Adolescent violence: the genesis
Abstract
Introduction: Recently the “Blue Whale Experience” has put the adolescents on fire. The surge in adolescent violence has become a matter of great concern in the last few decades. The inter-personal conflict builds the foundation block, which generates the spark of violence, if it is not resolved in gentleman manner. A dance between genes and environmental experiences really shape the child’s developing brain. A rapid period of brain development can be fostered by quality of responsiveness of caregivers and community environment. Numerous studies uncover a link between cognitive skills and adolescent violence. In the light of these facts this study was designed to know the environmental factors which correlate with the indulgence of violence.
Material and Method: 480 students aged 10-18 years were surveyed regarding the indulgence in violence during last one year. The characteristics of different interacting environmental factors were also drilled.
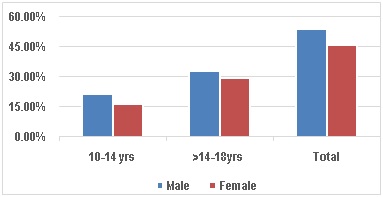
Results: The prevalence of violent act was 27.91% in which boys and girls were 13.75% and 14.16% respectively. Boys were outnumbered than girls as perpetrators while girls were victimized more. The interacting proximal environmental factors viz upper lower SES, mother and father education 2hr and academic failure which correlate with the indulgence in violence of students in our study point an inappropriate and low quality responsiveness. Which are perceived by the adolescents during their early years of life. These children react according to such memory and cognition in any situation inappropriately ie antisocially and indulge themselves in violence during their adolescence. They accept a socially disapproved ideology to form a negative identity formation.
Discussion: These factors can be used at school level to mark the students at risk to offer the available preventive tools to achieve the best results.
Downloads
References
Merrick J, Kandel I, Vardi G. Trends in adolescent violence. Int J Adolesc Med Health. 2003 Jul-Sep;15(3): 285-7.
Krug EG, Mercy JA, Dahlberg LL, et al. The world report on violence and health. Lancet. 2002 Oct 5;360(9339):1083-8.
Smith-Khuri E, Ronaldo I. Across-national study of violence related behaviors in adolescents.JAMAPaediatricsjune 1, 2004, Vol 158, No. 6, Pages 510-608.doi:10.1001/archpedi.158.6.539.
Lai DW. Violence exposure and mental health of adolescents in small towns: an exploratory study. Can J Public Health. 1999 May-Jun;90(3):181-5.
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC). Violence-related behaviors among high school students--United States, 1991-2003. MMWR Morb Mortal Wkly Rep. 2004 Jul 30;53(29):651-5.
Carol Bellamy. The state of the world’s children 2001. NY, USA: UNICEF; https://www.unicef.org (Accessed 21 Nov 2018).
Early Childhood Development. https://www.worldbank.org. (Accessed 20 Nov 2018)
Paul E. Bellair& Thomas L. McNulty (2010) Cognitive Skills, Adolescent Violence, and the Moderating Role of Neighborhood Disadvantage, Justice Quarterly, 27:4, 538-559, DOI: 10.1080/07418820903130823
Carone N, Lingiardi V, Chirumbolo A, et al. Italian gay father families formed by surrogacy: Parenting, stigmatization, and children's psychological adjustment. Dev Psychol. 2018 Oct;54(10):1904-1916. doi: 10.1037/dev0000571.
Serve and return theory.Centre on developing child. Harvard University. https://developingchild.harvard.edu (Accessed 12 April 2018)
Rose Erickson, Parents' Effect on Child Behavior. www.livestrong.com (Accessed 25 September 2018)
Information processing theory.https://en.wikipedia.org (Accessed 22 September 2018).
Agarwal AK, Verma A, Adolescent Violence: Pointers of Perpetrators, Paripex-Indian journal of Research 2017;5:54-55 https://wwjournals.com/index.php/pijr/article/view/692.
Agarwal AK, Verma A, Agarwal M. Adolescent Violence: Proneness Factors of Victims. Ind J Youth Adol Health 2017; 4(2): 12-16.DOI.10.24321/2349.2880.201709
What Causes Teen Violence - Teen Violence. https://www.teenhelp.com (Accessed on 20 Aug 2017).
Online Bullying Among Youth 8-17 Years Old – India Cross-Tab Marketing Services & Telecommunications Research Group for Microsoft Corporation. http//download.microsoft.com (Accessed 21 Dec 2016).
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Youth risk behavior surveillance—United States, 2011. MMWR, Surveillance Summaries 2012;61(no.SS-4).www.cdc.gov/mmwr/pdf/ss/ss6104.pdf. (Accessed 22 Feb 2017).
Sharma MK1, Marimuthu P. Prevalence and psychosocial factors of aggression among youth. Indian J Psychol Med. 2014 Jan;36(1):48-53. doi: 10.4103/0253-7176.127249.
Deb S, Modak S. Prevalence of violence against children in families in Tripura and its relationship with socio-economic factors. J Inj Violence Res. 2010 Jan;2(1):5-18. doi: 10.5249/jivr.v2i1.31.
Ziggy’s Blog: Teen Trends: Teen Violence On The Rise!.http://ziggysblogs.blogspot.com/2011/09/teen-trends-teen-violence-on-rise.htm (Accessed 16 Feb 2019).
Miller E, McCauley H, Virata MC, Decker M, et al. Coaching boys into men: Preliminary success of a sexual violence prevention program. Journal of Adolescent Health. 2011;48:S85–S86.
Maccoby, E. E., & Martin, J. A. (1983). Socialization in the Context of the Family: Parent-Child Interaction. In P. H. Mussen,& E. M. Hetherington (Eds.), Handbook of Child Psychology: Vol. 4. Socialization, Personality, and Social Development (pp. 1-101). New York: Wiley..
Brain Architecture.Centre on developing child. Harvard University. https://developingchild.harvard.edu. (Accessed 12 Jan 2019).
Huitt, W. (2003). The information processing approach to cognition. Educational Psychology Interactive. Valdosta, GA: Valdosta State University. http://www.edpsycinteractive.org/topics/cognition/infoproc.html (Accessed on 2 Mar 2019)
Cognitive Information Processing Theory. http://www.expertlearners.com (Accessed on 20 April2019).
Calbo, A. S., Busnello, F. B., Rigoli, M. M., Schaefer, L. S., & Kristensen, C. H. (2009). Bullying na escola: comportamento agressivo, vitimização e conduta pró-social entre pares [Bullying at school: Aggressive behavior, victimization, and prosocial behavior among peers]. ContextosClínicos, 2, 73-80. doi:10.4013/ctc.2009.22.01
Human behavior: Development in adolescence. Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com (Accessed on 25th july2018).
Angela oswalt, Early Childhood Emotional And Social Development: Identity And Self-Esteem,https://www.mentalhelp.net (Accessed on 23rd Feb 2019).
Teeter E, Phyllis A, Semrud-C, Assessment and Interventions for Neurodevelopmental Disorders.Child Neuropsychology. 2nd edition.89-103.
Copyright (c) 2019 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


