Group. Epidemiology of otitis media during the first seven years of life in children in greater Boston: a prospective, cohort study. J Infect Dis. 1989;160(1):83-94. doi: 10.1093/infdis/160.1.83.
Ishizaka K, Ishizaka T. Identification of γE-antibodies as a carrier of reaginic activity. J Immunol. 1967;99(6):1187-1198.
Kleine-Tebbe J, Poulsen LK, Hamilton RG. Quality management in IgE-based allergy diagnostics. J Lab Med. 2016;40(2):81-96. doi: 10.1515/labmed-2016-0013.
Bennich HH, Ishizaka K, Johansson SG, Rowe DS, Stanworth DR, Terry WD. Immunoglobulin E: a new class of human immunoglobulin. Immunol. 1968;15(3):323.
Kochwa S, Terry WD, Capra JD, Yang NL. Structural studies of immunoglobulin EI Physicochemical studies of the IgE molecule. Ann New York Acad Sci. 1971;190:49-70. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1971.tb13523.x.
Satwani H, Rehman A, Ashraf S, Hassan A. Is serum total IgE levels a good predictor of allergies in children. J Pak Med Assoc. 2009;59(10):698-702.
Dhar S, Malakar R, Chattopadhyay S, Dhar S, Banerjee R, Ghosh A. Correlation of the severity of atopic dermatitis with absolute eosinophil counts in peripheral blood and serum IgE levels. Indian J Dermatol, Venereol Leprol. 2005;71(4):246. doi: 10.4103/0378-6323.16615.
Stempel DA, Clyde Jr WA, Henderson FW, Collier AM. Serum IgE levels and the clinical expression of respiratory illnesses. J Pediatr. 1980;97(2):185-190. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(80)80471-9.
Foucard T, Johansson SG. Allergen‐specific IgE and IgG antibodies in pollen‐allergic children given immunotherapy for 2‐6 years. Clin Experiment Allerg. 1978;8(3):249-257. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2222.1978.tb03221.x.
Nagayama Y, Sakurai N, Kojima S, Funabashi S. Total and specific IgE responses in the acute and recovery phases of respiratory infections in children. J Asthma. 1987;24(3):159-166. doi: 10.3109/02770908709070932.
Borish L, Chipps B, Deniz Y, Gujrathi S, Zheng B, Dolan CM. TENOR Study Group. Total serum IgE levels in a large cohort of patients with severe or difficult-to-treat asthma. Ann Allergy, Asthma Immunol. 2005;95(3):247-253. doi: 10.1016/S1081-1206(10)61221-5.
Petridou ET, Chavelas C, Dikalioti SK, Dessypris N, Terzidis A, Nikoulis DI, et al. Breast cancer risk in relation to most prevalent IgE specific antibodies: a case control study in Greece. Anticancer Res. 2007;27(3B):1709-1713.
Sistonen P, Johnsson V, Koskenvuo M, Aho K. Serum IgE levels in twins. Human heredity. 1980;30(3):155-158. doi: 10.1159/000153120.
Habib H, Tayeb M, Qutub M, Samkari J. Total IgE and Absolute Eosinophils Count as a Predictor of Allergic Diseases in Children. Egyptian J Hospital Med. 2010;40(1):365-374. doi: 10.12816/ejhm.2010.17385.
Gandhi SS, Rao KR. A Study of Serum IgE Levels among Children of 6 Months to 5 Years of Age Group.
Siltanen M, Savilahti E, Pohjavuori M, Kajosaari M. Respiratory symptoms and lung function in relation to atopy in children born preterm. Pediatr pulmonol. 2004;37(1):43-49. doi: 10.1002/ppul.10402.
Croner S, Kjellman NI, Eriksson B, Roth A. IgE screening in 1701 newborn infants and the development of atopic disease during infancy. Arch Dis Childhood. 1982;57(5):364-368. doi: 10.1136/adc.57.5.364.
Razi E, Moosavi GA. Serum total IgE levels and total eosinophil counts: relationship with treatment response in patients with acute asthma. Jornal Brasileiro De Pneumologia. 2010;36(1):23-28. doi: 10.1590/S1806-37132010000100006.
Copyright (c) 2020 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


