A rare case of bullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma in a newborn
Keywords:
Bullous Congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma, Keratinization disorder
Abstract
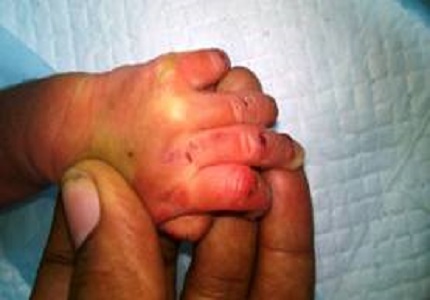
Bullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma is a rare disorder of keratinization. It is associated with defective keratinization leading to skin fragility, blistering and hyperkeratosis. This condition was difficult to distinguish from staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome. We report a case of Bullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma in a 72 hour old male baby and discussed the differential diagnosis and management of the disease.
Downloads
Download data is not yet available.
References
1. Brocq L. Erythrodermie congenital ichthyosiforme avec hyperepidermotrophie.Ann Dermatol Syphiligr. 1902;vol 4:pg [1-31].
2. DiGiovanna JJ, Bale SJ. Clinical heterogeneity in epidermolytic hyperkeratosis. Arch Dermatol. 1994 Aug;130(8):1026-35. [PubMed]
3. Cheng J, Syder AJ, Yu QC, Letai A, Paller AS, Fuchs E. The genetic basis of epidermolytic hyperkeratosis: a disorder of differentiation-specific epidermal keratin genes. Cell. 1992;vol 70:[ 811-819]. [PubMed]
4. Chipev CC1, Korge BP, Markova N, Bale SJ, DiGiovanna JJ, Compton JG, Steinert PM. A leucine----proline mutation in the H1 subdomain of keratin 1 causes epidermolytic hyperkeratosis. Cell. 1992 Sep 4;70(5):821-8. [PubMed]
5. Kwak J, Maverakis E. Epidermolytic hyperkeratosis. Dermatol Online J. 2006 Sep 8;12(5):6. [PubMed]
6. El Shabrawi-Caelen L, McCalmont TH. Perinuclear eosinophilic bands: a clue to keratin gene mutation. J Cutan Pathol. 2010 Jul;37(7):718-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0560.2010.01555.x. [PubMed]
7. Bergman R, Khamaysi Z, Sprecher E. A unique pattern of dyskeratosis characterizes epidermolytic hyperkeratosis and epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma. Am J Dermatopathol. 2008;vol 30: pg[101-105].
8. Kempers S, Katz HI, Wildnauer R, Green B. An evaluation of the effect of an alpha hydroxy acid-blen skin cream in the cosmetic improvement of symptoms of moderate to severe xerosis, epidermolytic hyperkeratosis, and ichthyosis. Cutis. 1998; vol 61:pg [347-350].
2. DiGiovanna JJ, Bale SJ. Clinical heterogeneity in epidermolytic hyperkeratosis. Arch Dermatol. 1994 Aug;130(8):1026-35. [PubMed]
3. Cheng J, Syder AJ, Yu QC, Letai A, Paller AS, Fuchs E. The genetic basis of epidermolytic hyperkeratosis: a disorder of differentiation-specific epidermal keratin genes. Cell. 1992;vol 70:[ 811-819]. [PubMed]
4. Chipev CC1, Korge BP, Markova N, Bale SJ, DiGiovanna JJ, Compton JG, Steinert PM. A leucine----proline mutation in the H1 subdomain of keratin 1 causes epidermolytic hyperkeratosis. Cell. 1992 Sep 4;70(5):821-8. [PubMed]
5. Kwak J, Maverakis E. Epidermolytic hyperkeratosis. Dermatol Online J. 2006 Sep 8;12(5):6. [PubMed]
6. El Shabrawi-Caelen L, McCalmont TH. Perinuclear eosinophilic bands: a clue to keratin gene mutation. J Cutan Pathol. 2010 Jul;37(7):718-9. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0560.2010.01555.x. [PubMed]
7. Bergman R, Khamaysi Z, Sprecher E. A unique pattern of dyskeratosis characterizes epidermolytic hyperkeratosis and epidermolytic palmoplantar keratoderma. Am J Dermatopathol. 2008;vol 30: pg[101-105].
8. Kempers S, Katz HI, Wildnauer R, Green B. An evaluation of the effect of an alpha hydroxy acid-blen skin cream in the cosmetic improvement of symptoms of moderate to severe xerosis, epidermolytic hyperkeratosis, and ichthyosis. Cutis. 1998; vol 61:pg [347-350].
CITATION
DOI: 10.17511/ijpr.2016.i01.15
Published: 2016-01-31
How to Cite
Dr Thumjaa Annamalai, Dr Vamsikrishna Reddy kandriga, & Dr Sindhu maru. (2016). A rare case of bullous congenital ichthyosiform erythroderma in a newborn. Pediatric Review: International Journal of Pediatric Research, 3(1), 77-79. https://doi.org/10.17511/ijpr.2016.i01.15
Section
Case Report
Copyright (c) 2016 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


