Profile of scald injury among Paediatrics patient attending tertiary care hospital
Abstract
Background: Scald injuries among children are a significant cause of mortality and morbidity. This is compounded by the additional risk factors such as poverty, higher birth order and urban slums which are seen in developing countries. But very few studies are available regarding the burden of this issue. This study seeks to assess the same.
Methods: A prospective observational study was conducted in a tertiary care hospital for one year.A total of 66 children less than 12 years of age were included. Their demographic profile and treatment outcome were studied.
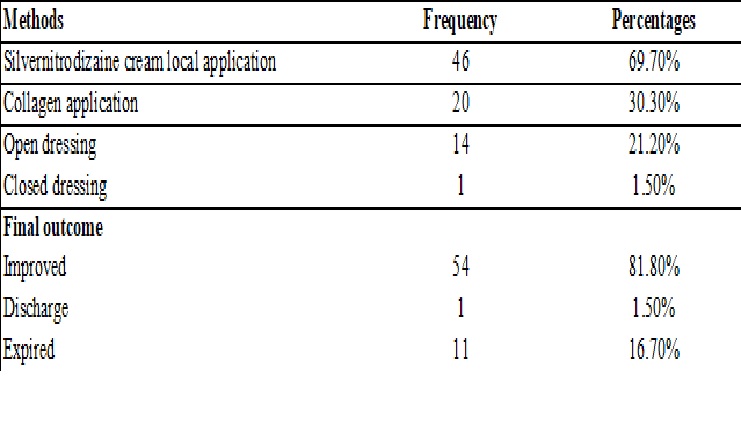
Results: Most participants were less than 10 years old and almost half had first degree burns. Hot water scalds were the most common etiology followed by household liquid foods such as sambar and kanji. Most burns affected the front of the body. Silver nitrodiazine was the most common treatment followed by collagen application and open dressing. After treatment 81.5% improved. The mortality was 16.7%.
Conclusions: Scald injuries are a common cause of morbidity among young children. Most incidents occur at home and are preventable. This indicates the need for parental education and the child safety measures for reducing mortality and morbidity due to scalds.
Downloads
References
2. Morrow SE, Smith DL, Cairns BA, Howell PD, Nakayama DK, Peterson HD. Etiology and outcome of pediatric burns. J Pediatr Surg. 1996 Mar;31(3):329–33.[pubmed]
3. Miller TR, Romano EO, Spicer RS. The cost of childhood unintentional injuries and the value of prevention. Future Child. 2000;10(1):137–63.[pubmed]
4. Gillam S, Abbott S, Banks-Smith J. Can primary care groups and trusts improve health? BMJ. 2001 Jul;323(7304):89–92.[pubmed]
5. Bijur PE, Kurzon M, Overpeck MD, Scheidt PC. Parental alcohol use, problem drinking, and children’s injuries. JAMA. 1992 Jun;267(23):3166–71.[pubmed]
6. Reading R, Langford IH, Haynes R, Lovett A. Accidents to preschool children: comparing family and neighbourhood risk factors. Social Science & Medicine. 1999 1999/02/01/;48(3):321-30.
7. Hatamabadi HR, Mahfoozpour S, Alimohammadi H, Younesian S. Evaluation of factors influencing knowledge and attitudes of mothers with preschool children regarding their adoption of preventive measures for home injuries referred to academic emergency centres, Tehran, Iran. Int J InjContrSafPromot. 2014;21(3):252–9.[pubmed]
8. Feldman KW, Schaller RT, Feldman JA, McMillon M. Tap water scald burns in children. 1997. Inj Prev. 1998 Sep;4(3):238–42.[pubmed]
9.Agbenorku P. Early childhood severe scalds in a developing country: A 3-year retrospective study. Burns & Trauma. 2013 12/18;1(3):122-7.
10. Corp IB. Released 2013. IBM SPSS Statistics for Windows, Version 22.0. Armonk, NY: IBM Corp.
11. Yeoh C, Nixon JW, Dickson W, Kemp A, Sibert JR. Patterns of scald injuries. Archives of Disease in Childhood. 1994 1994-08-01 00:00:00;71:156-8.[pubmed]
12. Palmieri TL, Alderson TS, Ison D, O’Mara MS, Sharma R, Bubba A, et al. Pediatric soup scald burn injury: etiology and prevention. J Burn Care Res. 2008 Jan-Feb;29(1):114–8.[pubmed]
13. Rimmer RB, Weigand S, Foster KN, Wadsworth MM, Jacober K, Matthews MR, et al. Scald burns in young children—a review of Arizona burn centerpediatric patients and a proposal for prevention in the Hispanic community. J Burn Care Res. 2008 Jul-Aug;29(4):595–605.[pubmed]
14. Delgado J, Ramírez-Cardich ME, Gilman RH, Lavarello R, Dahodwala N, Bazán A, et al. Risk factors for burns in children: crowding, poverty, and poor maternal education. Inj Prev. 2002 Mar;8(1):38–41.[pubmed]
15. Millan LS, Gemperli R, Tovo FM, Mendaçolli TJ, Gomez DS, Ferreira MC. Estudoepidemiológico de queimadurasemcriançasatendidasem hospital terciárionacidade de São Paulo. Revista Brasileira de CirurgiaPlástica. 2012 2012;27(4):611-5.
16. Marashi SM, Sanaei-Zadeh H, TaghizadehBehbahani A, Ayaz M, Akrami M. Paediatric burn injuries requiring hospitalization in Fars, Southern Iran. Ann Burns Fire Disasters. 2016 Dec;29(4):245–8.[pubmed]
Copyright (c) 2018 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


