Accidental poisoning its magnitude and implications in children
Abstract
Background: Paucity of data due to underreporting of accidental poisoning (AP) poses obstacle in assessing the trend, incidence, and mortality in pediatric population.
Objective: Estimating the magnitude and assessing the pattern of AP in children was the primary objective. Describing the affected age group, common agents, and assessment of clinical features were the secondary objectives.
Materials & Methods: Children aged 1month- 12years with history of AP were included; those with allergic reactions to plant products, food and idiosyncratic reactions to drugs were excluded.
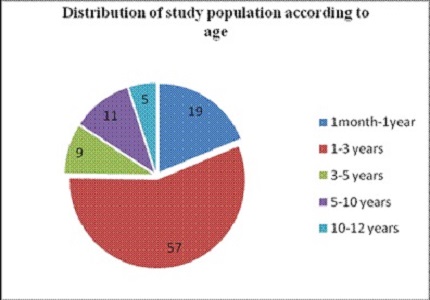
Result: 101 children accounted for 1.7% of total pediatric admission. Accidental ingestion of poisons (90.09%) and poisoning due to insect and snake bites (9.90%) were reported. Males (n=62) outnumbered females. Patients from urban area (68.2 %), children aged1-3 years (56.43%) wereaffected the most. All incidents were unintentional and occured in the home surroundings.April (n=21), March (n=20) recorded higher number followed by December (n=14). Hydrocarbon poisoning (43.56%) was most common followed by poisoning due to medicaments (18.8 %,), chemicals (12.87%), and food poisoning (9.90%). Insect bites & stings were seen in 9.90%. Supportive treatment was given to 49.5%, further gastric absorption prevented in 24.45 % and specific antidote to 7.9% patients.Three patients died due to scorpion bite, Phenytoin and kerosene ingestion.
Conclusion: AP is a preventable emergency. Incidence, agents, clinical features, treatment administered and therapeutic outcome of AP in children are comparable to the available national data. Preventive measures, strict legislative actions and restriction of availability of hazardous chemicals will reduce the incidence.
Downloads
References
2. Martin TC, Brinkman W. The spectrum of accidental childhood poisoning in the Caribbean. Rev PanamSaludPublica. 2002 Nov;12(5):313-6.
3. Kasilo OM, Nhachi CF.A pattern of acute poisoning in children in urban Zimbabwe: ten years experience. Hum ExpToxicol. 1992 Sep;11(5):335-40. [PubMed]
4. Bronstein AC, Spyker DA, Cantilena LR Jr, Green JL, Rumack BH, Giffin SL. 2009 Annual Report of the American Association of Poison Control Centers National Poison Data System (NPDS): 27th Annual Report. ClinToxicol (Phila). 2010 Dec;48(10):979-1178. doi: 10.3109/15563650.2010.543906.
5. Pillay VV. MKR Krishna's Hand book of Forensic Medicine and Toxicology. 12th Ed. Paras Publication. Hyderabad: 276-299, 2001. [PubMed]
6. Budhathoki S1, Poudel P, Shah D, Bhatta NK, Dutta AK, Shah GS, et al. Clinical profile and outcome of children presenting with poisoning or intoxication:a hospital based study. Nepal Med Coll J. 2009 Sep;11(3):170-5. [PubMed]
7. Sommerfelt K, Vogt H. Accidental poisoning in children. TidsskrNorLaegeforen. 1990 Aug 10;110(18):2345-8.[Abstract, article in Norwegian]. [PubMed]
8. Pearn J, Nixon J, Ansford A, Corcoran A. Accidental poisoning in childhood: five year urban population study with 15 year analysis of fatality. Br Med J (Clin Res Ed). 1984 Jan 7;288(6410):44-6. [PubMed]
9. Chowdhury FR, Rahman AU, Mohammed FR, Chowdhury A, Ahasan HA, Bakar MA. Acute poisoning in southern part of Bangladesh--the case load is decreasing. Bangladesh Med Res Counc Bull. 2011 Aug;37(2):61-5. [PubMed]
10. [No author listed]. Children and poisoning.Unicef. WHO.Available from http://www.who.int/violence_injury_prevention/child/injury/world_report/Poisoning_english.pdf.
accessed on 26 May 2016. [PubMed]
11. Martins CB , de Andrade SM, de Paiva PA. Accidental poisoning among children and adolescents in a county in southern Brazil.Cad SaudePublica. 2006 Feb;22(2):407-14.[Abstract, article in Portuguese]. [PubMed]
12. NalliahRP , Anderson IM, Lee MK, Rampa S, Allareddy V, Allareddy V. Children in the United States make close to 200,000 emergency department visits due to poisoning each year. PediatrEmerg Care. 2014 Jul;30(7):453-7. doi: 10.1097/PEC.0000000000000160. [PubMed]
13. Satpathy R, Das BB. Accidental poisoning in childhood.J Indian Med Assoc. 1979 Dec 1;73(11):190-2. [PubMed]
14. Buhariwalla RJ, Sanjanwalla..Poisoning in children: A study of 303 cases.Indian Pediatr. 1969 Mar;6(3):141-5. [PubMed]
15. Agarwal V, Gupta A. Accidental poisoning in children. Indian Pediatr. 1974 Sep;11(9):617-21. [PubMed]
16. Buch NA, Ahmed K, Sethi AS. Poisoning in children.Indian Pediatr. 1991 May;28(5):521-4. [PubMed]
17. Azkunaga B , Mintegi S, Salmón N, Acedo Y, Del Arco L; Grupo de Trabajo de Intoxicaciones de la Sociedad Española de Urgencias de Pediatría. Poisoning in children under age 7 in Spain.Areas of improvement in the prevention and treatment.AnPediatr (Barc). 2013 Jun;78(6):355-60. doi: 10.1016/j.anpedi.2012.09.016.[Abstract, article in Spanish].
18. Mucci N, Alessi M, Binetti R, Magliocchi MG. Profile of acute poisoning in Italy. Analysis of the data reported by Poison Centres.Ann Ist Super Sanita. 2006;42(3):268-76. [PubMed]
19. Abbas SK, Tikmani SS, Siddiqui NT. Accidental poisoning in children. J Pak Med Assoc. 2012 Apr;62(4):331-4.
20. Jayashree M, Singhi S. Changing trends and predictors of outcome in patients with acute poisoning admitted to the intensive care. J Trop Pediatr. 2011 Oct;57(5):340-6. doi: 10.1093/tropej/fmq099. [PubMed]
21. BrataGhosh V1, Jhamb U, Singhal R, Krishnan R. Common childhood poisonings and their outcome in a tertiary care center in Delhi.Indian J Pediatr. 2013 Jun;80(6):516-8. doi: 10.1007/s12098-012-0879-5. [PubMed]
22. Kouéta F, Dao L, Yé D, Fayama Z, Sawadogo A. Acute accidental poisoning in children: aspects of their epidemiology, aetiology, and outcome at the Charles de Gaulle Paediatric Hospital in Ouagadougou (Burkina Faso). Sante. 2009 Apr-Jun;19(2):55-9. doi: 10.1684/san.2009.0157. [PubMed]
23. MargonatoFB , Thomson Z, Paoliello MM. Acute intentional and accidental poisoning with medications in a southern Brazilian city. Cad SaudePublica. 2009 Apr;25(4):849-56. [PubMed]
24. Sever M, Saz EU, Koşargelir M. An evaluation of the pediatric medico-legal admissions to a tertiary hospital emergency department.UlusTravmaAcilCerrahiDerg. 2010 May;16(3):260-7.
25. Belonwu RO, Adeleke SI.A seven-year review of accidental kerosene poisoning in children atAminu Kano Teaching Hospital, Kano.Niger J Med. 2008 Oct-Dec;17(4):380-2. [PubMed]
26. Khadgawat R, Garg P, Bansal P, Arya A, Choudhary B.Accidental poisoning.Indian Pediatr. 1994 Dec;31(12):1555-7. [PubMed]
27. Singh A, Choudhary SR. Accidental poisoning in childrenIndian Pediatr. 1996 Jan;33(1):39-41. [PubMed]
28. Gontko K, MitkowskaJ ,Panienski P, Ratajczak K. Acute poisonings in children in the years 2010-2012--single-centre study in Poznań. PrzeglLek. 2013;70(8):533-7. [Abstract, article in Polish] [PubMed]
29. BeikircherM ,Berenzi P, Mantovan F. Prevention of accidental poisonings in the household with children under 6 years of age. Kinderkrankenschwester. 2012 May;31(5):190-3. [Abstract, article in German] [PubMed]
Copyright (c) 2016 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


