Role of beta-2 microglobulin in renal dysfunction of Neonates with Birth Asphyxia
Abstract
Objective: study was conducted to assess role of beta-2 microglobulin in renal dysfunction of Neonates with Birth Asphyxia.
Methods: Study is a Case control studyand a total of 140 babies were selected for study group as cases of birth asphyxia and 70 normal term babies were selected as control group randomly. Urine samples were taken on day 1, 3 and day 7 in all the babies and beta 2 microglobulin (B2M) values were estimated in all the babies by ELISA method from urine samples.
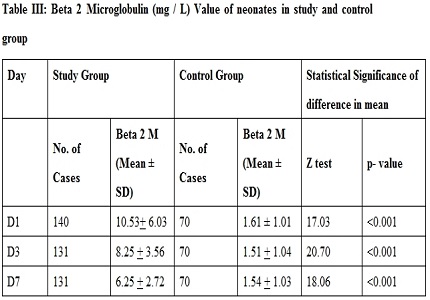
Results: The mean value of beta 2 microglobulin ( B2M) in neonates with birth asphyxia were 10.53 + 6.03, 8.25 + 3.56, 6.25 + 2.72 mg / L and in neonates of control group were 1.61 + 1.01, 1.51 + 1.04 and 1.54 + 1.03 mg / L on day 1, 3 and 7. The p-value for these two groups was < 0.001, which is highly significant.
Conclusion: beta 2 microglobulin (B2M) is a sensitive indicator for renal dysfunction. It can even detect subclinical renal impairments in neonates with birth asphyxia which are usually missed by standard renal function tests. It can also be used as early marker or screening test for renal impairments.
Downloads
References
2. Mehta KP, Ali US, Shankar L, Tirthani D, Ambadekar M. Renal dysfunction detected by beta-2 microglobulinuria in sick neonates. Indian Pediatr. 1997 Feb;34(2):107-11. [PubMed]
3. Willis F, Summers J, Minutillo C, Hewitt I. Indices of renal tubular function in perinatal asphyxia. Arch Dis Child Fetal Neonatal Ed. 1997 Jul;77(1): F57-60. [PubMed]
4. Bethea M, Forman DT. Beta 2-microglobulin: its significance and clinical usefulness. Ann Clin Lab Sci. 1990 May-Jun;20(3):163-8. [PubMed]
5. Engle WD, Arant BS Jr. Renal handling of beta-2-microglobulin in the human neonate. Kidney Int. 1983 Sep;24(3):358-63. [PubMed]
6. Mehta KP. Neonatal renal failure. Indian Pediatr. 1991 Jan;28(1):7-9. [PubMed]
7. Pereira S, Pereira BJ. Renal dysfunction in the critically ill neonate--a tropical perspective. Indian Pediatr. 1991 Jan;28(1):11-8. [PubMed]
8. Chen JY, Lee YL, Liu CB. Urinary beta 2-microglobulin and N-acetyl-beta-D-glucosaminidase (NAG) as early markers of renal tubular dysfunction in sick neonates. J Formos Med Assoc. 1991 Feb;90(2):132-7.
9. Jenik AG,Cernadas J M C, Gorenstein A, Ramirez J A,Vain N,Armadans M,and Ferraris J R.A Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Trial of the Effects of Prophylactic Theophylline on Renal Function in Term Neonates With Perinatal Asphyxia, Pediatrics 2000; 105(4): 45.
10. Karlowicz MG, Adelman RD. Nonoliguric and oliguric acute renal failure in asphyxiated term neonates. Pediatr Nephrol. 1995 Dec;9(6):718-22. [PubMed]
11. Ballard JL, Khoury JC, Wedig K, Wang L, Eilers-Walsman BL, Lipp R. New Ballard Score, expanded to include extremely premature infants. J Pediatr. 1991 Sep;119(3):417-23.
12. Stoll BJandKliegman RM.The Newborn Infant In:Beherman RE, Kliegman RM and Jenson HB. Textbook of pediatrics, 17th edn. Philadelphia, WB Saunders Company, 2004:527.
13. Tack ED, Perlman JM, Robson AM. Renal injury in sick newborn infants: a prospective evaluation using urinary beta 2-microglobulin concentrations. Pediatrics. 1988 Mar;81(3):432-40.
14. Aperia A, Broberger U. Beta-2-microglobulin, an indicator of renal tubular maturation and dysfunction in the newborn. Acta Paediatr Scand. 1979 Sep;68(5):669-76. [PubMed]
Copyright (c) 2016 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


