A study on pattern of lower respiratory tract infections in children below 12 years of age admitted to KIMS hospital, amalapuram.
Abstract
Background: Acute respiratory infections (ARI) in children less than five years are the leading causes of mortality. A study was conducted to know the incidence of different types of LRTIs and the common causative organisms.
Methods: Routine investigations were carried out on 824 hospitalized children over 18 months and with special investigations like X-ray chest, USG chest, blood culture, pleural fluid analysis, tuberculin skin test, and CBNAAT for tuberculosis.the data were analyzed.
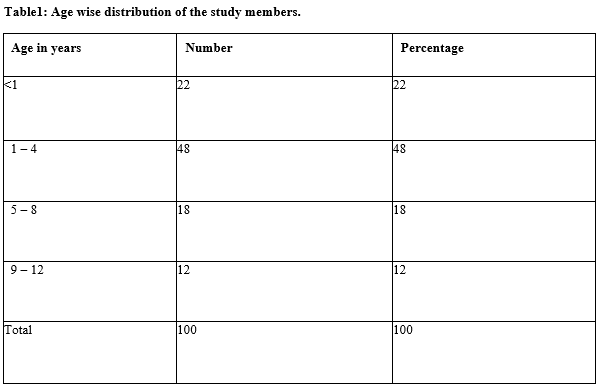
Results: Out of 100 cases, 2 cases were diagnosed as tuberculosis. Others, i.e., 97 improved and discharged. The minimum hospital stay was 3 days, and the maximum was 21 days. The incidence of LRTI in children was maximum (48%) in 1 – 4 years age and Protein-energy malnutrition (PEM ) was detected in 72% children. PEM I was maximum (35%) followed by PEM II (16%), PEM III (12%) and PEM IV (9%. Bronchopneumonia was diagnosed maximum (52%) followed by bronchiolitis (12%). Mantoux test was positive in 21%. Staphylococcus aureus was isolated maximum and no significant drug resistance was identified.
Conclusion: Maximum incidence of LRTIs were detected between the age group of 1 – 4 years, malnutrition was an associated factor.
Downloads
References
WHO.World health organization pneumonia. 2012. Available from http://www.who.Int/medicalcentre/factsheets/em/.
Francis BV, Abhilash TG. Study of acute respiratory tract infections in children. Internat J Sci Res.2016; 5(9): 1791 – 2. doi: 10.18203/2349-3291.ijcp20173775.
Alter SJ, Vidwan NK, Sobande PO, Omoloja A, Bennett JS. Common childhood bacterial infections. Current Probl Pediatric Adolescent Health Care.2011; 41: 256 – 83.
Erling V, Jalil F, Hanson LA, Zaman S. The impact of climate on the prevalence of respiratory tract infection in early childhood in Lahore, Pakistan. J PubHealth.1999; 21: 331 – 9. DOI: 10.1093/pubmed/21.3.331
Munagala VK, Mahesh RMU, Kanda J, Ponugoti M. Clinical study of lower respiratory tract infections in children attending a tertiary care hospital. Int J Contemp Pediatr 2017; 4: 1733-8. doi: 10.18203/2349-3291.ijcp20180535.
Bikash, Devasri C, Daisy P, Deka A .drug prescribing pattern in the respiratory tract infection in children aged 1 to 12 years at the outpatient department at Silchar medical college and hospital, Assam, Ind J pharm Biomed Sci 2016; 06: 537 – 45.
Sharma D, Kuppuswamy K, Bhoorasamy A. Prevalence of the acute respiratory tract Infections(ARI) and their determinants in under 5 children in urban and rural areas of Kancheepuram district, south India.ann Troup Med public health 2013; 6: 513 – 8. Available at https://www.atmph.org/text.asp?2013/6/5/513/133700
Peter D Phelan, Anthony Olin sky, Colin F, Robertson. The epidemiology of Acute respiratory infections. Textbook of pediatrics on “Respiratory illness in children.” Blackwell Scientific Publications, 4th Edition, 1994: 27 – 42.
Paramesh H. Epidemiology of asthma in children in India. Ind J Of pediatrics 2002; 69: 309-12. doi: 10.1007/BF02723216.
Lakhani JK, Sanjeev Joshi. Intercostal tubedrainage practical tips. Karnataka PediatricJ 2004; 18:14 – 16. doi: 10.1055/s-0029-1208074. Epub 2009 Feb 23
Paul LMcCarthy, Sydney Z Spiesel Carole, Stashwick A, Ronald C Ablow, Stuart J Masters, Thomas F Dolan Jr. Radiographic findings and etiologic diagnosis in ambulatory childhood pneumonia. Clin Pediatrics 1981; 20:686 – 91. doi: 10.1177/000992288102001101.
Kabra SK, Broor S, Rakesh Lodha, Maitreyi RS, Ghosh M, Pandey RM, Puranik M. Brief reports can we identify acute severe viral lower respiratory tract infection clinically? Ind Pediatrics 2004; 41: 245 – 9. https://www.indianpediatrics.net/mar2004/mar-245-249.htm
Yellanthoor R B, Shah V K B. prevalence of malnutrition among under five year old children with acute lower respiratory tract infection hospitalized at Udupi district hospital. Arch pediatric infectious disease.2014; 2(2): 203 – 6. DOI : 10.5812/pedinfect.14373
GunnarDStickler,AlanDHoffman,WilliamFTaylor. Problemsinthe clinical and roentgenographic diagnosis of pneumonia in young children. Clin Pediatrics 1984; 23: 398 – 399. doi: 10.1177/000992288402300707
Kumar KGR, Sameer Bakshi, Samantaray JC, Banerjee UanArya LS. Trans thoraciclungaspirationin theetiology of pneumonia. Ind J Of Pediatrics 2004; 71: 129 – 32. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3291.ijcp20163682
Black RE, Allen LH, Bhutta ZA, Caulfield LE, de Onis M,Ezzati M et al. Maternal And child under nutrition: global and regional exposures and health consequences. Lancet 2008; 371: 243 – 60. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(07)61690-
Daniel E Roth, Laura E Caulfield Majid Ezzati Robert E Black, WHO/ Acute lower respiratory infections in children: opportunities for reducing the global burden through nutritional interventions who bulletin 11.4.2019. doi: 10.2471/blt.07.049114.
Shally Awasthi, Ektakalra, Siddhartha Roy, Saumya Awasthi. Prevalence and Risk-Factors of Asthma and Wheeze in School going childrenin Lucknow. Ind Peditrics. 2014; 41: 1205 – 9. http://www.indianpediatrics.net/dec2004/dec-1205-1...
K. Ramakrishnan P, S harish. Study on various lower respiratory tract infections in school going children. The Ind J Of Pediatrics 2006; 73: 881 – 88. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2349-3291.ijcp20173775
Saket Kumar, Shally Awasthi, Amita Jain, Srivastava RC. Blood zinc levels in children hospitalized with severe pneumonia – A case-control study. Ind Pediatrics 2004; 41: 486 – 90.
Copyright (c) 2021 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


