ABCC6 MISSENSE MUTATION AND SEVERE RESISTANT SYSTEMIC HYPERTENSION IN A CHILD.
Abstract
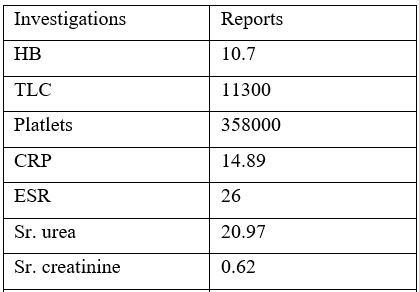
Pseudoxanthoma elasticum (PXE) is a rare multisystem disorder characterised by progressive calcification and fragmentation of elastic fibres. Recent genetic advances have identified the underlying defect in the ABCC6 gene on chromosome 16p13.1. Patients typically develop cutaneous, ocular, and cardiovascular manifestations, but there is considerable phenotypic variability. Skin changes are usually apparent in adulthood and rarely observed in childhood. Since the prognosis of PXE largely depends on the extent of extracutaneous organ involvement, early recognition, intervention, and lifestyle adjustments are important to reduce morbidity.
Downloads
References
2. Gomes RS, Quirino IG, Pereira RM, Vitor BM, Leite AF, Oliveira EA, Simões e Silva AC. Primary versus secondary hypertension in children followed up at an outpatient tertiary unit. Pediatr Nephrol. 2011 Mar;26(3):441-7. doi: 10.1007/s00467-010-1712-x.
3. Hannah-Shmouni F, Gubbi S, Spence JD, Stratakis CA, Koch CA. Resistant Hypertension: A Clinical Perspective. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am. 2019 ;48(4):811-828. doi: 10.1016/j.ecl.2019.08.010.
4. Aggarwal A, Rodriguez-Buritica D. Monogenic Hypertension in Children: A Review With Emphasis on Genetics. Adv Chronic Kidney Dis. 2017 ;24(6):372-379. doi: 10.1053/j.ackd.2017.09.006.
5. Laube S, Moss C. Pseudoxanthoma elasticum. Arch Dis Child. 2005 Jul;90(7):754-6. doi: 10.1136/adc.2004.062075. PMID: 15970621; PMCID: PMC1720489.
6. Nollet L, Campens L, De Zaeytijd J, et al Clinical and subclinical findings in heterozygous ABCC6 carriers: results from a Belgian cohort and clinical practice guidelines Journal of Medical Genetics 2022;59:496-504.
7. Verschuere S, Navassiolava N, Martin L, Nevalainen PI, Coucke PJ, Vanakker OM. Reassessment of causality of ABCC6 missense variants associated with pseudoxanthoma elasticum based on Sherloc. Genet Med. 2021 ;23(1):131-139. doi: 10.1038/s41436-020-00945-6.
8. Le Saux O, Martin L, Aherrahrou Z, Leftheriotis G, Váradi A and BramptonCN (2012) The molecular and physiological roles of ABCC6: more thanmeets the eye. Front. Gene. 3:289. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2012.00289
Copyright (c) 2025 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


