Microbiological profile of Nosocomial infections in the pediatric patients admitted to intensive care unit
Abstract
Aim: Nosocomial infections are major public health concern in intensive care unit which is associated with increase in the morbidity and the mortality. Our aim is to study the incidence of nosocomial infection, site of infection, pathogens involved and their susceptibility.
Methods: Children those who were admitted to intensive care unit for more than 48 hours were included. Clinical samples like blood, urine, sputum, wound/pus swab, intravenous catheter tips, endotracheal aspirates, urinary catheter, central venous catheter, inter costal drainage catheter tip were collected and sent for culture and sensitivity.
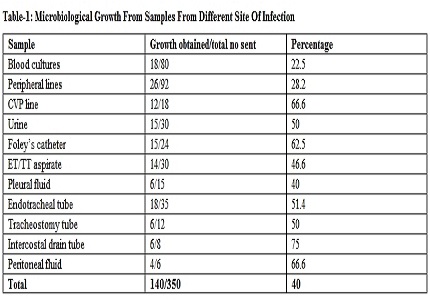
Result: Out of 350 patients, 70 patients had nosocomial infection. The overall nosocomial infection rate was 20%. Most common infections were bloodstream infections followed by pneumonia and urinary tract infections. Nosocomial infection related mortality was most commonly due to pneumonia. Staphylococcus aureus were the most common blood stream isolates. Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Acinetobacter baumanii were the most common species found in pneumonia.
Conclusion: The presence of nosocomial infection was associated with prolonged period of hospitalization and use of invasive devices which is associated with increased mortality and morbidity and increased cost of health care.
Downloads
References
2. Asembergiene J, Gurskis V, Kevalas R, Velinteliene R, Nosocomial infections in the pediatric intensive care units in Lithuania. Medicina (Kaunas). 2009;45(I):29-36. [PubMed]
3. Abramczyk ML, Carvalho WB, Carvalho ES, Medeiros EAS. Nosocomial infection in a pediatric intensive care unit in a developing country. Braz J Infect Dis. 2003 Dec;(6): 375-380. [PubMed]
4. Hossein Masoumi Asl, Alireza Nateghian. Epidemiology of nosocomial infections in a pediatric intensive care unit (PICU), Iranian Journal of Clinical Infectious diseases 2009;4(2): 83-86.
5. Deep A, Ghildiyal R, Kandian S, Shinkre N. Clincal and microbiological profile of nosocomial infections in the pediatric intensive care unit (PICU), Indian Pediatr. 2004 Dec; 41(12):1238-46. [PubMed]
6. Garner JS, Jarvis WR, Emori TG, Horan TC, Hughes JM, CDC definitions for nosocomial infections, 1988, Am J Infect Control June 1988;16(3):128-40. [PubMed]
7. Clinical and laboratory standards institute. Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing; 17th informational supplement, CSLI M100-S17. Vol.27 no.1. Wayne, PA USA: Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute; 2007;46-114.
8. Chandrashekar G S, Sanchita Shettigar, Ronald Roche, Microbial profile of nosocomial infections in the paediatric intensive care unit at a tertiary care hospital,Int j clin surg adv. 2014; 2(4): 1-8.
9. Zaveri Jitendra R, Patel Shirishkumar M, Nayak Sunil N, A study on bacteriological profile and drug sensitivity and resistance pattern of isolates of patients admitted in intensive care unit of tertiary care hospital in Ahmadabad.NATIONAL JOURNAL OF MEDICAL RESEARCH vol 2 issue 3: july –sept 2012:p330-334.
10. Porto JP, Mantese OC, Arantes A, Freitas C, Gontijo Filho PP, Ribas RM. Nosocomial infection in a pediatric intensive care unit of a developing country: NHSN surveillance. Rev Soc Bras Med Trop 2012 Jul-Aug:45(4):475-9. [PubMed]
11. Richards MJ, Edwards JR, Culver DH, Gaynes RP. Nosocomial infections in pediatric intensive care units in the united states. National Nosocomial Infections Surveillance System, Pediatrics. 1999 Apr;103(4):e39.
12. Lodha R, Chandra U, Natchu M, Nanda M, Kabra SK. Nosocomial infections in pediatric intensive care units. Indian J Pediatr Nov. 2001;68(11):1063-1070. [PubMed]
13. Patwardhan RB, Dhakephalkar PK, K.B. Niphadkar KB, Chopade BA. A study on nosocomial pathogens in ICU with special reference to multi resistant Acinetobacter baumannii harbouring multiple plasmids. Indian J Med Res 128, August 2008, 178-187. [PubMed]
14. Bowen-Jones J, Wesley A, Vand Den Ende J. Nosocomial colonization and infection in a pediatric respiratory intensive care unit. S Afr Med J 1992;82:309-13. [PubMed]
Copyright (c) 2016 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


