Impact of iron deficiency on cognitive functions and effect of iron supplement in children between 5-10 years: Indian perspective
Abstract
Background: Data on iron deficiency anemia (IDA) and cognitive function in Indian children aged 5-10 years is limited.
Objective: To study the extent of IDA, its impact on cognition and evaluate the effect of iron supplementation on cognitive function in children with IDA.
Methods: Children aged 5-10 years (n=193) were grouped into overt (group I n=71,,Ia- received iron supplements, Ib –without iron supplement), latent (group II, n=48, IIa- received iron supplements, IIb –without iron supplement)) anemia and non anemia (Group III, n=74) categories. Basic hematological investigations (HB, MCV, peripheral smear and total iron binding capacity) were done at baseline to categorize into groups. Cognitive function tests were performed at baseline and at the end of the study. Deworming with broad spectrum anthelmintic agent Albendazole(400mg stat) followed by iron supplements for 3 months was administered to Group Ia and IIa children.
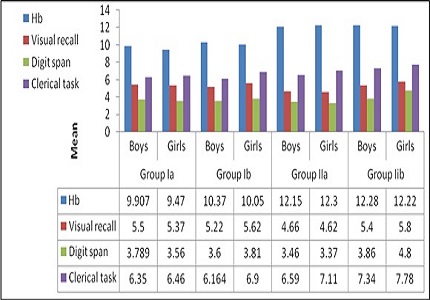
Results: Of 193 children, 119 (61.65%) had Iron deficiency, seventy (36.27%) had overt anemia and 49(25.397%) had latent form. Mean ± SD Haemoglobin at baseline was 11.80 ±1.71gm/dL, MCV 82.07± 4.69 femolitres, TIBC was 403.58 ± 58.77µg/dL. Cognitive functions were significantly (p<0.005) higher in non anemic children. Iron supplements were administered for 3 months to 58 students. Treatment compliance was 96.0%.Hemoglobin >12gms/dL was seen in 80.83% (156/193) had < 12 gms/dL, after iron supplements; Mean ± SD Haemoglobin was 12.76±1.39gm/dL and that of visual recall, digit span and clerical task changed from 5.63±1.08, 4.03±1.0, and 7.16±1.4, respectively to 6.34 ±0.82, 4.35 ±0.78 And 7.98 ±1.19 respectively. Higher scores were seen in those with Haemoglobin> 12 gms/dL.
Conclusion: Non anemic children perform better than those with anemia; performance of those with latent anemia is better than those with overt anemia. Iron supplementation helps in improved performance in these children.
Downloads
References
2. Dallman PR. Iron deficiency: does it matter? J Intern Med. 1989 Nov;226(5):367-72. [PubMed]
3. Jauregui-Lobera I: Iron deficiency and cognitive functions. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat. 2014 Nov 10;10:2087-95. doi: 10.2147/NDT.S72491. eCollection 2014. [PubMed]
4. Detzel P, Wieser S. Food fortification for addressing iron deficiency in Filipino children: benefits and cost-effectiveness. Ann NutrMetab. 2015;66Suppl 2:35-42. doi: 10.1159/000375144. [PubMed]
5. Deinard AS, List A, Lindgren B, Hunt JV, Chang PN. Cognitive deficits in iron-deficient and iron-deficient anemic children.J Pediatr. 1986 May;108(5 Pt 1):681-9. [PubMed]
6. Eden AN. Iron deficiency and impaired cognition in toddlers: an underestimated and undertreated problem. Paediatr Drugs. 2005;7(6):347-52. [PubMed]
7. Oski FA, Honig AS. The effects of therapy on the developmental scores of iron-deficient infants.J Pediatr. 1978 Jan;92(1):21-5. [PubMed]
8. Pollitt E, Hathirat P, Kotchabhakdi NJ, Missell L, Valyasevi A. Iron deficiency and educational achievement in Thailand. Am J ClinNutr. 1989 Sep;50(3 Suppl):687-96; discussion 696-7. [PubMed]
9. Webb TE, Oski FA. Iron deficiency anemia and scholastic achievement in young adolescents. J Pediatr. 1973 May;82(5):827-30. [PubMed]
10. Pollitt E. Iron deficiency and educational deficiency. Nutr Rev. 1997 Apr;55(4):133-41. [PubMed]
11. Taras H. Nutrition and student performance at school. J Sch Health. 2005 Aug;75(6):199-213. [PubMed]
12. Hermoso M, Vucic V, Vollhardt C, Arsic A, Roman-Vinas B, et al. (2011) The Effect of Iron on Cognitive Development and Function in Infants, Children and Adolescents: A Systematic Review. Ann NutrMetab. 2011;59(2-4):154-65. doi: 10.1159/000334490. [PubMed]
13. Falkingham M, Abdelhamid A, Curtis P, Fairweather-Tait S, Dye L, Hooper L. The effects of oral iron supplementation on cognition in older children and adults: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Nutr J. 2010 Jan 25;9:4. doi: 10.1186/1475-2891-9-4. [PubMed]
14. Tran TD, Biggs BA, Tran T, Simpson JA, Hanieh S, Dwyer T et al. Impact on Infants’ Cognitive Development of Antenatal Exposure to Iron Deficiency Disorder and Common Mental Disorders. PLoS One. 2013 Sep 23;8(9):e74876. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0074876. eCollection 2013.
15. Algarín C, Nelson CA, Peirano P, Westerlund A, Reyes S, Lozoff B. Iron-deficiency anemia in infancy and poorer cognitive inhibitory control at age 10 years. Dev Med Child Neurol. 2013 May;55(5):453-8. doi: 10.1111/dmcn.12118. [PubMed]
16. Fuglestad AJ, Georgieff MK, Iverson SL, Miller BS, Petryk A, Johnson DE et al. Iron deficiency after arrival is associated with general cognitive and behavioral impairment in post-institutionalized children adopted from Eastern Europe.Matern Child Health J. 2013 Aug;17(6):1080-7. doi: 10.1007/s10995-012-1090-z. [PubMed]
17. Matiashvili K, Manjavidze N, Ghonghadze T. Influence of ferrotherapy on psychomotor development of children of yearly age with iron deficiency anemia. Georgian Med News. 2012 May;(206):38-41. [PubMed]
18. Lozoff B, Jimenez E, Smith JB. Double burden of iron deficiency in infancy and low socioeconomic status: a longitudinal analysis of cognitive test scores to age 19 years. Arch PediatrAdolesc Med. 2006 Nov;160(11):1108-13. [PubMed]
19. Metallinos-Katsaras E, Valassi-Adam E, Dewey KG, Lönnerdal B, Stamoulakatou A, Pollitt E. Effect of iron supplementation on cognition in Greek preschoolers. Eur J ClinNutr. 2004 Nov;58(11):1532-42. [PubMed]
20. Soewondo S. The effect of iron deficiency and mental stimulation on Indonesian children's cognitive performance and development.Kobe J Med Sci. 1995 Apr;41(1-2):1-17. [PubMed]
21. Soewondo S, Husaini M, Pollitt E. Effects of iron deficiency on attention and learning processes in preschool children: Bandung, Indonesia. Am J ClinNutr. 1989 Sep;50(3 Suppl):667-73; discussion 673-4. [PubMed]
22. Best C, Neufingerl N, van Geel L, van den Briel T, Osendarp S. The nutritional status of school-aged children: why should we care? Food Nutr Bull. 2010 Sep;31(3):400-17. [PubMed]
23. Baumgartner J, Smuts CM, Malan L, Kvalsvig J, van Stuijvenberg ME, Hurrell RF et al. Effects of iron and n-3 fatty acid supplementation, alone and in combination, on cognition in school children: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled intervention in South Africa. Am J ClinNutr. 2012 Dec;96(6):1327-38. doi: 10.3945/ajcn.112.041004.
24. Perignon M, Fiorentino M, Kuong K, et al. Stunting, Poor Iron Status and Parasite Infection Are Significant Risk Factors for Lower Cognitive Performance in Cambodian School-Aged Children. Sengupta S, ed. PLoS ONE. 2014;9(11):e112605. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0112605.
25. Sachdev H, Gera T, Nestel P. Effect of iron supplementation on mental and motor development in children: systematic review of randomised controlled trials. Public Health Nutr. 2005 Apr;8(2):117-32.
26. Seshadri S, Gopaldas T. Impact of iron supplementation on cognitive functions in preschool and school-aged children: the Indian experience. Am J ClinNutr. 1989 Sep;50(3 Suppl):675-84; discussion 685-6. [PubMed]
27. DeMaeyer EM, Dallman P, Michael GJ, Hallberg L, Sood SK, Srikantia S G, World Health Organization. Preventing and Controlling Iron Deficiency Anemia Through Primary Health Care. Geneva, World Health Organization, 1989. Available from http://www.who.int/iris/handle/10665/39849#sthash.QAdApF1Q.dpuf last accessed 5 June 2016. [PubMed]
28. Dutt A. Cognitive Screening Tools & Neuropsychological Tests in India. A list.Available from http://www.wfnteachcogn.in/downloads/Cognitive%20Tests%20and%20Screening%20Tools_India.pdf Accessed on 20 May 2016.
29. Black RE, Victora CG, Walker SP, Bhutta ZA, Christian P, de Onis M,, et al. Maternal and child undernutrition and overweight in low-income and middle-income countries. Lancet. 2013 Aug 3;382(9890):427-51. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(13)60937-X [PubMed]
30. Sungthong R, Mo-suwan L, Chongsuvivatwong V, Geater AF. Once-weekly and 5-days a week iron supplementation differentially affect cognitive function but not school performance in Thai children. J Nutr. 2004 Sep;134(9):2349-54. [PubMed]
31. Swaminathan S, Edward BS, Kurpad AV. Micronutrient deficiency and cognitive and physical performance in Indian children. Eur J ClinNutr. 2013 May;67(5):467-74. doi: 10.1038/ejcn.2013.14. [PubMed]
32. Walter T. Effect of iron-deficiency anemia on cognitive skills and neuromaturation in infancy and childhood.Food Nutr Bull. 2003 Dec;24(4 Suppl):S104-10. [PubMed]
33. Beltrán-Navarro B, Matute E, Vásquez-Garibay E, Zarabozo D. Effect of chronic iron deficiency on neuropsychological domains in infants. J Child Neurol. 2012 Mar;27(3):297-303. doi: 10.1177/0883073811416867. [PubMed]
34. Madan N, Rusia U, Sikka M, Sharma S, Shankar N. Developmental and neurophysiologic deficits in iron deficiency in children. Indian J Pediatr. 2011 Jan;78(1):58-64. doi: 10.1007/s12098-010-0192-0. [PubMed]
35. Monga M, Walia V, Gandhi A, Chandra J, Sharma S. Effect of iron deficiency anemia on visual evoked potential of growing children. Brain Dev. 2010 Mar;32(3):213-6. doi: 10.1016/j.braindev.2009.02.009. [PubMed]
36. Ayala R, Otero GA, Porcayo Mercado R, Pliego-Rivero FB. Delayed CNS maturation in iron-deficient anaemic infants.NutrNeurosci. 2008 Apr;11(2):61-8. doi: 10.1179/147683008X301342. [PubMed]
37. Lozoff B. Iron deficiency and child development. Food Nutr Bull. 2007 Dec;28(4 Suppl):S560-71. [PubMed]
38. Glazer Y, Bilenko N. Effect of iron deficiency and iron deficiency anemia in the first two years of life on cognitive and mental development during childhood. Harefuah. 2010 May;149(5):309-14, 335. [Article in Hebrew]
39. Agaoglu L, Torun O, Unuvar E, Sefil Y, Demir D. Effects of iron deficiency anemia on cognitive function in children. Arzneimittelforschung. 2007;57(6A):426-30. [PubMed]
40. Bryan J1, Osendarp S, Hughes D, Calvaresi E, Baghurst K, van Klinken JW. Nutrients for cognitive development in school-aged children.Nutr Rev. 2004 Aug;62(8):295-306. [PubMed]
41. Baumgartner J, Barth-Jaeggi T. Iron interventions in children from low-income and middle-income populations: benefits and risks. CurrOpinClinNutrMetab Care. 2015 May;18(3):289-94. doi: 10.1097/MCO.0000000000000168. [PubMed]
42. Nokes C, Grantham-McGregor SM, Sawyer AW, Cooper ES, Bundy DAP. Parasitic helminth infection and cognitive function in school children.Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series B: Biological Sciences. 1992;247: 77–81.
43. Sakti H, Nokes C, SubagioHertanto W, Hendratno S, Hall A, Bundy DA et al. Evidence for an association between hookworm infection and cognitive function in Indonesian school children. Tropical Medicine & International Health.1999; 4: 322–334. doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3156.1999.00410.x
44. Jardim-Botelho A., Raff S, DeÁvila Rodrigues R, Hoffman HJ, Diemert DJ, Corrêa-Oliveira R, et al. Hookworm, Ascarislumbricoides infection and polyparasitism associated with poor cognitive performance in Brazilian schoolchildren. Tropical Medicine & International Health.2008;13:994–1004. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3156.2008.02103.x
45. Partnership for Child Development. Heavy schistosomiasis associated with poor short-term memory and slower reaction times in Tanzanian schoolchildren. Tropical Medicine & International Health.2002; 7: 104–117.doi: 10.1046/j.1365-3156.2002.00843.x
46. Boivin MJ, Giordani B. Improvements in cognitive performance for schoolchildren in Zaire, Africa, following an iron supplement and treatment for intestinal parasites. J. Pediatr. Psychol. (1993) 18 (2): 249-264.doi: 10.1093/jpepsy/18.2.249.
47. Gopaldas T, Kale M, Bharadwaj P. Prophylactic Iron supplementation for under privileged school boys. Impact on selected tests of cognitive functions.IndianPediatr. 1985 Oct;22(10):737-43.
48. Sen A, Kanani SJ. Impact of iron-folic acid supplementation on cognitive abilities of school girls in Vadodara.Indian Pediatr. 2009 Feb;46(2):137-43. [PubMed]
Copyright (c) 2016 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


