Assessment & correlation of gestational age in newborns with head circumference: A Hospital-based cross-sectional study in Central India
Abstract
Introduction: Preterm birth is the leading cause of death in children younger than 5 years worldwide. Although preterm survival rates have increased in high-income countries, preterm newborns still die because of a lack of adequate newborn care in many low-income and middle-income countries. This study was aimed to find out the effectiveness of anthropometric measurement, a simple and inexpensive method, for identifying premature babies at birth.
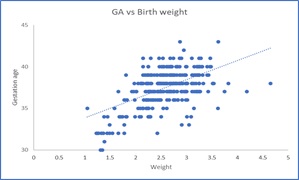
Method: We conducted a cross-sectional study in a tertiary care hospital with 350 consecutively live-born newborns. Their birth weight, mid-arm circumference, length and head circumference were measured and compared with gestational age assessed by New Ballard score. We summarized the variables using descriptive statistics, and the strength of association was determined through correlation analysis. The correlation was strong for head circumference. Linear regression analysis was done to develop predictive equations.
Result: Amongst 350 newborns, 76% were term and 24% were preterm. Pearson's correlation coefficient between gestational age as assessed by New Ballard score and head circumference, birth weight, mid-arm circumference and length all showed a significant positive correlation in the decreasing order [maximum with head circumference (r = 0.566)]. Linear regression analysis was done to develop predictive equations.
Conclusion: Head circumference measurement can be a surrogate marker to predict prematurity as a significant correlation is seen between it and gestational age assessed by the New Ballard score. Further studies are needed to cross-validate our result.
Downloads
References
https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/preterm-birth
Liu L, Oza S, Hogan D, Chu Y, Perin J, Zhu J, et al. Global, regional, and national causes of under-5 mortality in 2000-15: an updated systematic analysis with implications for the Sustainable Development Goals. Lancet. 2016 Dec 17;388(10063):3027-3035. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(16)31593-8.
Bang AT, Bang RA, Baitule S, Deshmukh M, Reddy MH. Burden of morbidities and the unmet need for health care in rural neonates--a prospective observational study in Gadchiroli, India. Indian Pediatr. 2001 Sep;38(9):952-65.
Blanc AK, Wardlaw T. Monitoring low birth weight: an evaluation of international estimates and an updated estimation procedure. Bull World Health Organ. 2005 Mar;83(3):178-85.
Ballard JL, Khoury JC, Wedig K, Wang L, Eilers-Walsman BL, Lipp R. New Ballard Score, expanded to include extremely premature infants. J Pediatr. 1991 Sep;119(3):417-23. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(05)82056-6.
Ministry of Health and Family Welfare, Government of India. National Family Health Survey (NFHS- 3), 2005- 06: India. Key findings. Mumbai: International Institute for Population Sciences;2007. p. 24.
United Nations Children’s Fund. National factsheet; Coverage Evaluation Survey. UNICEF;2009. New Delhi: United Nations Children’s Fund [cited 2018 April 22]. Available from: http://www.indiaenvironmentportal.org. in/files/National_Factsheet_30_August_no_logo.pdf.
Ngirabega JD, Hakizimana C, Wendy L, Munyanshongore C, Donnen P, Dramaix-Wilmet M. Fiabilité des mesures anthropométriques dans le suivi de la croissance à base communautaire des enfants en milieu rural au Rwanda [Reliability of anthropometric measurements performed by community nutrition workers in a community-based pediatric growth-monitoring program in rural Rwanda]. Rev Epidemiol Sante Publique. 2010 Dec;58(6):409-14. French. doi: 10.1016/j.respe.2010.07.002.
Johnson W, Cameron N, Dickson P, Emsley S, Raynor P, Seymour C, et al. The reliability of routine anthropometric data collected by health workers: a cross-sectional study. Int J Nurs Stud. 2009 Mar;46(3):310-6. doi: 10.1016/j.ijnurstu.2008.10.003.
Use of a simple anthropometric measurement to predict birth weight. WHO Collaborative Study of Birth Weight Surrogates. Bull World Health Organ. 1993;71(2):157-63.
Kc A, Nelin V, Vitrakoti R, Aryal S, Målqvist M. Validation of the foot length measure as an alternative tool to identify low birth weight and preterm babies in a low-resource setting like Nepal: a cross-sectional study. BMC Pediatr. 2015 Apr 17;15:43. doi: 10.1186/s12887-015-0361-4.
Singhal, S., Tomar, A., Masand, R., & Purohit, A. (2014). A simple tool for assessment of gestational age in newborns using foot length. Journal of Evolution of Medical and Dental Sciences, 3(23), 6424-6430.
Mukherjee S, Roy P, Mitra S, Samanta M, Chatterjee S. Measuring new born foot length to identify small babies in need of extra care: a cross-sectional hospital based study. Iran J Pediatr. 2013 Oct;23(5):508-12.
Huque F, Hussain AM. Detection of low birth-weight new born babies by anthropometric measurements in Bangladesh. Indian J Pediatr. 1991 Mar-Apr;58(2):223-31. doi: 10.1007/BF02751125.
Sreeramareddy CT, Chuni N, Patil R, Singh D, Shakya B. Anthropometric surrogates to identify low birth weight Nepalese newborns: a hospital-based study. BMC Pediatr. 2008 Apr 25;8:16. doi: 10.1186/1471-2431-816.
Sajjadian, N., Shajari, H., Rahimi, F., Jahadi, R., & Barakat, M. G. (2011). Anthropometric measurements at birth as predictor of low birth weight. Health, 3(12), 752-756.
Thawani R, Dewan P, Faridi MM, Arora SK, Kumar R. Estimation of gestational age, using neonatal anthropometry: a cross-sectional study in India. J Health Popul Nutr. 2013 Dec;31(4):523-30. doi: 10.3329/jhpn.v31i4.20051.
Yadav R, Bhatnagar P, Gunjan, et al. Gestational age assessment in newborns using regression equation of anthropometric parameters singly or in combination. Int J Biomed Res. 2016;7(8):600–605. doi:10.7439/ijbr
Gandhi, D., Masand, R., & Purohit, A. A simple method for assessment of gestational age in neonates using head circumference. Global Journal for Research Analysis, 3(5), 211-213.
Sasanow SR, Georgieff MK, Pereira GR. Mid-arm circumference and mid-arm/head circumference ratios: standard curves for anthropometric assessment of neonatal nutritional status. J Pediatr. 1986 Aug;109(2):311-5. doi: 10.1016/s0022-3476(86)80393-6.
Das NK, Nandy S, Mondal R, Ray S, Hazra A. Gestational Age Assessment with Anthropometric Parameters in Newborns. Oman Med J. 2018 May;33(3):229-234. doi: 10.5001/omj.2018.42.
Kapoor, A., & Soni, T. N. (2020). Neonatal Foot Length as Surrogate Marker for Prematurity: A Hospital Based Cross-Sectional Study in Central India. Journal of Nepal Paediatric Society, 40(3), 217-223.
Pandey, V. D., Singh, V., Nigam, G. L., Usmani, Y., & Yadav, Y. (2015). Fetal foot length for assessment of gestational age: A comprehensive study in North India. Sch J Appl Med Sci, 3(1C), 139-44.
Tiruneh C. Estimation of Gestational Age Using Neonatal Anatomical Anthropometric Parameters in Dessie Referral Hospital, Northeast Ethiopia. Risk Manag Healthc Policy. 2020 Dec 15;13:3021-3029. doi: 10.2147/RMHP.S280682.
Rajesh N , Kiran P. Identification of an anthropometric surrogate to low birth weight in newborns: ahospital based cross sectional study. Int J Community Med Public Health. 2018 May;5(5):2066-2071. DOI: http://dx.doi.org/10.18203/2394-6040.ijcmph2018172
Lee AC, Mullany LC, Ladhani K, Uddin J, Mitra D, Ahmed P, et al. Validity of Newborn Clinical Assessment to Determine Gestational Age in Bangladesh. Pediatrics. 2016 Jul;138(1):e20153303. doi: 10.1542/peds.2015-3303.
Copyright (c) 2021 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


