A study to access the hemoglobin level and sociodemographic profile of underfive children having Pica
Abstract
Introduction: Pica is a disorder that occurs when children persistently eat one or more non-food substances over the course of at least one month. Pica may result in serious medical problems, such as intestinal blockage, poisoning, parasitic infection, and sometimes death. The typical non-food substances that children with pica ingest tend to vary with age.
Method: This prospective study was undertaken at a pediatric outdoor department Career Institute of Medical Sciences Lucknow since Jan 2019 to Mar 2019. All the under five years children visiting pediatric clinic with direct or indirect history of pica were enrolled for the study. The mothers were interviewed in depth regarding their sociodemographic profile and Hemoglobin level of all the children done.
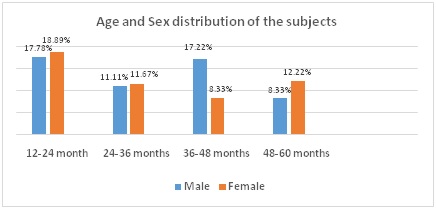
Results: In our study most of the children belongs to the age group 12-24 months 66(36.67%). Most of the parents were educated upto secondary education only and belong to joint families.Children belongs to rural area 111(61.6%) were more in number and Only 87(48.33%) of the children were exclusive breast fed. In our study only 20.56% children have normal hemoglobin level while 79.44% children have hemoglobin level below 12.0gm/dl and classified as anemic children, out of which 35.56% children have mild anemia, 25.00% children have moderate anemia and 18.89% children had severe anemia.
Conclusion: Pica is mostly related with micronutrient deficiencies. Because of lower breastfeeding rate and delayed starting of complementary feeding the children are prone for micronutrient deficiencies leading to pica behavior in children. Knowledge of pica is the key for prevention.
Downloads
References
2. AndreaBarkoukis, M.A., Natalie Staats Reiss: Feeding And Eating Disorders Of Infancy Or Early Childhood: Pica; https://www.mentalhelp.net.
3. American Psychiatric Association. (1994). Diagnostic and statisticalmanual of mental disorders (4th ed.). Washington, DC: Author.
4. Ellis CR, Schnoes CJ. Eating disorder: Pica Med J 2002; 3: 8.
5. Coltman CA Jr. Pagophagia and iron lack. JAMA. 1969 Jan 20;207(3):513-6.[pubmed]
6. Kathula SK. Craving lemons: another form of pica in iron deficiency. Am J Med. 2008 Jul;121(7):e1. doi: 10.1016/j.amjmed.2008.02.017.[pubmed]
7. Kettaneh A, Eclache V, Fain O, et al. Pica and food craving in patients with iron-deficiency anemia: a case-control study in France. Am J Med. 2005 Feb;118(2):185-8. DOI:10.1016/j.amjmed.2004.07.050.[pubmed]
8. Pagophagia and anemia. Nutr Rev. 1969 Feb;27(2):52-4. DOI:10.1111/j.1753-4887.1969.tb04956.x.[pubmed]
9. Grivetti LE. Culture, diet and nutrition: selected themes and topics. BioScience.1978;28(3):171–177.
10. Barker D. Tooth wear as a result of pica. Br Dent J. 2005 Sep 10;199(5):271-3. DOI:10.1038/sj.bdj.4812651.[pubmed]
11. Ukaonu C, Hill DA, Christensen F. Hypokalemic myopathy in pregnancy caused by clay ingestion. Obstet Gynecol. 2003 Nov;102(5 Pt 2):1169-71.[pubmed]
12. Falcomata TS, Roane HS, Pabico RR. Unintentional stimulus control during the treatment of pica displayed by a young man with autism. RASD. 2007. pp. 350–359.
13. Scully RE, Mark EJ, McNeely WF, Ebeling SH, et al. Case records of the Massachusetts General Hospital. Weekly clinicopathological exercises. Case 20-1997. A 74-year-old man with progressive cough, dyspnea, and pleural thickening. N Engl J Med. 1997 Jun 26;336(26):1895-903.[pubmed]
14. Ravinder K. Gupta, RituGupta.Clinical Profile of Pica in Childhood. Jksciences2005;7(2)
15. Ravi Bhatia, Dr. Gunjan Bhatia.Pattern, beliefs associated with Pica in children aged 1-10 years- A studyof 119 cases.Indian Journal of Basic and Applied Medical Research; Dec 2015;5(1).
16. Jin Soo Moon.Nutritional management of breastfeeding infants for the prevention of common nutrient deficiencies and excesses.Korean J Pediatr. 2011; 54(7)
17. Singhi S, Ravishanker R, Singhi P, et al. Low plasma zinc and iron in pica. Indian J Pediatr. 2003 Feb;70(2):139-43.[pubmed]
18. Robinson, B. A., Tolan, W., & Golding-Beecher, O. (1990). Childhood pica: Some aspects of the clinical profile in Manchester, Jamaica. West Indian Medical Journal, 39, 20–26.
19. Ali, Z. (2001). Pica in people with intellectual disability: A literature review of aetiology, epidemiology and complications. Journal of Intellectual and Developmental Disability, 26, 205–215.[pubmed]
20. Hackworth SR, Williams LL. Pica for foam rubber in patients with sickle cell disease. South Med J. 2003 Jan;96(1):81-3. DOI:10.1097/01.SMJ.0000047974.56740.1A.[pubmed]
21. Lemanek, K. L., Brown, R. T., Armstrong, F. D., Hood, C., Pegelow,C., & Woods, G. (2002). Dysfunctional eating patterns and symptoms of pica in children and adolescents with sickle cell disease. Clinical Pediatrics, 41(7), 493–500.
22. Rose EA, Porcerelli JH, Neale AV. Pica: common but commonly missed. J Am Board Fam Pract. 2000 Sep-Oct;13(5):353-8.[pubmed]
23. Duker PC, Nielen M. The use of negative practice for the control of pica behavior. J BehavTher Exp Psychiatry. 1993 Sep;24(3):249-53.[pubmed]
24. Santiago-Sanchez, C. A., Garau-Diaz, P., & Lugo-Vicente, H. L.(1996). Trichobezoar in an 11-year-old girl: A case report. Pediatric Surgery Update [online serial]. Retrieved from http://home.coqui.net/titolugo/articles.htm.
25. Wahbeh, G., Wyllie, R., & Kay, M. (2002). Foreign body ingestion in infants and children: Location, location, location. Clinical Pediatrics, 41, 633–640
26. Burke, L., & Smith, S. L. (1999). Treatment of pica: Considering least intrusive options when working with individuals who have a developmental handicap and live in a community setting. Developmental Disabilities Bulletin, 27(1). Retrieved from http://www.ualberta.ca/~jpdasddc/bulletin/articles/burke1999.html.
27. Katsiyannis, A., Torrey, G., & Bond, V. Current considerations in treating pica. Teaching Exceptional Children, 1998;30(4), 50–53.
28. Kirchner, J. Management of pica: A medical enigma. American Family Physician,2001; 63, 1177
29. Lofts RH, Schroeder SR, Maier RH. Effects of serum zinc supplementation on pica behavior of persons with mental retardation. Am J Ment Retard. 1990 Jul;95(1):103-9.[pubmed]
Copyright (c) 2019 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


