Relevance of lung ultrasound in diagnosis of severe neonatal pneumonia
Abstract
Introduction: Neonatal pneumonia is a serious respiratory infection accounting for 10% of the neonatal deaths.
Objective: The aim and objective of our study was to evaluate the accuracy of lung ultrasound to diagnose neonatal pneumonia.
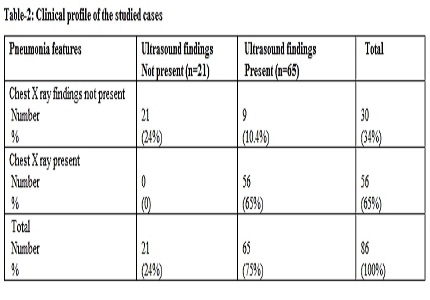
Methods: A 3-year prospective observational study was done between October 2013 to September 2016 in the neonatal ICU of Vydehi institute of medical sciences. About 86 neonates presented with features of pneumonia of which 21 cases had no x ray or ultrasonographic features. The control group comprised 65 neonates with no pulmonary disease are taken into the control group and compared.
Results: 86 neonates were included in this study with clinical features of pneumonia of which 21 cases had no x rays or ultrasonographic features, so were not taken into the study group. Of the 65 cases included in the study; 39 were males and 26 females. In the 65 cases studied, 63 (96%) had tachypnea, retractions in 42(64%) and grunting in 38(58%) of the cases. Three (4.6%), of the studied cases died while the remaining 62(93%) cases improved and were discharged.
Conclusion: In conclusion, the study confirms that lung ultrasonography is useful in the diagnosis of neonatal pneumonia.
Downloads
References
2. Wilson-Costello D, Rao PS, Morrison S, Hack M. Radiation exposure from diagnostic radiographs in extremely low birth weight infants. Pediatrics. 1996 Mar;97(3):369-74. [PubMed]
3. Yang PC, Luh KT, Chang DB, Yu CJ, Kuo SH, Wu HD. Ultrasonographic evaluation of pulmonary consolidation. Am Rev Respir Dis. 1992 Sep;146(3):757-62. [PubMed]
4. Blaivas M. Lung ultrasound in evaluation of pneumonia. J Ultrasound Med. 2012 Jun;31(6):823-6. [PubMed]
5. Cortellaro F, Colombo S, Coen D, Duca PG. Lung ultrasound is an accurate diagnostic tool for the diagnosis of pneumonia in the emergency department. Emerg Med J. 2012 Jan;29(1):19-23. doi: 10.1136/emj.2010.101584. Epub 2010 Oct 28.
6. Volpicelli G, Elbarbary M, Blaivas M, et al. International Liaison Committee on Lung Ultrasound (ILC-LUS) for International Consensus Conference on Lung Ultrasound (ICC-LUS). International evidence-based recommendations for point-of-care lung ultrasound. Intensive Care Med. 2012 Apr;38(4):577-91. doi: 10.1007/s00134-012-2513-4. Epub 2012 Mar 6.
7. Cattarossi L. Lung ultrasound: its role in neonatology and pediatrics. Early Hum Dev. 2013 Jun;89 Suppl 1:S17-9. doi: 10.1016/S0378-3782(13)70006-9. [PubMed]
8. Liu J . Lung ultrasonography for the diagnosis of neonatal lung disease. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med. 2014 May ; 27 ( 8 ): 856 - 861 . doi: 10.3109/14767058.2013.844125. Epub 2013 Oct 17. [PubMed]
9. Chen SW, Fu W, Liu J, Wang Y. Routine application of lung ultrasonography in the neonatal intensive care unit. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017 Jan;96(2):e5826. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000005826. [PubMed]
Copyright (c) 2017 Author (s). Published by Siddharth Health Research and Social Welfare Society

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.


 OAI - Open Archives Initiative
OAI - Open Archives Initiative


